Evaluation of the Anticancer Effect of Saussurea costus Root Extract Against Induced Hepatic and Renal Cancer in White Mice: A Histopathological Study
Evaluation of the Anticancer Effect of Saussurea costus Root Extract Against Induced Hepatic and Renal Cancer in White Mice: A Histopathological Study
Zahra Abdulameer Al-Zayadi1, Hana Kadum Shanan1, Al Salihi Karima Akool2*
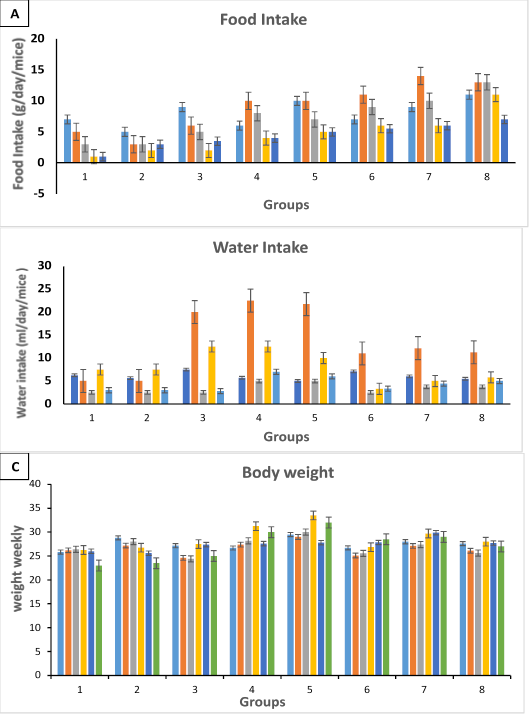
Shows the effects of date extract on (A) weekly food intake, (B) weekly water intake, and (C) body weights of the tested mice groups.
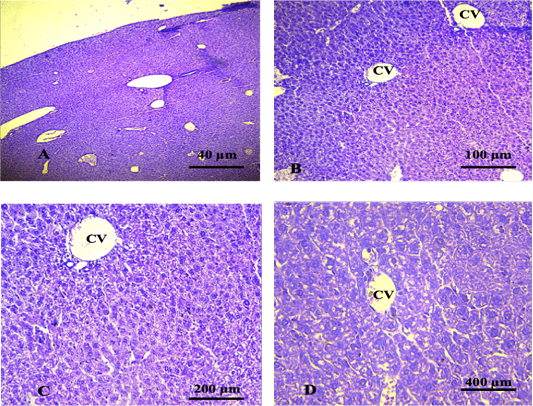
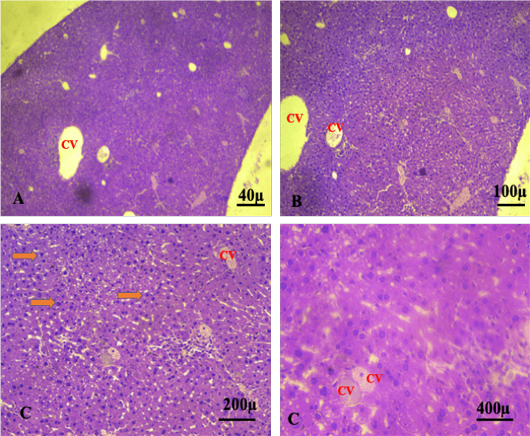
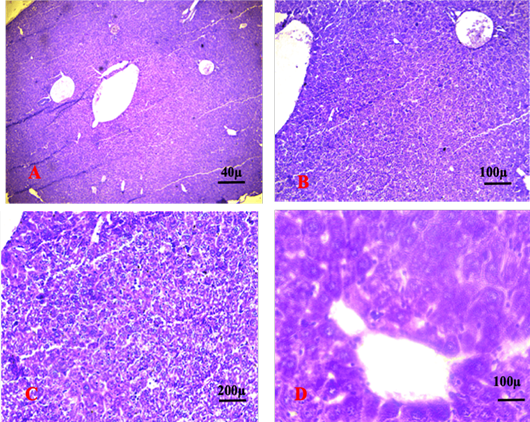
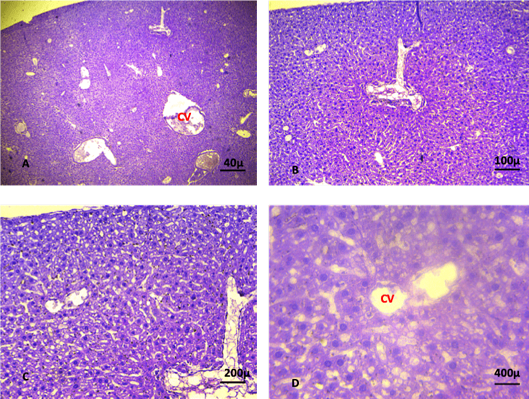
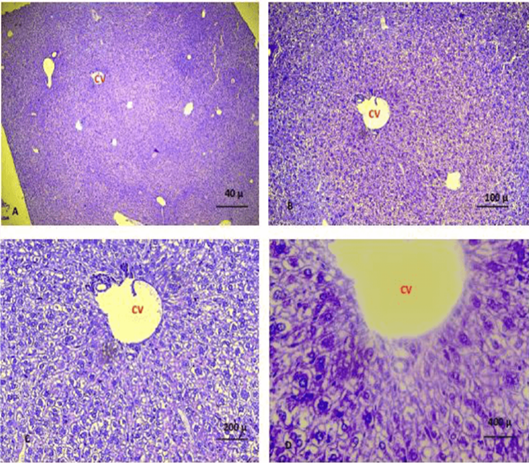
Shows liver of the control group showing normal histological features. The sections revealed normal organisation of the hepatic cells surrounded the central vein. (CV): central vein. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40) (H and E).
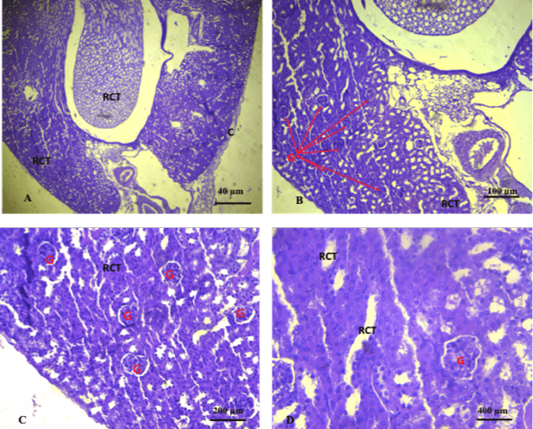
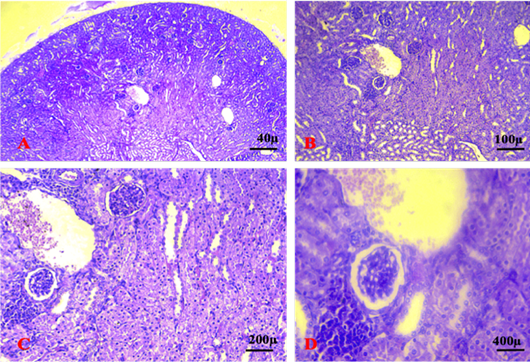
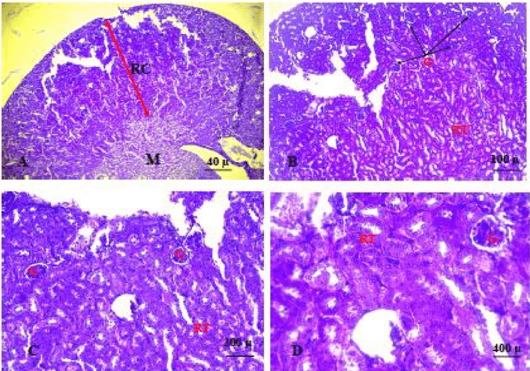
Shows section of the kidney of the control group. The sections revealed normal glomeruli (G) with normal urinary space (US) and renal convoluted tubules (RCT) (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40) (H and E).
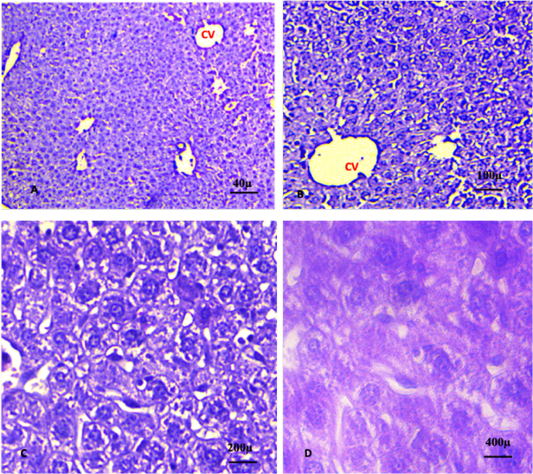
A, B, C, D shows liver of the control group 3 (plant extract alone). The sections revealed normal organisation of the hepatic cells surrounded the central vein. (CV): central vein. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
A, B, C, D shows the kidneys of the control group 2 (plant extract alone). Sections showing normal histological features of the kidney. The sections revealed normal glomeruli (G) with normal urinary space (US) and renal convoluted tubules (RCT) (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
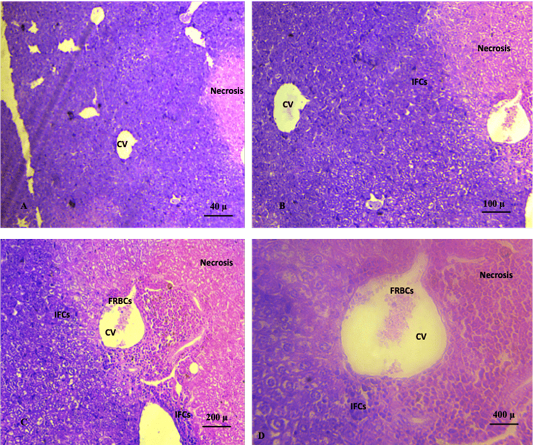
5th weeks: Shows liver section for Group 3/ chemotherapy alone (2.5mg/Kg Ebetrex) revealing large necrosis hepatic area and heavy infiltration of inflammatory cells around central vein. A congestion and free RBCs were also seen in the section. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
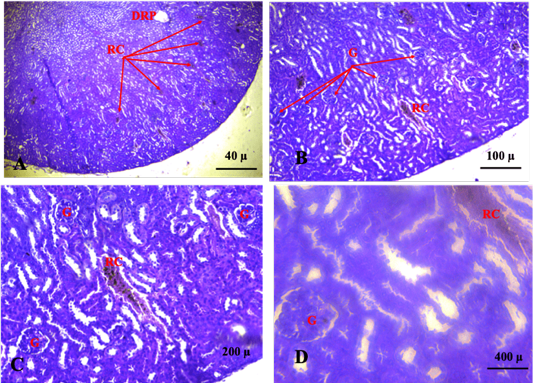
3rd and 4th and 5th weeks: Shows kidney sections with various degenerative changes of the glomeruli and renal tubules. Congestion was also seen. (G: Glomeruli, RC: Renal Congestion, DRP: Damage renal parenchyma). (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
A, B, C, D shows the liver control group 3 (Cancer alone without treatment) at 5th week of intraperitoneal injection of Polyvinyl pyrrolidone K-30. Hepatic cell degeneration associated with nuclear pyknosis (orange arrow) and cancer cell aggregation (ACs) around the portal area, accompanied by the infiltration of inflammatory cell and congestion (CV: central vein). (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40) (H and E).
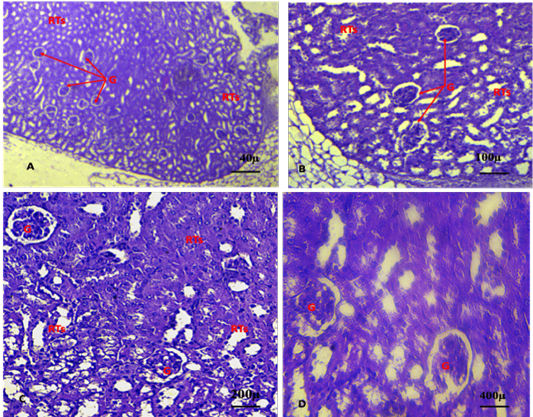
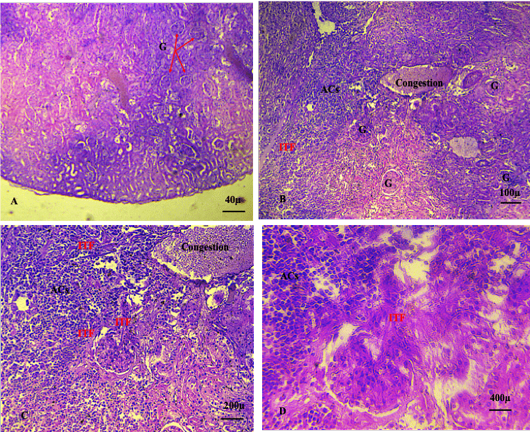
A, B, C, D shows advanced stages of renal cancer characterised by Intra-tumoral fibrosis (ITF), severe damage of renal parenchyma, including degeneration of renal convoluted tubules and congestion. (ACs: Abnormal cell aggregation, G: glomeruli). (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40) (H and E).
A, B, C, D shows liver sections with sever degeneration and necrosis of the hepatic cells accompanied by congestion and infiltration of inflammatory cells. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
A, B, C & D: Shows the kidney section in group 5 at 5th week revealing severe degeneration and necrosis of glomeruli accompanied by widening of the glomerular wall and damaged renal tubules. Aggregations of immature cancer cell and heavily invaded the renal parenchyma lead to loss of normal histological features. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H&E).
A, B, C, D shows sections of the liver at the 5th week of the experiment revealed slight degeneration of the hepatic cells, congestion, fatty degeneration, necrosis of hepatic cells around the central vein and absence of immature cancer cells (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
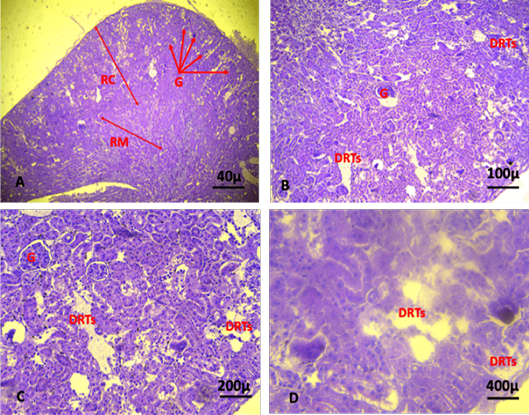
A, B, C, D shows section of kidney at the 5th week of the experiment. The kidney section revealed severe degeneration and necrosis of renal parenchyma, damage of renal tubules, infiltration of the inflammatory cells and severe congestion and absence of immature cancer cell aggregation (Damage of renal tubules: DRTs; renal cortex: RC; Renal medulla: RM; Glomeruli: G). (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
A, B, C, D shows liver sections of mice in group 7 at 4th week of experiment. Liver sections revealed slight degeneration and few infiltrations of inflammatory cells. Additionally, normal structural organization of the central vein and portal area was seen and no obvious immature cancer cell was seen (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
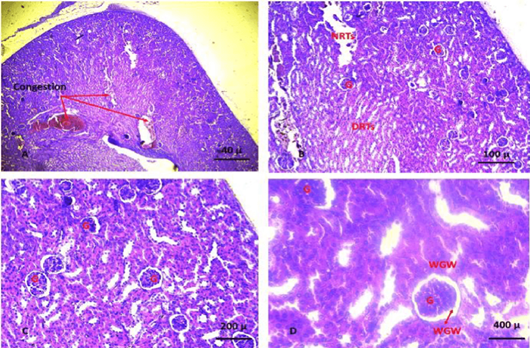
A, B, C, D shows section of kidney of group 7 at the 5th week of the experiment. The kidney sections revealed severe congestion, degeneration and necrosis of renal parenchyma and renal tubules, infiltration of the inflammatory cells, absence of immature cancer cell aggregation (Damaged renal tubules: DRTs; Necrosis of renal tubules: NRTs; Glomeruli: G; Widening of glomerular wall: WGW). (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
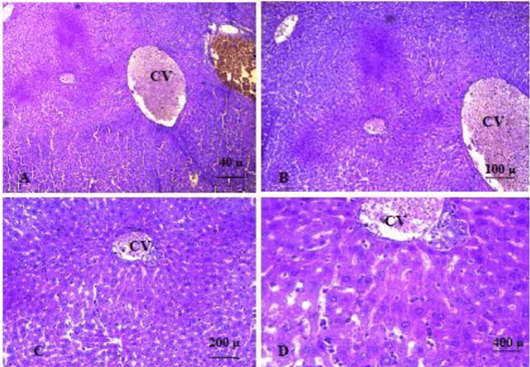
A, B, C, D shows liver of mice in group 8 at 5th week of the experiments, the liver section showed slight degeneration and few infiltrations of inflammatory cells. Additionally, severe congestion of the central vein and portal area was seen. No obvious immature cancer cell was seen. (A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H and E).
A, B, C, D: Shows kidney sections of mice in group 8 at 5th week of the experiments, the kidney section revealed slightly degeneration of renal cortex and medulla, infiltration of the inflammatory cells, degeneration of glomeruli, congestion, and no obvious aggregations of immature cancer cell A. X 4, B. X10, C.X20, D. X40). (H&E).