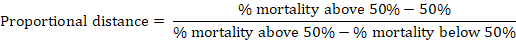Isolation and Identification of Newcastle Disease Viruses from Naturally Infected Chickens
Isolation and Identification of Newcastle Disease Viruses from Naturally Infected Chickens
Yasser Asaad Hameed Al-Shareef, Firas Hussain Kadim Abawi*
PCR products of the amplification of partial region of F gene of NDV. The size of the PCR product is 535 bp. The gel was 1.5% and the DNA dye is RedSafe (Intron, Korea). V: 90, Time: 45 minutes. M: DNA ladder.
Clinical signs and gross lesions in chickens suspected to be naturally infected with NDV (A) Hemorrhages on cecal tonsils, (B) Hemorrhages on proventriculus gland tips, (C) Broiler chicken of 28 days infected with NDV showing edematous black eye.
Effect of NDV on inoculated ECE. A and B Chicken embryo (57-59 hours Post inoculation) is diffusely red and the subcutaneous tissue of the head is filled with blood and the blood vessels over the body were prominent. C Control non-inoculated NDv chicken.
Phylogenetic relationship of NDV isolates on the basis F gene.