Expression profile of Toll-like Receptors Pathway Genes in Chicken Erythrocytes Infected with Mycoplasma synoviae
Expression profile of Toll-like Receptors Pathway Genes in Chicken Erythrocytes Infected with Mycoplasma synoviae
Xin-yu Han1,2, Afrasyab Khan1,2, Ali Raza Jahejo1,2, Qian-qing Cheng1,2, Meng-li Qiao1,2, Raza Ali Mangi1,2, Muhammad Farhan Qadir1,2, Ding Zhang1,2, Ying Wang1,2, Yu-hai Bi1,3, Rui-wen Fan1,2 and Wen-xia Tian1,2*
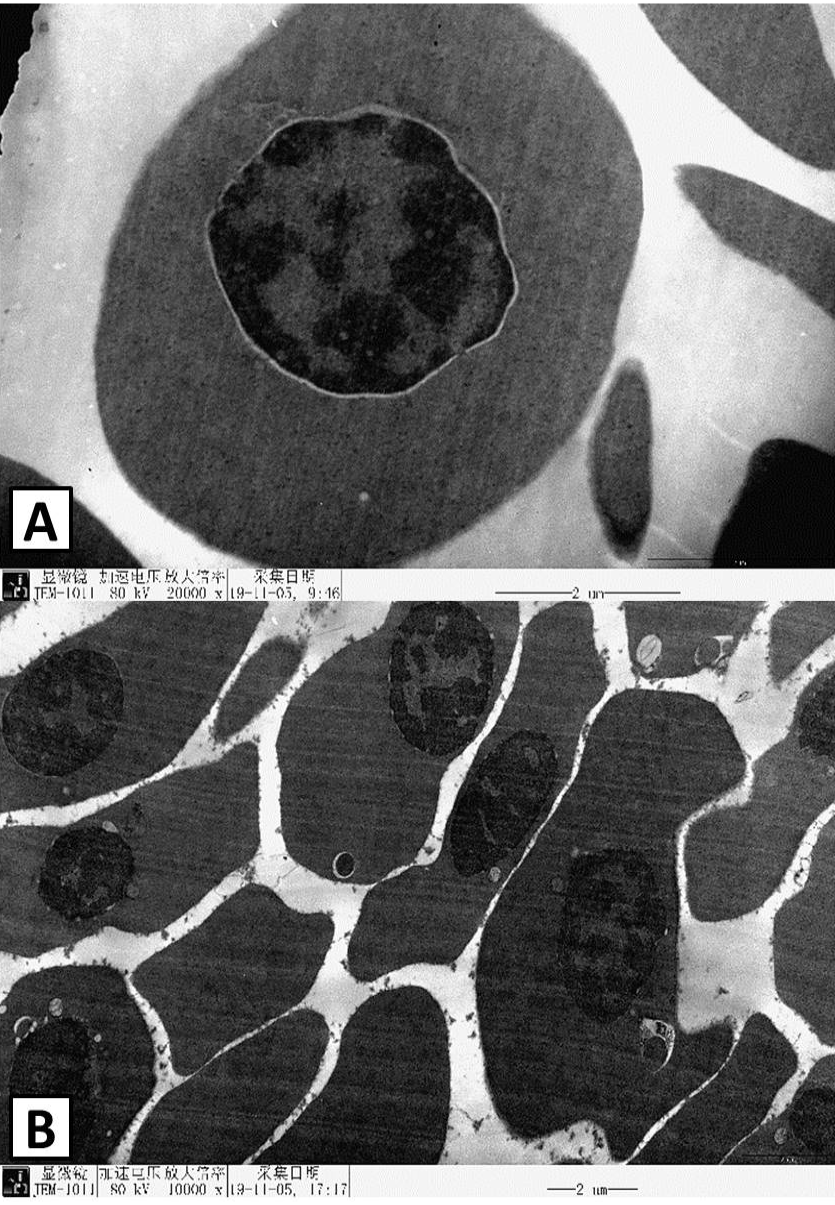
The transmission electron micrograph (TEM) revealed intearction between erythrocytes with M. synoviae.
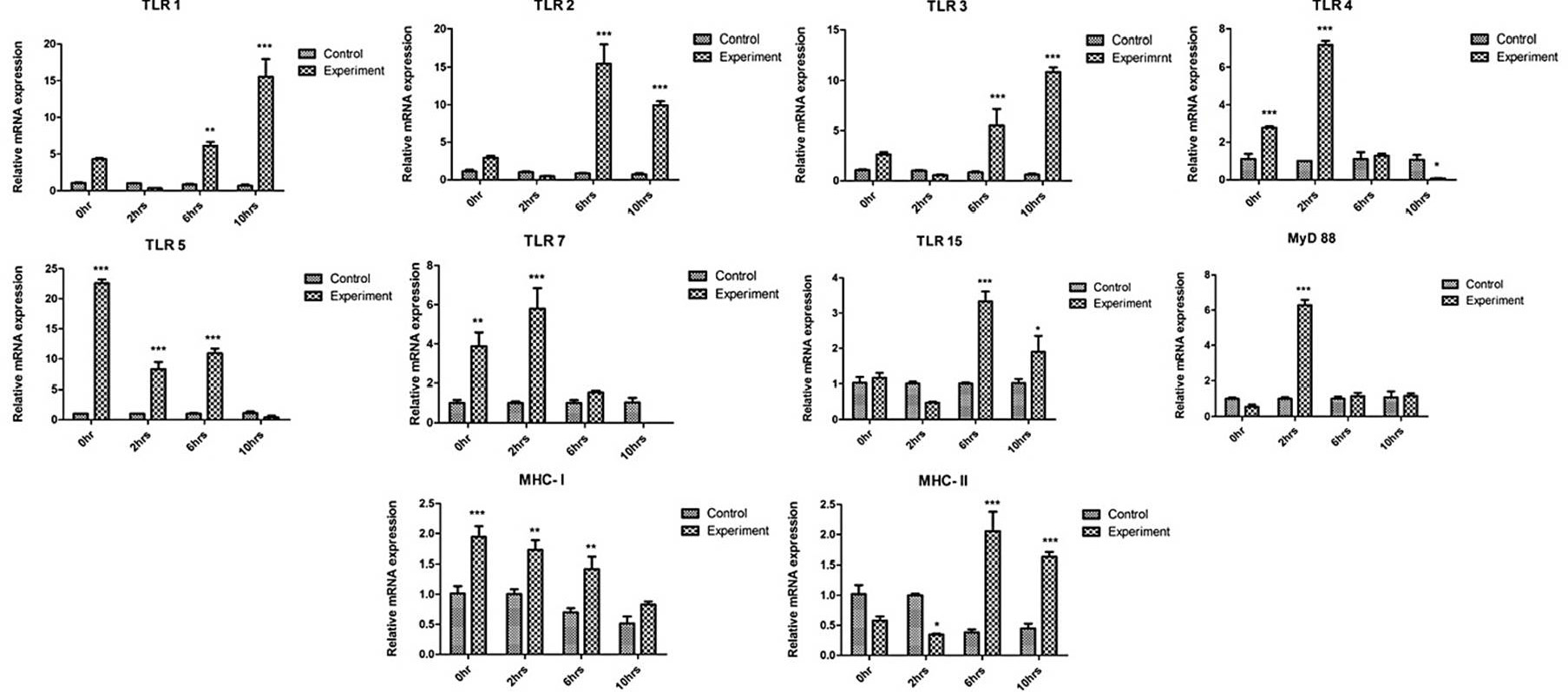
The expression pattern toll-like receptors pathway genes in chicken erythrocytes on 0, 2, 6, and 10 h. This experimental study group was as follows: the control group (Con, erythrocytes treated with PBS, n = 3) and the experiment group (Exp, erythrocytes infected with M. synoviae, n = 3). Expression levels of TLR pathway genes were relatively calculated to that of 18S rRNA the housekeeping genes via qRT-PCR. SEM (standard error of mean) represented, by error bars. Bars with asterisks indicate a significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001) Up or downregulated relative mRNA expression when compared to uninfected control group.