Effect of Fermented Feed Addition and Crude Protein Level on Performance of Local Chickens in the South of Vietnam
Effect of Fermented Feed Addition and Crude Protein Level on Performance of Local Chickens in the South of Vietnam
Pham Tan Nha*, Le Thu Thuy
Noi chicken in the experiment
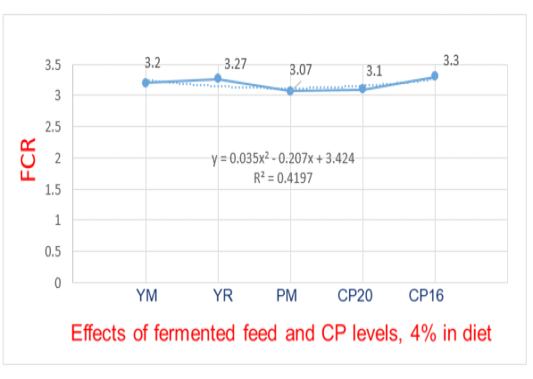
The effect of fermented feed and crude protein levels on FCR
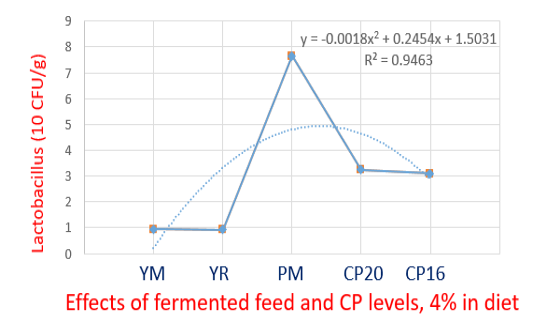
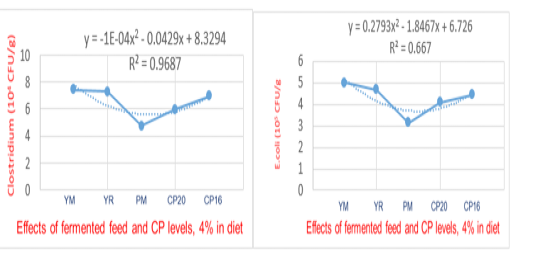
The effect of fermented feed on Lactobacillus In contrast, mixing fermented feed with a diet reduced E. coli and Clostridium in the gastrointestinal tract of Noi chickens after 14 weeks. This can be explained when probiotics increase, causing pathogenic bacteria such as E. coli and Clostridium (P<0.05) to decrease compared to not adding fermented feed. Especially the PM treatments was the best results (E. coli and Clostridium the lowest).
The effect of fermented feed on E. coli and Clostridium