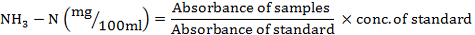Comparison of Nutritive Values and in vitro Degradability of Steam Treated Rice Straw with Chinese Wild Rye and Alfalfa
Comparison of Nutritive Values and in vitro Degradability of Steam Treated Rice Straw with Chinese Wild Rye and Alfalfa
Muhammad Naeem1,2, Nasir Rajput1,2, Sher Ali3, Asmatullah Kaka2, Dildar Hussain Kalhoro2, Mehvish Rajput2 and Tian Wang1,*
In vitro dry matter digestibility (IVDMD %) and organic matter digestibility (IVOMD %) of steam treated rice straws, alfalfa hay and Chinese wild rye. AH, alfalfa hay; CWR, Chinese wild rye; TRS-I, rice straw treated with steam explosion at 15.5 kgf/cm2 for 90 sec; TRS-II, rice straw treated with steam explosion at 15.5 kgf/cm2 for 120 sec. abc Mean values that do not share a common letter are significantly different (P<0.05); n = 5. Values are presented as mean ±SE.
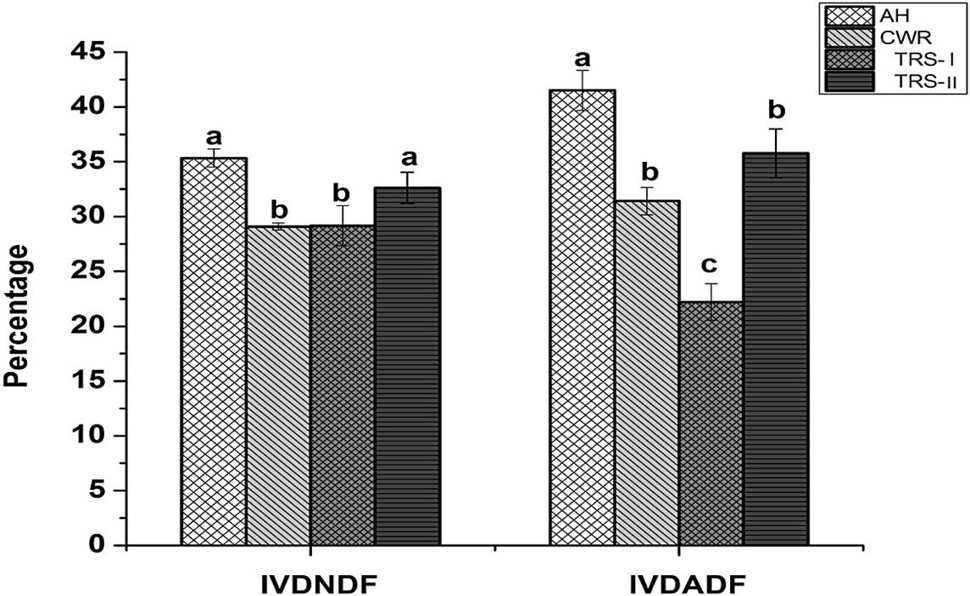
In vitro DNDF (%) and DADF (%) steam treated rice straws, alfalfa hay and Chinese wild rye. For abbreviations and statistical details, see Figure 1.
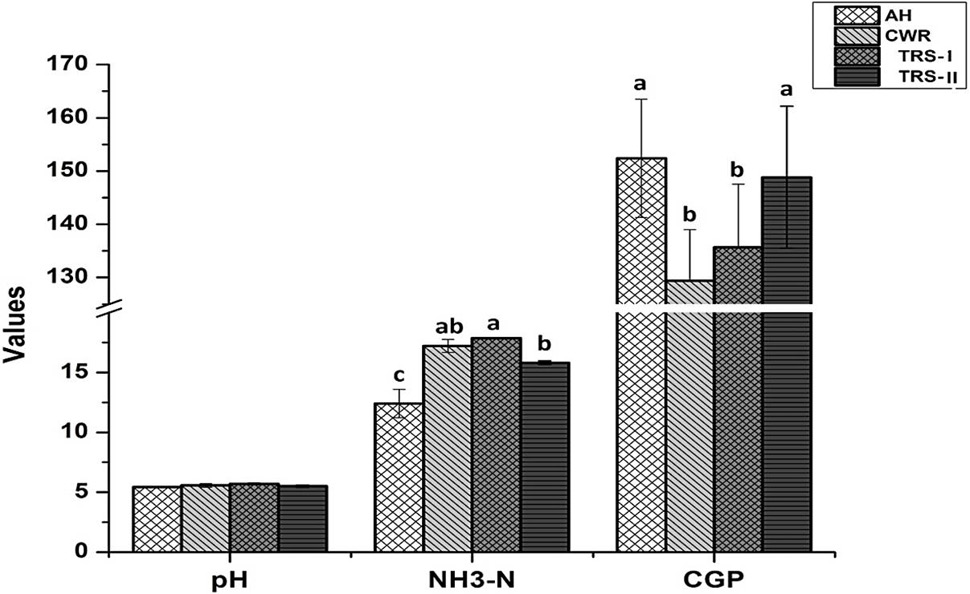
In vitro cumulative gas production (CGP), pH and NH3-N (mg/100ml) concentrations of steam treated rice straws, alfalfa hay and Chinese wild rye. For abbreviations and statistical details, see Figure 1