A 24 BP Indel Prolactin Gene Polymorphism and Its Association with Some Reproductive Traits in Color Dual-Purpose VLV Hens in Southern Vietnam
Ngoc Tan Nguyen1*, Thi Tuong Vi Trang1, Thi Thuy Tien Nguyen2, Tuan Thanh Hoang2, Duc Thoa Nguyen2
1Faculty of Biological Sciences, Nong Lam University in Ho Chi Minh City - Linh Trung Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; 2Vigova Poultry Research and Development Center - 496/101 Duong Quang Ham Street, Ward 6, Go Vap District, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
*Correspondence | Ngoc Tan Nguyen, Faculty of Biological Sciences, Nong Lam University in Ho Chi Minh City - Linh Trung Ward, Thu Duc City, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; Email: nntan@hcmuaf.edu.vn, ngoctan0068@gmail.com
Figure 1:
Representative VLV chicken breed. (A and B) adult VLV rooster and hen at the time of sample collection (38 weeks of age); (C) VLV in a confined ground area at the growing stage, and (D) caged hens at the laying stage.
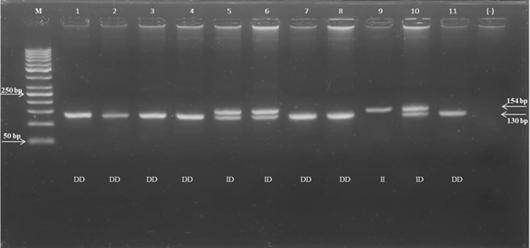
Figure 2:
Representative electrophoresis of the PCR products of 24 bp indel in the promoter region of the prolactin gene on 2% agarose gel. M: DNA ladder (50 bp). No. 1-4; 7-8 and 11: individual samples with DD genotype; Nos. 5-6 and 10: ID genotype; No. 9: II genotype; (-): Negative control.
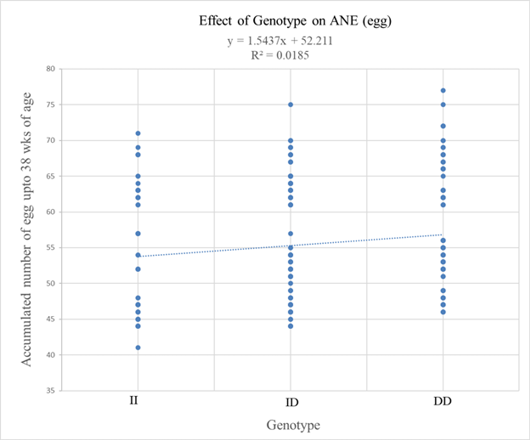
Figure 4:
Genotype effects of the 24 bp indel prolactin gene on the accumulated number of eggs laid by VLV hens up to 38 weeks of age. ANE: accumulated number of eggs.
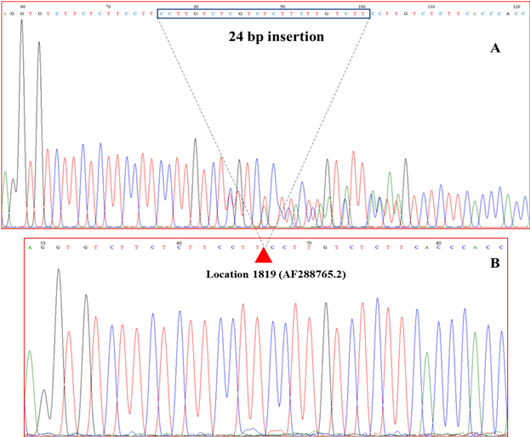
Figure 3:
Representative two sequences of the 24 bp PRL/indel in the promoter region. A: insertion of 24 bp (I allele) and B: deletion of 24 bp (D allele) at site 1819 (AF288765.2).