Susceptibility Evaluation of Different Legume Seed Genotypes against Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) under Laboratory Conditions
Susceptibility Evaluation of Different Legume Seed Genotypes against Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) under Laboratory Conditions
Muhammad Faizan1, Muhammad Nasir1, Muhammad Waqar Hassan1*, Ghulam Sarwar2 and Moazzam Jamil3
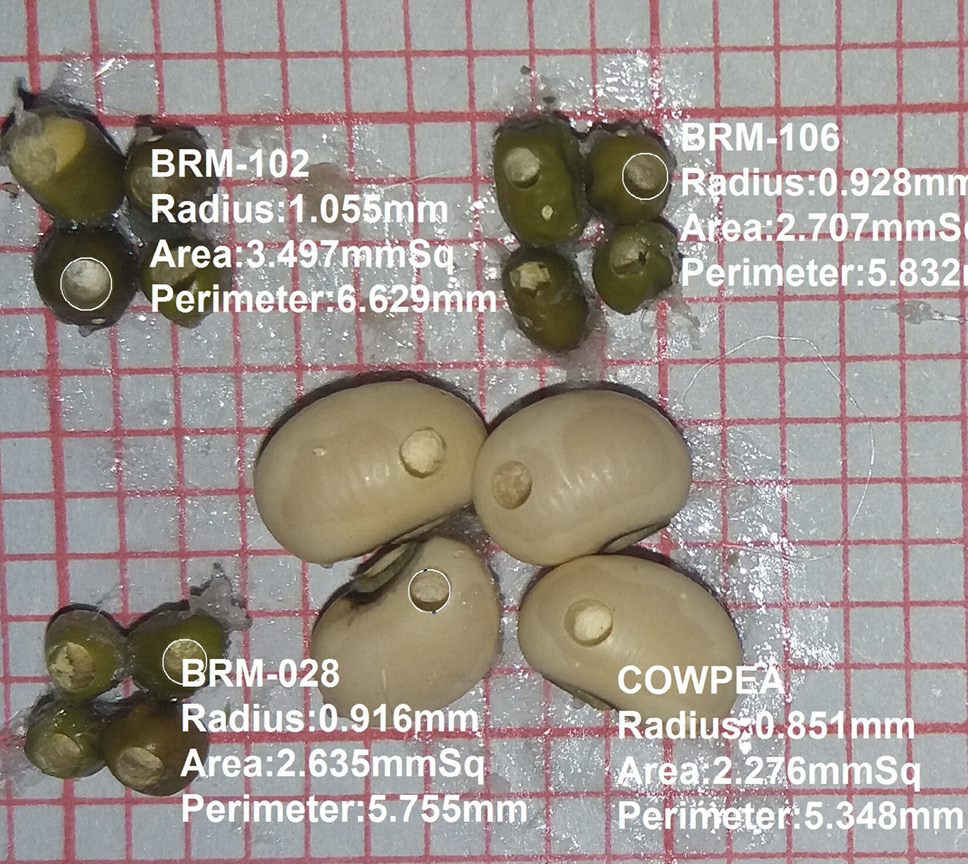
A: Cowpea (host variety), B: Mung bean (BRM-102), C: Mung bean (BRM-106), D: Mung bean (BRM-28). Seed size assessment on graph paper. 1BD:25 mm, 1SD: 2.5 mm. Seeds placed length wise along one side and width wise along other side. Assessments include individual seed lengths, widths and area. BD, Big division; SD, Small division.
A: Cowpea (host variety), B: Chickpea (Bittle-16), C: Chickpea (BWP-white), D: Chickpea (Sadiq-2021). Seed size assessment on graph paper. 1BD:25 mm, 1SD: 2.5 mm. Seeds placed length wise along one side and width wise along other side. Assessments include individual seed lengths, widths and area.
Top left: Mung bean (BRM-102), Top right: Mung bean (BRM-106), Bottom left: Mung bean (BRM-028), Bottom right: Cowpea (host). Mature insects exit holes size (three holes per treatment) assessment on graph paper with T capture software in laptop computer calibrated through scale captured with those images.