Study on the Extracting Technology for Antioxidant Oligopeptides from Donkey Meat by Two-Step Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Study on the Extracting Technology for Antioxidant Oligopeptides from Donkey Meat by Two-Step Enzymatic Hydrolysis
Lanjie Li1, Jingjing Zhang2, Ruiyan Zhang2, Ning Zhang2, Zixiang Wei2, Guiqin Liu1,*, Riaz Hussain Pasha3, Muhammad Akram Khan4 and Saif-Ur-Rehman5
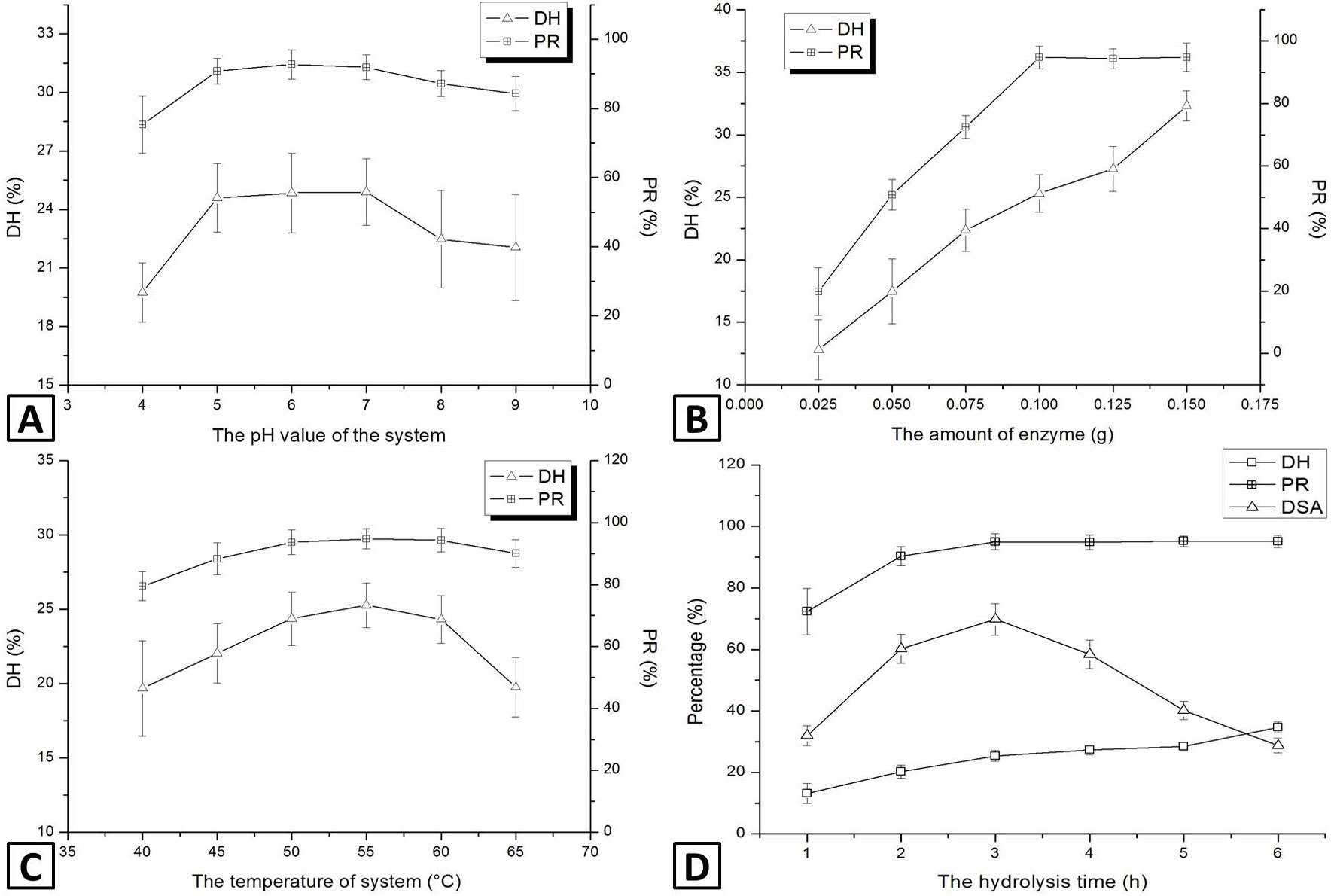
Effects of pH (A), enzyme concentration (B), temperature at pH 5.96 (C) and hydrolysis time (D) on DH, PR, and DSA. The pH was 5.96. The enzyme: Substrate ratio was 0.7%. The reaction temperature was 55ºC. Data are presented as mean±SD (n=6). Error bars represent SDs.
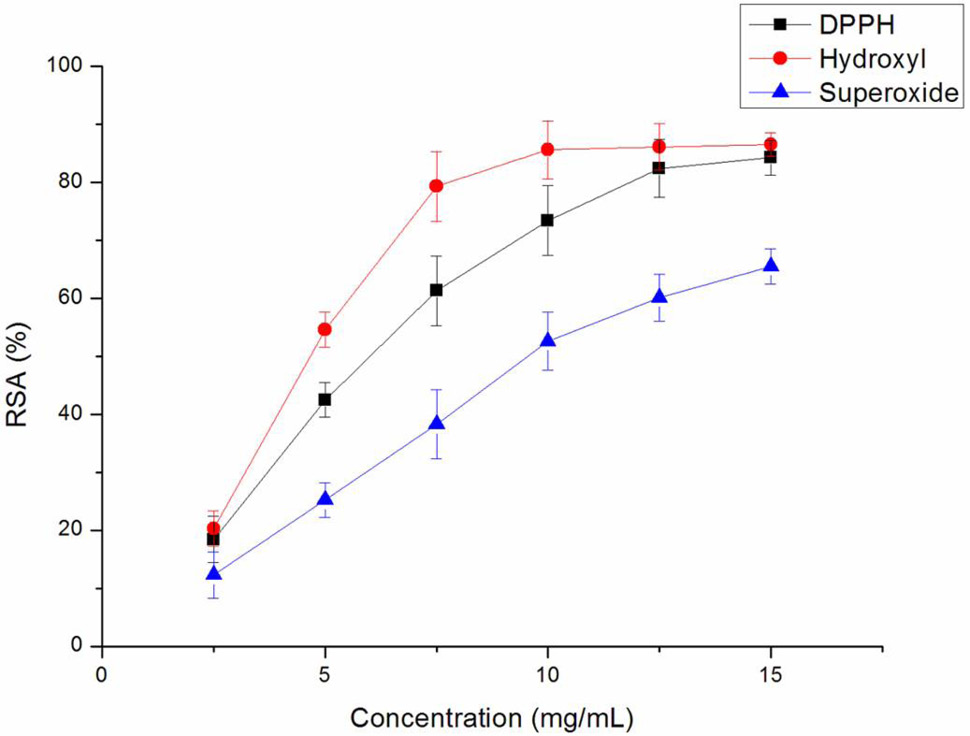
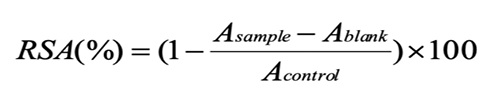
The DPPH, hydroxyl, superoxide radical scavenging activities of Hydrolysates. Data are presented as mean±SD (n=6). Error bars represent SDs.
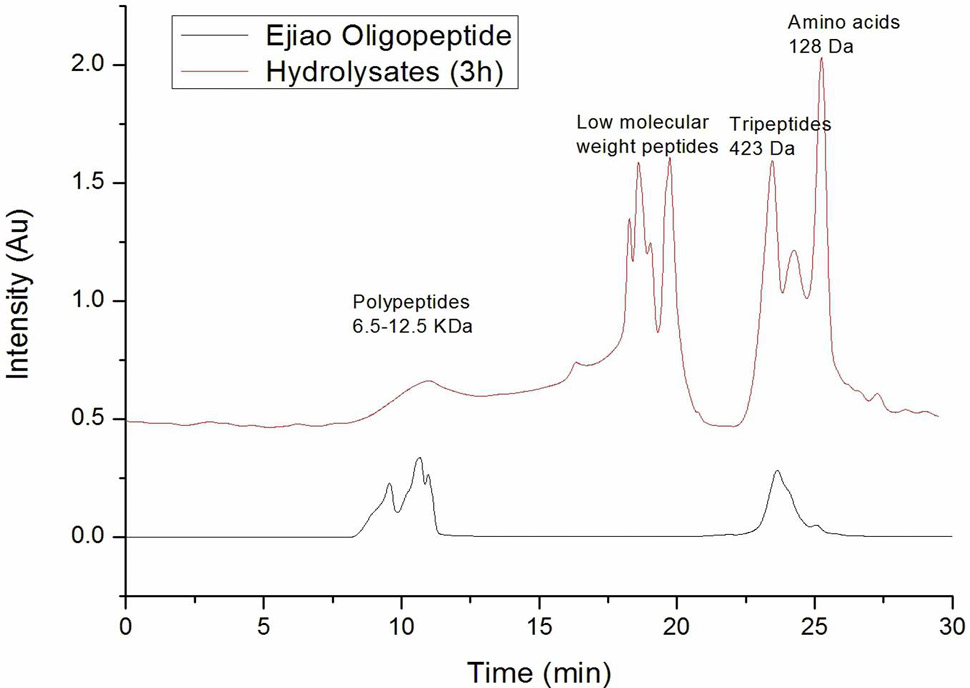
The molecular weight distribution of Ejiao Oligopeptid and Hydrolysates (3 h).