Protective Effects of Ginger Ethanolic Extract, Chitosan Nanoparticles, and Ginger Ethanolic Extract-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles on Pancreatic DNA Damage and Histological Changes in Dogs with Alloxan-Nicotinamide Induced Type 2 Diabetes
Protective Effects of Ginger Ethanolic Extract, Chitosan Nanoparticles, and Ginger Ethanolic Extract-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles on Pancreatic DNA Damage and Histological Changes in Dogs with Alloxan-Nicotinamide Induced Type 2 Diabetes
Rasema Majeed, Alaa Kamil Mahmood*
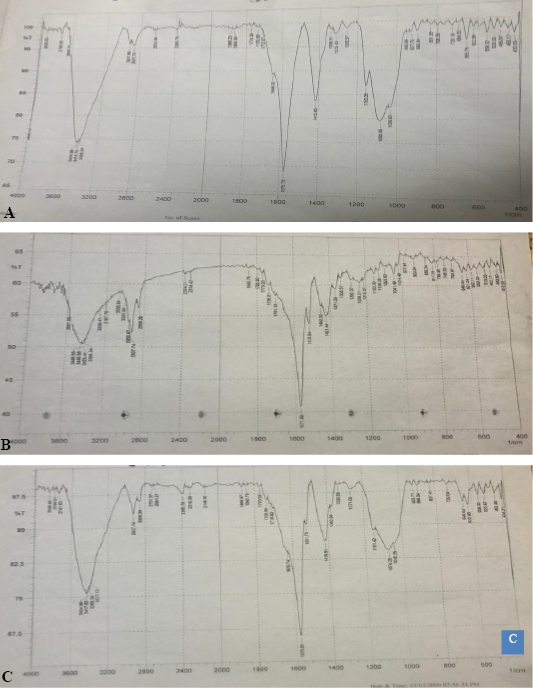
FTIR spectra of chitosan nanoparticles (A), ginger ethanolic extract (B), and ginger ethanolic extract-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (C).
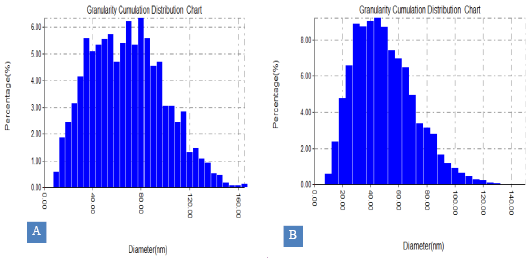
Average size of chitosan nanoparticles (CNPs) (A) and ginger ethanolic extract-loaded CNPs (GEE-CNPs) as obtained by atomic force microscopy.
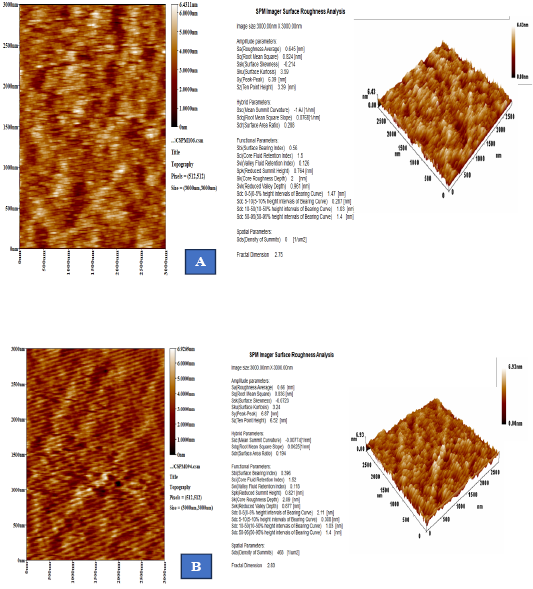
Atomic force microscopy of chitosan nanoparticles (CNPs) (A) and ginger ethanolic extract-loaded CNPs (GEE-CNPs) (B) synthesized using ionic gelation methods illustrate 2D and 3D topological.
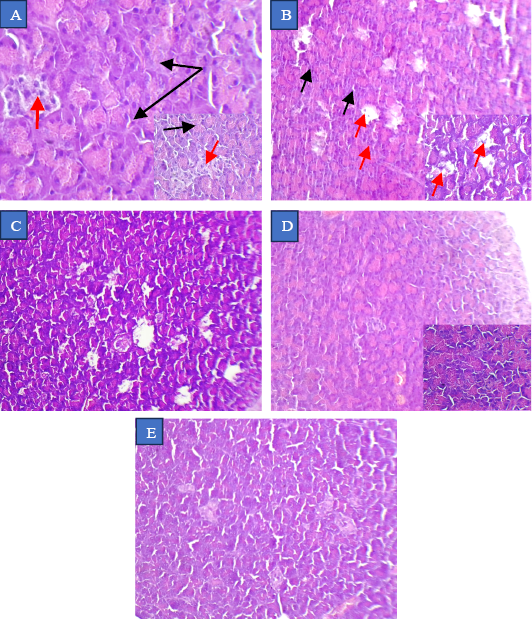
Pancrease in adult dog (H&E stain) in (A) Negative control group (non diabetic, not treated) showing normal tissue. (B) Positive control group (diabetic, saline treated) induced by alloxan–nicotinamide showing pancreatic damage. (C) Ginger ethanolic extract (GEE) group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE for 6 weeks) showing. (D) GEE-chitosan nanoparticles (GEE-CNPs) group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE-CNPs) for 6 weeks) group showing. (E) CNPs group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW CNPs) showing.
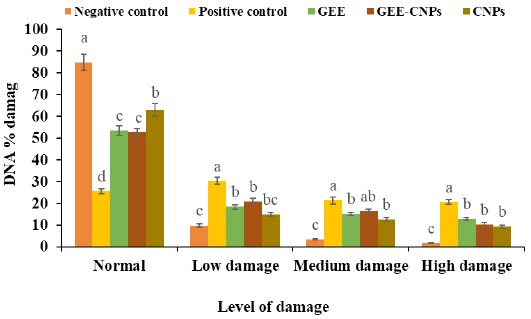
Comparative analysis of DNA damage categories in pancreatic tissue of dogs across different treatment groups. Negative Control group (non-diabetic, untreated), Positive Control group (diabetic, saline treated) induced by alloxan–nicotinamide). Ginger ethanolic extract (GEE) group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE for 6 weeks). GEE-chitosan nanoparticles (GEE-CNPs) group(diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE-CNPs for 6 weeks). CNPs group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW CNPs for 6 weeks). Bars with different letters are statistically significant(P<0.05). Error bars represent the standard error of mean(SEM).
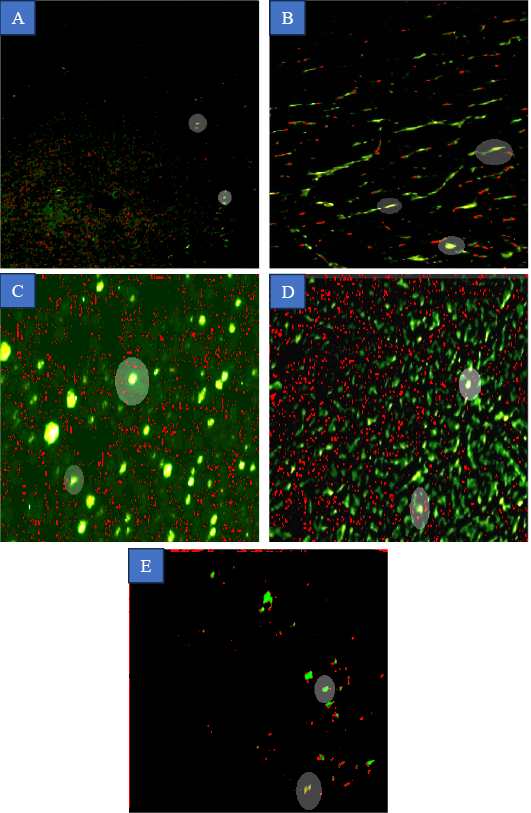
Images of comets of DNA damage categories in pancreatic tissue of dogs in (A) Negative contro group (non diabetic, not treated). (B) Positive control group (diabetic, saline treated) induced by alloxan–nicotinamide. (C) Ginger ethanolic extract (EE) group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE for 6 weeks). (D) GEE-chitosan nanoparticles (GEE-CNPs) group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW GEE-CNPs) for 6 weeks) group. (E) CNPs group (diabetic, treated with 81.7 mg/kg BW CNPs).