Protective Effect of Quercetin Treatment against Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress in a Male Rat Model
Protective Effect of Quercetin Treatment against Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress in a Male Rat Model
Nouf Alharbi*, Mai Elobeid and Promy Virk
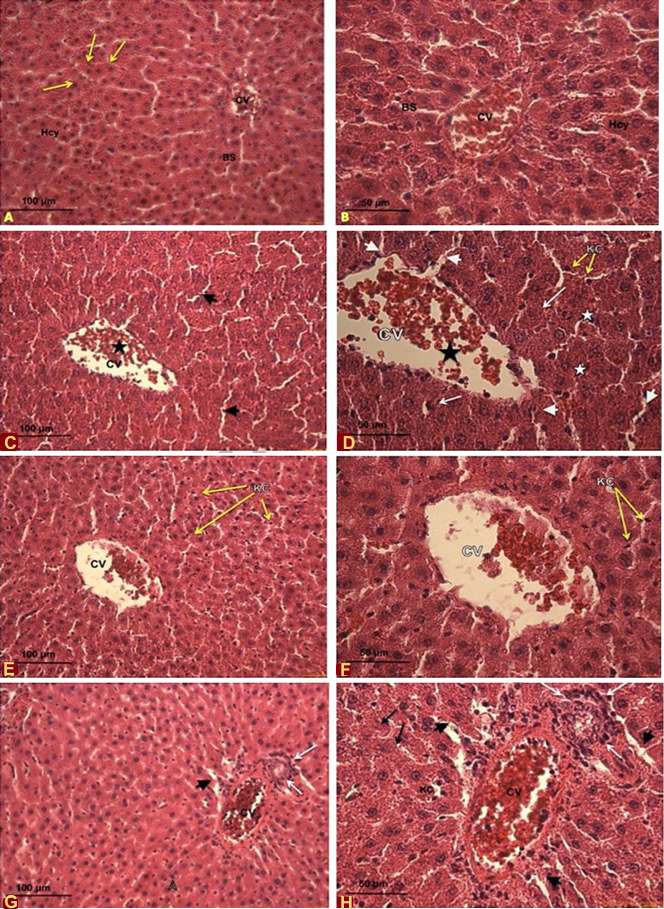
Effects of cadmium and quercetin on the histological sections of male Sprague-Dawley rate. A, B, control rates livers at 10x and 20x magnification, respectfully. A shows the central vein (CV), normal arrangement of hepatocytes (Hcy) along the hepatic cord (arrows) with normal blood sinusoids (BS) and B shows the central vein (CV), normal arrangement of hepatocytes (Hcy) along the hepatic cord (arrows) with normal blood sinusoids (BS); C, D, liver of rates oraly administrated with CdCl2 at 5mg/kg bw/d at 20x (C) and 40x (D) magnification. C shows disorganized hepatic architecture, dilated blood sinusoids (arrow heads), and dilated central vein (CV) (star); D shows dilated central vein (CV) (black star), dilated blood sinusoids (Arrow heads) congested with blood cells. Notice red blood cells (black arrow), Kupffer cells (KC) (yellow arrows), the disintegration in the tissue (white star), and degenerated hepatocytes and necrosis (arrows). E, F, liver of rates oraly administrated with quercetin at 5mg/kg bw/d at 20x (E) and 40x (F) magnification. E shows mild restoration of hepatic tissue. Notice Kupffer cell (KC) (yellow arrows), less disintegration in the central vein (CV) and more organized hepatocytes (star); F shows mild restoration of hepatic tissue. Notice red blood cells (black arrow), Kupffer cells (KC) (yellow arrows), less disintegration in the central vein (CV) and more organized hepatosytes. G, H, liver of rates oraly administrated with quercetin at 70mg/kg bw/d at 20x (G) and 40x (H) magnification. G shows disorganized hepatic architecture with disintegrated and highly congested central vein (CV) (star), inflammatory cell infiltration (white arrows), H shows dilated blood sinusoids (arrow heads) and increase in number of Kupffer cells (yellow arrows); B shows dilated blood sinusoids (arrow heads), necrosis (black arrows) and disintegration and congestion in the central vein (CV) (star) and inflammatory cell infiltration (white arrows). Notice the increase in number of Kupffer cells (yellow arrows).
Magnification: A, 10x; B, C, E, G, 20x; D,F, H, 40x.
Stain: Haematoxylin and Eosin
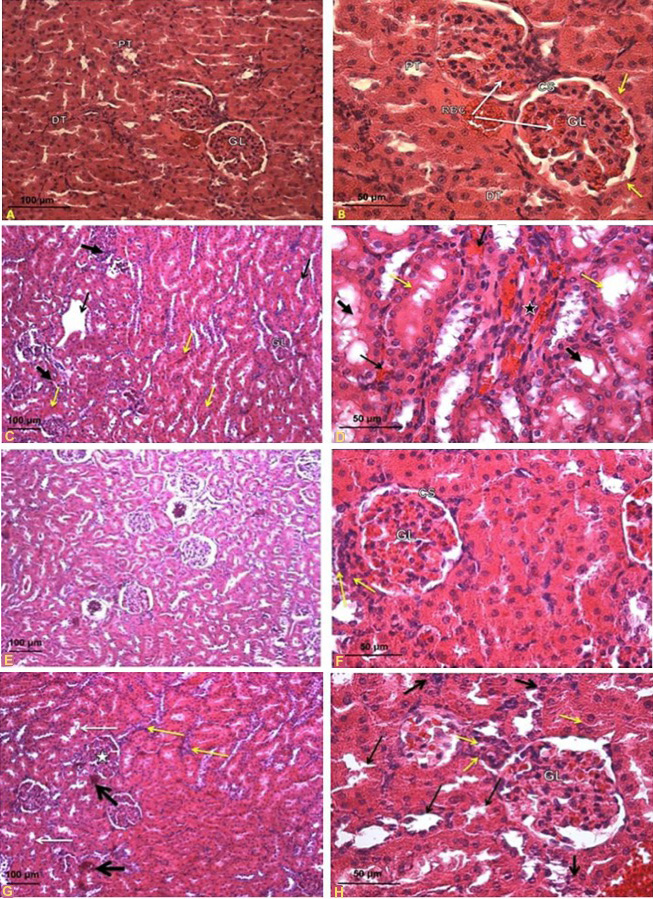
Effects of oral administration of cadmium and quercetin on the histological section of male Sprague-Dawley rate. A, B, control rates kidneys at 20x (A) and 40x (B) magnification. A shows the normal structure in the cortical region. Notice the renal glomerulus (GL), the proximal convoluted tubules (PT) and distal convoluted tubules (DT); B shows the normal intact cortical region. Notice the red blood cells (RBC), renal glomerulus (GL) with epithelium cells (arrows), proximal convoluted tubules (PT) and the distal convoluted tubules (DT) showed normal structure. C, D, kidneys of rats oraly administrated with CdCl2 at 5mg/kg bw/d at 10x (C) and 40x (D) magnification, respectively. C shows kidney of rats exposed to cadmium (5 mg/kg bw/d) (10x) showing collapsed glomerulus (star), tubular dilation (black arrows), diffuse hemorrhage (yellow arrows) and infiltration by lymphocytes (thick arrow), collapsed glomerulus (GL), hyper-cellularity and collapsed lumina of tubules; D shows collapsed glomerulus (GL) (star), intense hemorrhage (arrow), detached brush border of proximal convoluted tubules (yellow arrows), hyper-cellularity and flattened tubular cells and lumina are relatively dilated (thick arrows). E, F, kidneys of rates oraly administrated with quercetin at 5mg/kg bw/d at 10x (E) and 40x (F) magnification. E shows mild restoration with near normal appearance in renal glomeruli (G), glomerular capsule (BC) with distinct capsular space (CS); F shows reduced the damage induced by cadmium. Notice lymphocytes infiltration (yellow arrow), renal glomeruli (GL) and glomerular capsule with distinct capsular space (CS). G, H, kidneys of rats oraly administrated with quercetin at 70mg/kg bw/d at 10x (G) and 40x (H) magnification. G shows tubular dilation (white arrows), collapsed glomerulus (GL) (star), lymphocytes infiltration (yellow arrow) and intense hemorrhage (black arrow); H shows collapsed glomeruli (GL), glomerular space (CS), tubular dilation (arrows), hyper-cellularity (thick arrows) and lymphocytes infiltration (yellow arrow).
Magnification: A, 20x; B, D, F, G, 40x; C, E, G, 10x.
Stain: Haematoxylin and Eosin