In vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritic Potential of Ethanolic Acacia modesta Extract on CFA-Induced Adjuvant Arthritic Rats
In vivo Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Arthritic Potential of Ethanolic Acacia modesta Extract on CFA-Induced Adjuvant Arthritic Rats
Farah Abid1,2, Mohammad Saleem1,3*, Tahir Maqbool4, Tania Ahmed Shakoori5, Faheem Hadi4, Tahir Muhammad4, Saira Aftab4, Yasir Hassan7 and Shabana Akhtar4,6*
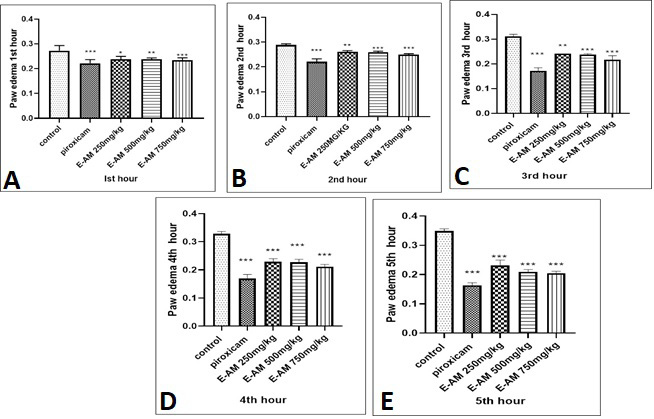
Effect of different concentrations of ethanolic extract of Acacia modesta for different time intervals on paw edema induced by Carrageenan. A showing treatment at 1st h, B is at 2nd h, C at 3rd h, D at 4th h and E at 5th h. ***, **, * showing P≤0.05, P≤ 0.01, P≤ 0.001.
Effect of different concentrations of ethanolic extract of Acacia modesta on carrageenan induced arthritis at different days, body weight, gross microscopic evaluation of rat paw and histopathology of rat paw where in case of 1; CFA induced arthritis and body weight, A showing carrageenan induced arthritis at different days and B showing treatment group where E-OM with 750mg/kg dose showed an increase in body weight at 28 day as compared with arthritic group. In case of 2; gross microscopic evaluation of rat paw. A showing bone erosion B is showing pannus formation C is showing vascular degenerative changes in case of 3; histological appearance of pannus formation, bone erosion and vascular degenerated changes (A-F). All histopathological parameters i.e. bone erosion, pannus formation and vascular degenerative changes were also reduced in arthritic rats as compared to Piroxicam. Gross microscopic rat paw evaluation at end of CFA model depicts severe edema in arthritic rats, less pannus formation and bone erosion in rats treated with E-AM. ***, **, * showing P≤0.05, P≤ 0.01, P≤ 0.001.
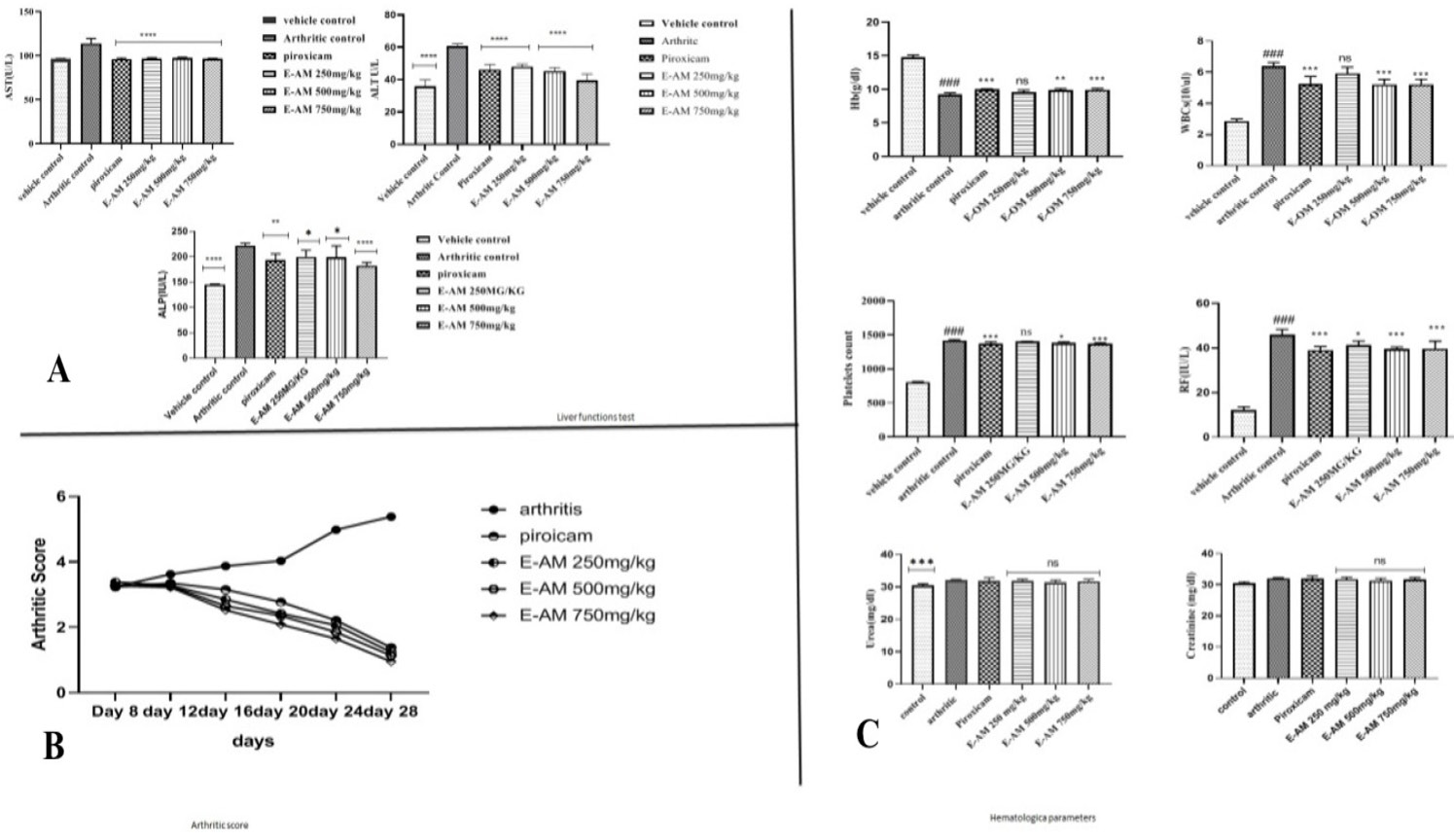
Effect of different concentrations of ethanolic extract of Acacia modesta on liver function tests (A), hematological parameters (B) and arthritic score (C). A, Liver markers ALP, ALT and AST were calculated by one-way ANOVA and Dennett’s multiple comparison test. E-AM treated extracts showed a normal ALP, ALT and AST levels. B, Hematological parameters E-AM showed ameliorating effect on hematological parameters at a dose of 750 mg/kg. C, arthritic index the normal control group did not show any swelling throughout the study. Treatment with the E-AM and piroxicam effectively reduce the arthritic index in comparison to arthritis control group from day 16 to 28. The maximum arthritic index observed at 28th day that was restored by E-AM at 750mg/kg compared with low doses. ***, **, * showing P≤0.05, P≤ 0.01, P≤ 0.001.
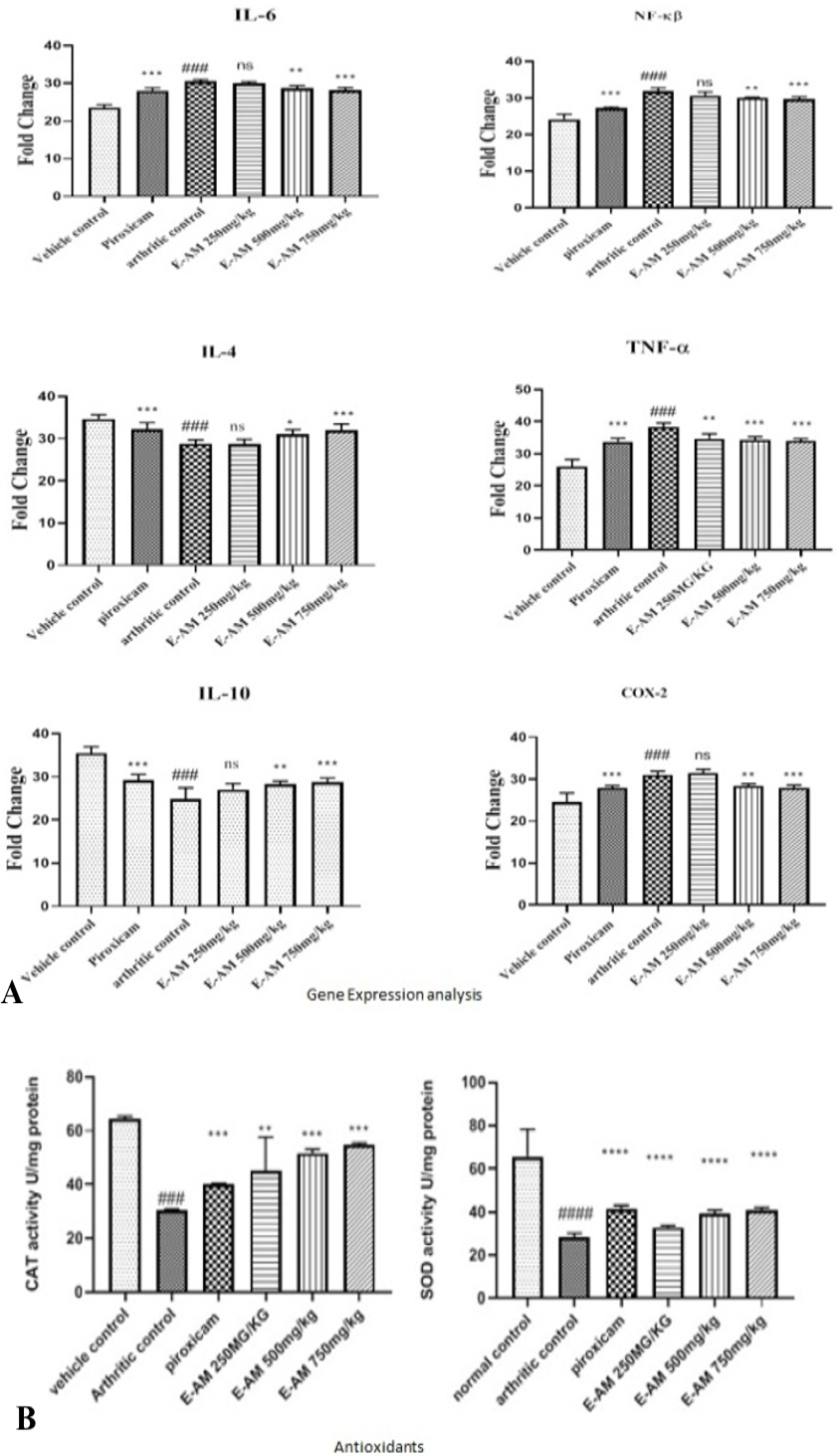
Effect of different concentrations of ethanolic extract of Acacia modesta on gene expression analysis (A), and antioxidative potential superoxide dismutase and catalase (B). The gene expression of several inflammatory biomarkers were evaluated following 28 days of study in wistar rats for mRNA expression of IL4, IL6, IL10, NF-κβ1, TNF-a, COX-2. In case of antioxidants SOD and CAT there was a significant decline of antioxidants compared to arthritic group. ***, **, * showing P≤0.05, P≤ 0.01, P≤ 0.001.
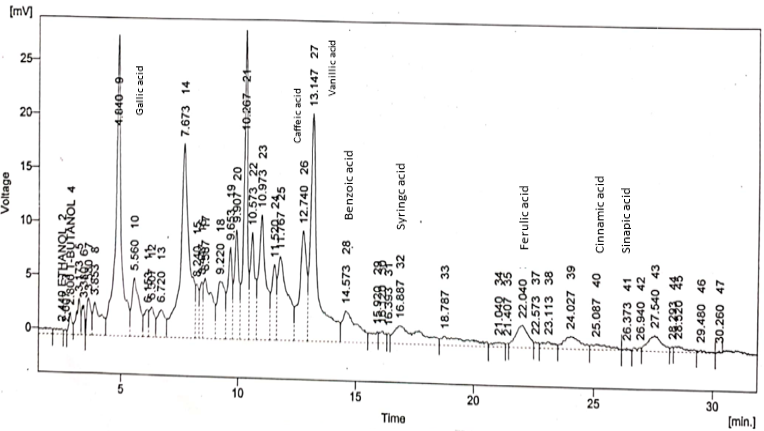
HPLC peaks of various natural compounds with their retention time found in E-AM extract.