Histopathological and Cytogenetic Effects of Hyperdoses of Vitamin D in Female Rats
Histopathological and Cytogenetic Effects of Hyperdoses of Vitamin D in Female Rats
Ghaith Z. Hasan Al-Askari *, Eman H. Yousif Al-Taee
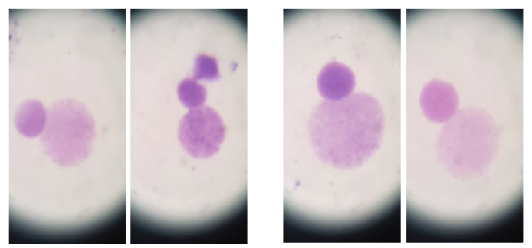
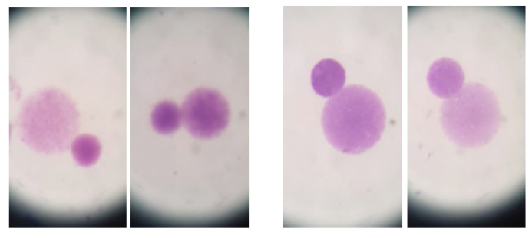
Shows the Micronucleus after 45 days from the beginning of experience
Shows the Micronucleus after 90 days from the beginning of experience
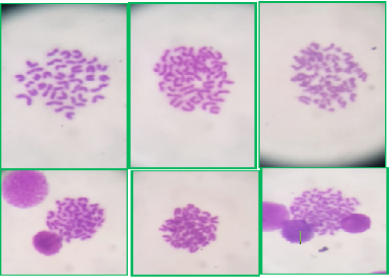
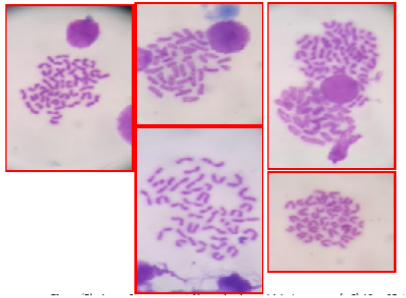
Shows the Chromosomal Aberration in high dose group (HG) After 45 days of experiment
Shows Chromosomal Aberration in the Low dose group (LG) After 45 days of experiment
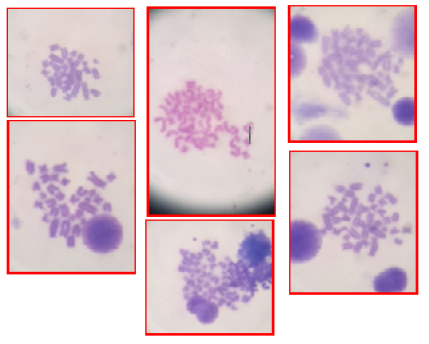
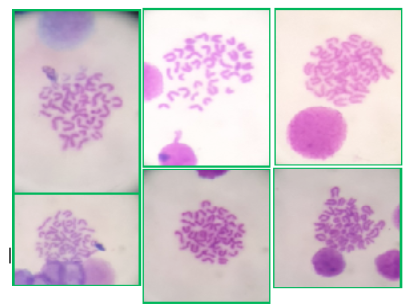
shows Chromosomal Aberration in the high dose group (HG) After 90 days of experiment
shows the Chromosomal Aberration in low dose group (LG) After 90 days of experiment
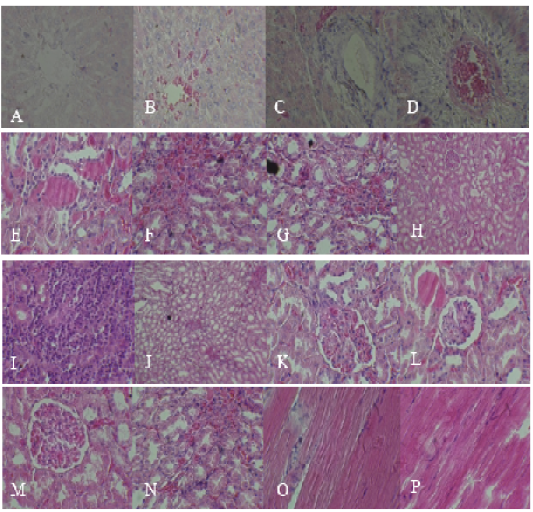
Histopathological section for different animals showing congestion of hepatic sinusoids and central vein (A), and cellular swelling (B), pericentral necrosis with infiltration of inflammatory cells (C), with fibrosis and congestion of central vein (D). The kidney sections show the presence of hyaline cast with sloughing of epithelial lining urinary tubules (E), congestion with infiltration of inflammatory cells (F, G, H and J), besides areas of necrosis (I), besides sloughing of epithelium lining urinary tubules (K), with dilatation of Bowman space (L) and congestion of the glomerular tuft with vacuolation in renal tubules (M), with degenerative changes (swelling) in the renal tubular epithelium (N). Muscle section shows infiltration of inflammatory cells besides edema causes separation of muscle’s fibers in addition to the presence of fragmentation and necrosis (O and P).
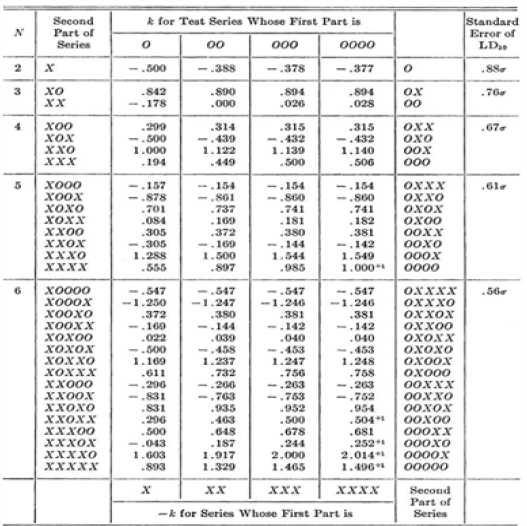
value of K for estimating LD50 from Up and Down. If the table is entered from the foot, the sign of K is to be reversed (Dixon, 1965).