Histological and Histochemical Comparative Study of the Tongue in White-Eared Bulbul (Pycnonotus leucotis) and Bronze Fallow Cockatiel (Nymphicus hollandicus)
Histological and Histochemical Comparative Study of the Tongue in White-Eared Bulbul (Pycnonotus leucotis) and Bronze Fallow Cockatiel (Nymphicus hollandicus)
Saif Dhulfiqar Abdulhasan Al-Khafaji, Siraj Moner Al-Kafagy*
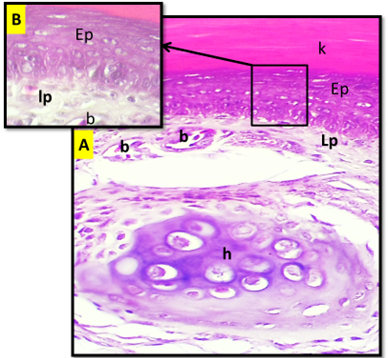
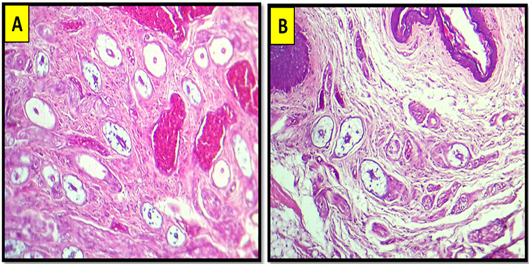
(A) Cross histological section of the apex of tongue in white eared bulbul show: Stratified squamous epithelium (Ep), keratinized layer (K), lamina properea (Lp), blood vessels (B), Hyaline cartilage (H). H&E stain. 20X. (B). Magnified section. 100x.
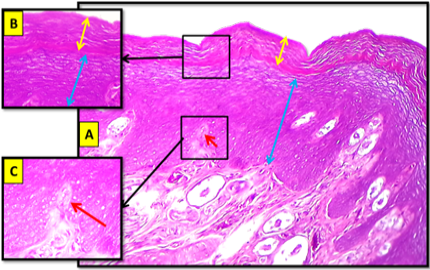
Longitudinal histological section of the apex of tongue in cockatiel show: Keratinized layer (yellow double head arrow), stratified squamous epithelium (blue double head arrow), papillary projection (red arrow). H&E stain. 20x. (B) and (C) magnified section. H&E stain. 40x.
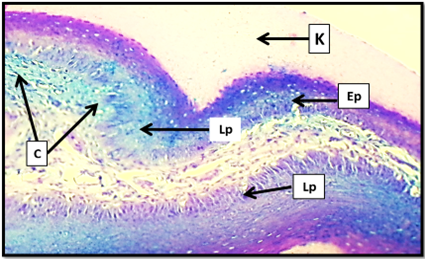
Cross histological section of the apex of tongue in white eared bulbul show: Keratinized layer (K), stratified squamous epithelium (Ep), lamina properia (Lp), collagen fibers (C). Masson trichrom stain. 20x.
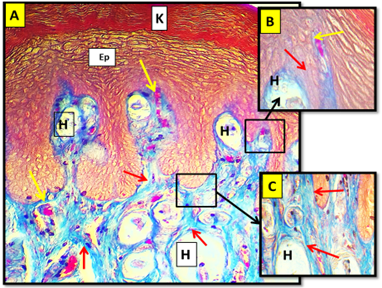
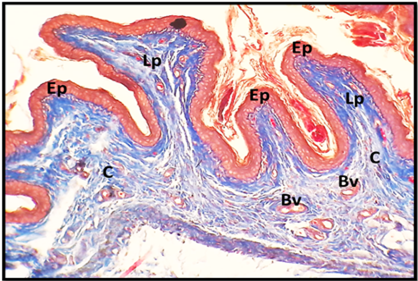
(A) Cross histological section of the apex of tongue in cockatiel show: Keratinized layer (K), stratified squamous epithelium (Ep), collagen fibers (red arrow), blood supply (yellow arrow), herbiest corpuscle (H). Masson trichrom stain. 20x. (B) and (C): Magnified section 40x.
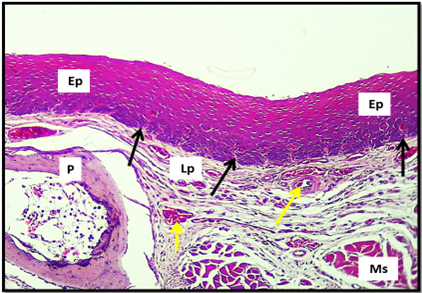
Cross histological section of the body of tongue in bulbul dorsal surface show: Stratified squamous epithelium non keratinized (Ep), lamina properea (Lp), papillary projection (black arrow), blood vessels (yellow arrow), skeletal muscle (Ms), paraglossum (P). H&E stain. 10x.
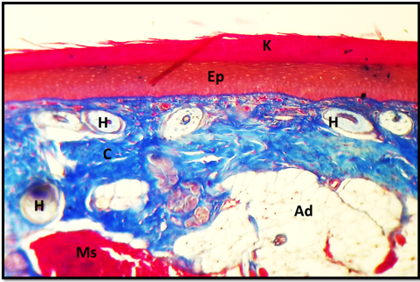
Cross histological section of the body of tongue in cockatiel show: stratified squamous epithelium (Ep), keratinized layer (K), connective tissue (C), skeletal muscle (Ms), herbiest corpuscles (H). Masson trichrom stain. 10x.
Cross histological section of the root of tongue in bulbul show: stratified squamous epithelium non keratinized (Ep), lamina properia (Lp), blood vessels (B), collagen bundles (C). H&E stain. 4x.
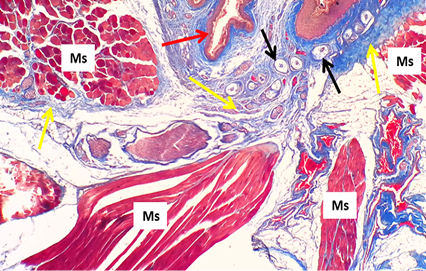
Cross histological section of the body of tongue (ventral surface) in cockatiel show: Skeletal muscle (Ms), stratified squamous epithelium (red arrow), herbiest corpuscle (black arrow), collagen bundles (yellow arrow).Masson trichrom stain. 10x.
Cross histological section of the tongue in cockatiel show: The distribution of the herbiest corpuscle H&E stain. 10x. A: Apex of the cockatiel tongue B: Root of the cockatiel tongue.
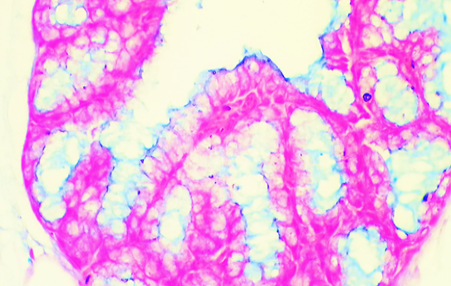
Histological section for lingual gland of bulbul show: The ligual gland was give positive reaction for Alcian blue stain that men the gland was have acidic mucopolysaccharid secretion. AB stain. 40x.
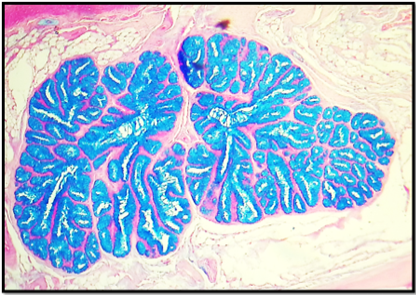
Histological section for lingual gland of cockatiel show: the ligual gland was give positive reaction for Alcian blue stain that men the gland was have acidic mucopolysaccharid secretion. AB stain. 10x.