Exploring Phenotypic Diversity of Human Iris Features and Skin Color in Punjabi and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Population of Pakistan
Exploring Phenotypic Diversity of Human Iris Features and Skin Color in Punjabi and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Population of Pakistan
Saliha Bashir*, Muhammad Shafique, Muhammad Shahzad, Muhammad Sohail Anjum and Ahmad Ali Shahid
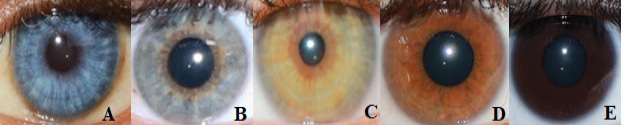
Eye color images collected from Pakistani population and characterized according to the Fitzpatrick Phototype Scale (A-E). This scale specifies five categories of eye color: A, blue; B, blue grey; C, green or light brown/green/hazel; D, light to dark brown and E, brownish black. For simplification, images were broadly assembled in three groups: 1, blue (equivalent to A and B in Fitzpatrick classification), 2, intermediate (equivalent to C in Fitzpatrick classification), 3, brown (equivalent to D and E in Fitzpatrick classification).
Skin color images collected from Pakistani population (A-E) and characterized according to the Fitzpatrick Phototype Scale. This scale specifies six shades of skin color: A, very pale; B, pale; C, light brown; D, medium brown; E, dark brown; F, brownish black. Based on this scale, we used three categories to characterize skin color: 1, white and beige skin color (equivalent to A and B in Fitzpatrick classification), 2, light brown to medium brown (equivalent to C and D in Fitzpatrick classification), 3, dark brown to brownish black skin (equivalent to E and F in Fitzpatrick classification).
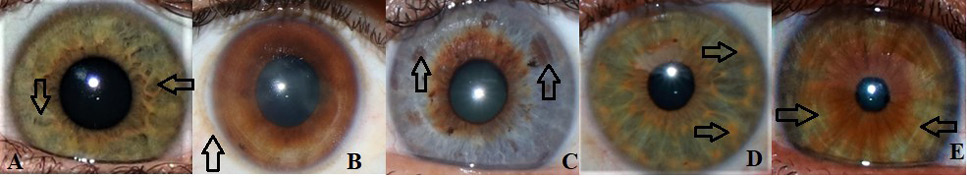
Images of iris features found in Pakistani population (A-E). Arrows are directing towards the iris patterns in images. Fuchs ‘crypts (A) are small or large diamond shaped cavities which appear in the anterior border layer of iris and arise during the constriction of pupillary membrane. Conjunctival melanosis (B) is brownish ring around the iris and/or isolated pigmented spots on sclera. Pigment spots (C) are distinct and well-defined brownish black regions of hyperpigmentation observed on iris surface. Nevi are pigmented spots that deform stromal layer while pigment dots that do not deform stromal layer are known as freckles. This feature is common in brown eyes. Wolfflin nodules (D) are small circular aggregates of collagen which are whitish orange in color and surround the outer boundary of iris. Contraction furrows (E) are discontinuous rings which look like wrinkles and formed during contraction and expansion of pupil. They expand along the outer border of iris.
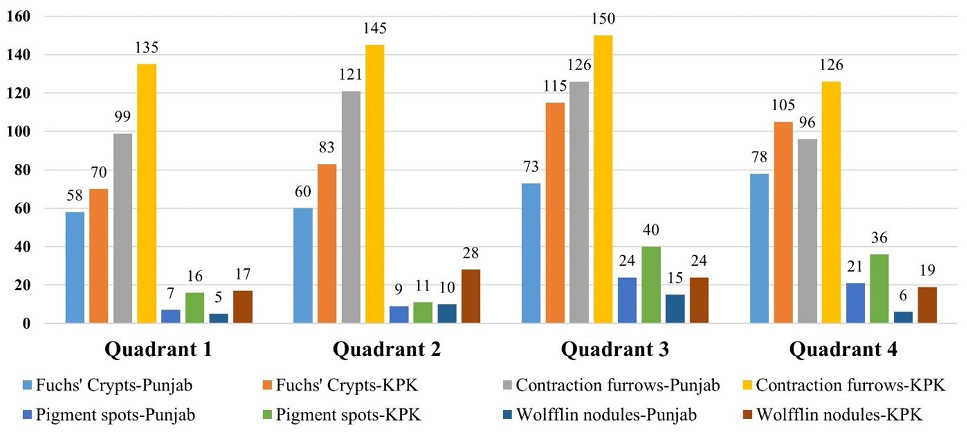
Count of surface features in four quadrants of iris.