Equine Herpes Virus 4 (EHV4) Investigation in Aborted Egyptian Mares; Molecular Detection, Isolation, and Phylogeny for Viral Glycoprotein B
Equine Herpes Virus 4 (EHV4) Investigation in Aborted Egyptian Mares; Molecular Detection, Isolation, and Phylogeny for Viral Glycoprotein B
Omnia Mohamed Khattab1*, Hala Kamel Abdelmegeed2, Mohamed Mahmoud Mashaly1, Mervat Hamdy1*, Naglaa Hagag1, Ayman Hamed3, Hanan Aly Fahmy3, Essam Ibrahim4, Momtaz Abdelhady Shahein2, Elsayyad Mohamed Ahmed2
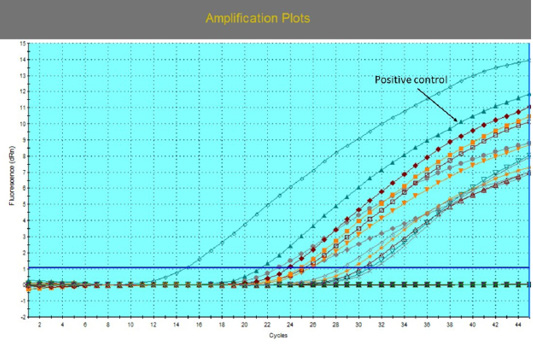
The amplification plot for EHV-4 qPCR with different threshold cycles (Ct) values for 16 positive samples. EVHV-4 stander was used as a positive control with Ct 18.
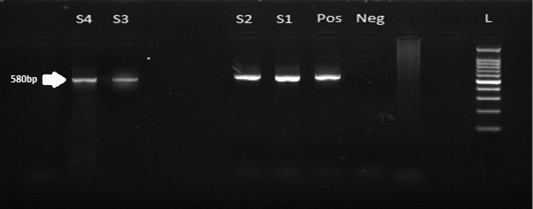
Nested PCR gel electrophoretic pattern of the EHV-4 gB gene, the specific band amplified at the expected size 580bp where: lanes S1, S2, S3, S4 for samples, L 100bp for Ladder, Pos for positive control, and Neg for the negative specimen.
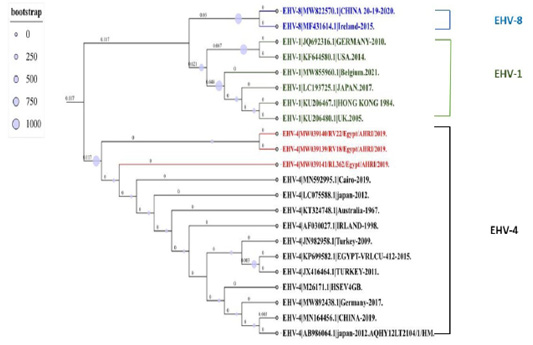
The maximum likelihood Phylogenetic tree is based on 409 pb gB gene fragment of EHV-4 isolated from Egypt using IQ-TREE with best Model Finders. The accession numbers with brief GenBank ID are located in each sequence from EHV-4, EH-8, AND EHV-1, The three Egyptian isolates are highlighted in red, and other clades are assigned different colors, and the numbers above the branch represent its length and the bootstrap values computed from 1000 bootstrap repeats. The tree is rooted in the middle.
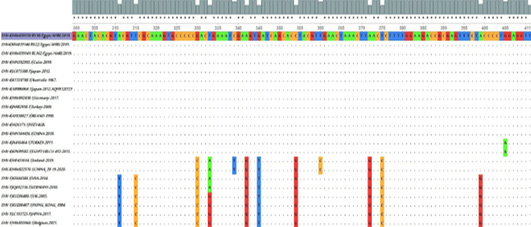
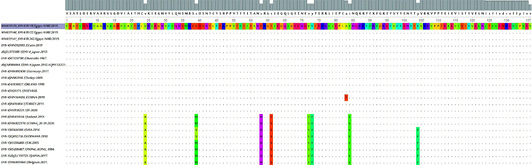
The nucleotide MSA for Partial gB gene from EHV-4 isolates (position 300-411) compared to other EHV4, EHV-8, and EHV1 retrieved from Gene Bank visualized in UGEN software. The dot (.) represents identity, while a single nucleotide highlights the differences.
The amino acids MSA for the partial gB gene sequence of the three identified EHV-4 isolates compared to other retrieved EHVs where a single alphabet highlights the differences among amino acids.