Efficient Decolorization of Water and Oil-Soluble Azo Dyes by Enterococcus avium Treated with HP-β-CD
Efficient Decolorization of Water and Oil-Soluble Azo Dyes by Enterococcus avium Treated with HP-β-CD
Peng Song1,2, Wei Feng2, Haiying Shi2,Jinsheng Zhao3, Renmin Liu3 and Wei Xu2,*
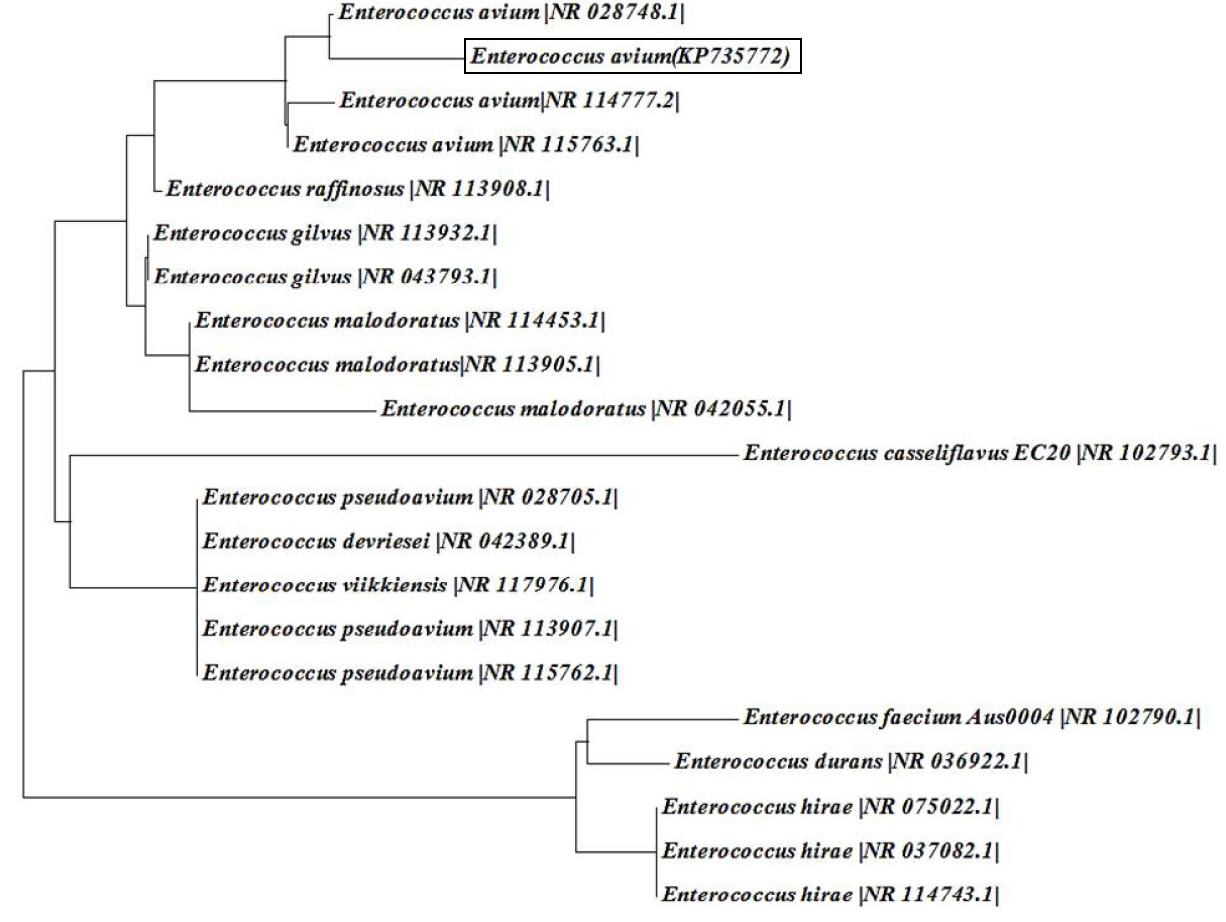
Neighbour-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the positions of strain ts1-17 (GenBank accession number KP735772) and related taxa. Bar=0.001 substitutions per nucleotide position.
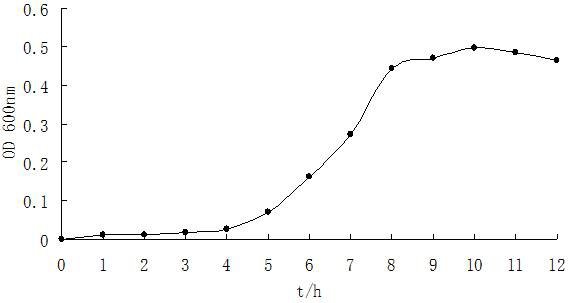
The cell growth curve of bacterium ts17 with 50mg/L Amaranth in 12 h.
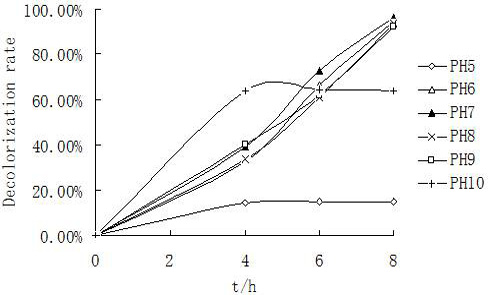
Effects of pH on decolorization rate of Amaranth by strain ts17 in 8 h.
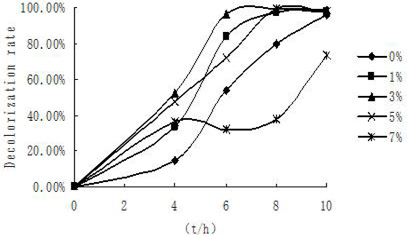
Effects of NaCl% on decolorization rate of Amaranth by strain ts17 in 10 h.
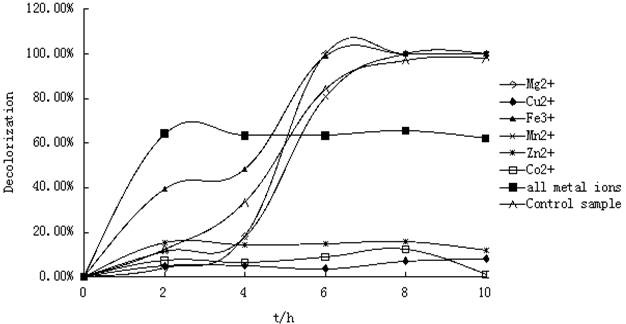
Effects of heavy metal ions on decolorization rate of Amaranth by strain ts17 in 10 h. Fig.5. Effects of heavy metal ions on decolorization rate of Amaranth by strain ts17 in 10 h.
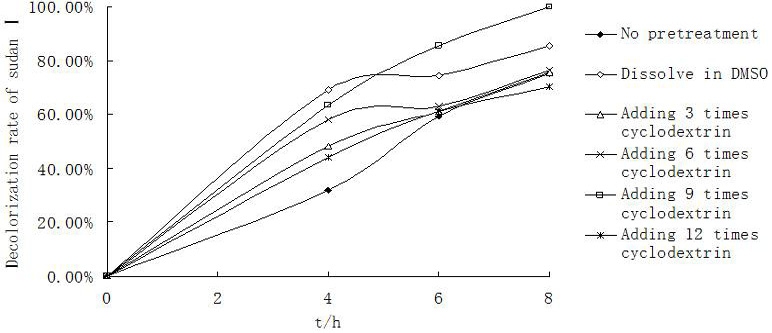
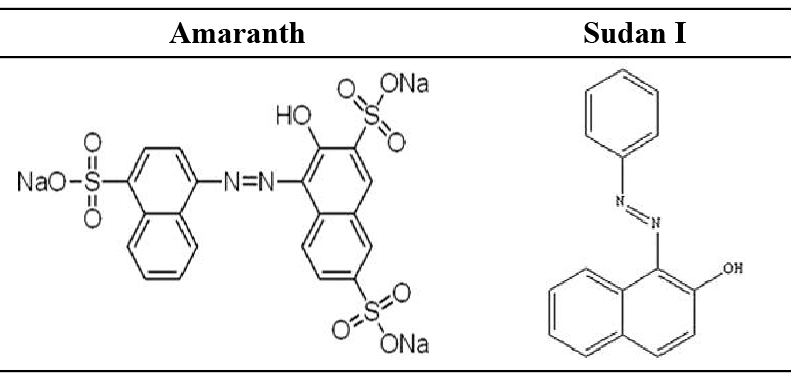
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis of Sudan I decolorization after different pretreatments by strain ts17 in 8 h.