Effects of Maternal Stress on the Behavioral and HPA Responses of Offspring Exposed to the Predator or Non-Predator Odor in Brandt’s Voles
Effects of Maternal Stress on the Behavioral and HPA Responses of Offspring Exposed to the Predator or Non-Predator Odor in Brandt’s Voles
Chen Gu1,2, Ze-Dong Xu1, Lin Chen1, Ming-Hui Gu1, Sheng-Mei Yang1, Ai-Qing Wang1, Bao-Fa Yin1* and Wan-Hong Wei1,2,3*
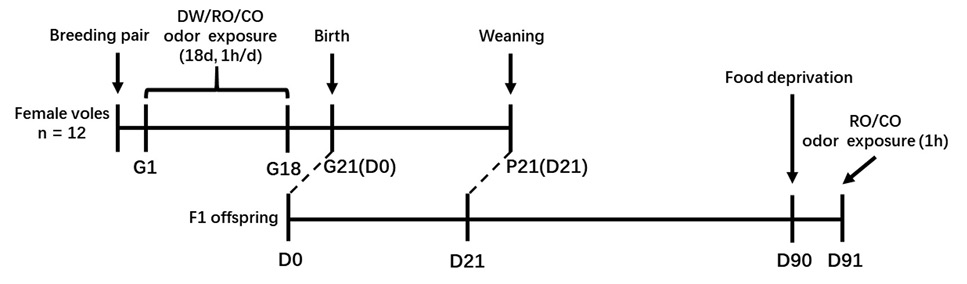
Schematic illustration of the experimental design used in this study. All assayed adult F1 offspring experienced maternal treatment via their dams (in utero) exposure and an offspring treatment directly in the test apparatus. The sample size in each offspring treatment (RO/CO) of each maternal treatment (DW/RO/CO) was 12 per group (6M + 6F). DW, Distilled water; RO, Rabbit odor; CO, Cat odor; M, male offspring; F, female offspring; G, Gestation day; P, Postpartum day; D, Postnatal day.
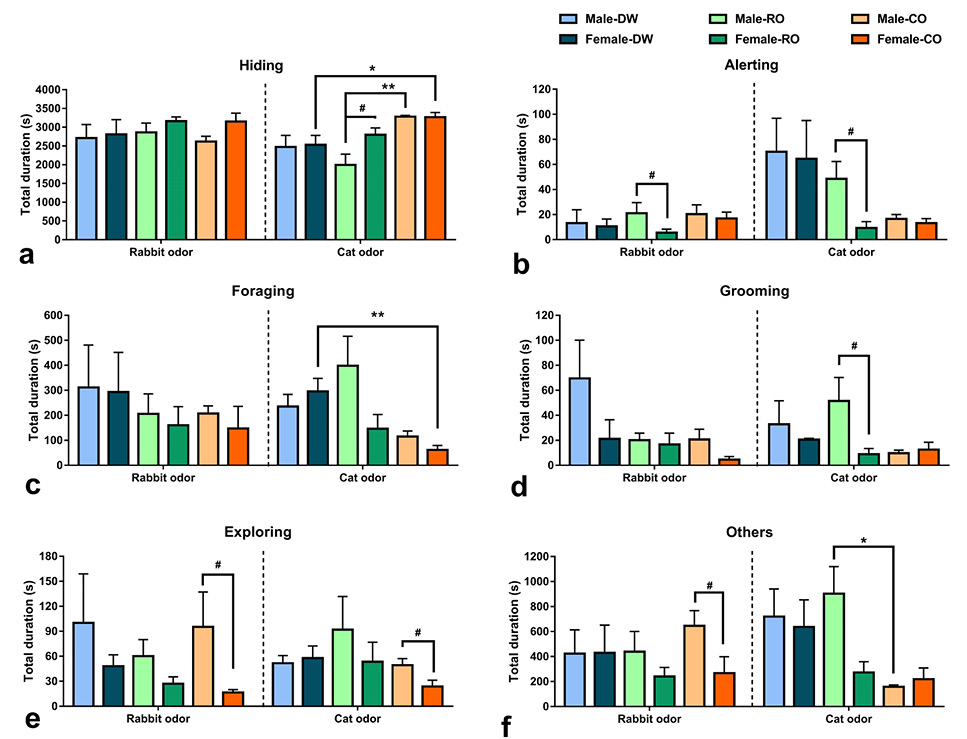
Behavioral responses to acute rabbit odor or cat odor of offspring from dams exposed to distilled water (DW), chronic rabbit urine odor (RO), and chronic cat urine odor (CO) while pregnant (a: hiding; b: alerting; c: foraging; d: grooming; e: exploring; f: others). Data are mean±SEM. Significant differences among vole offspring from different maternal treatments are indicated as follows: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Significant differences between male and female vole offspring are indicated as follows: #P < 0.05.
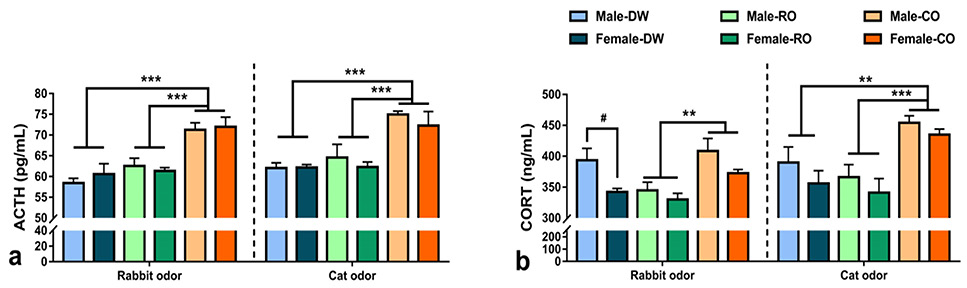
Hormonal responses to acute rabbit odor or cat odor of vole offspring from dams exposed to distilled water (DW), chronic rabbit urine odor (RO), and chronic cat urine odor (CO) while pregnant (a: ACTH; b: CORT). Data are mean±SEM. Significant differences among vole offspring from different maternal treatments are indicated as follows: **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Significant differences between male and female vole offspring are indicated as follows: #P < 0.05.
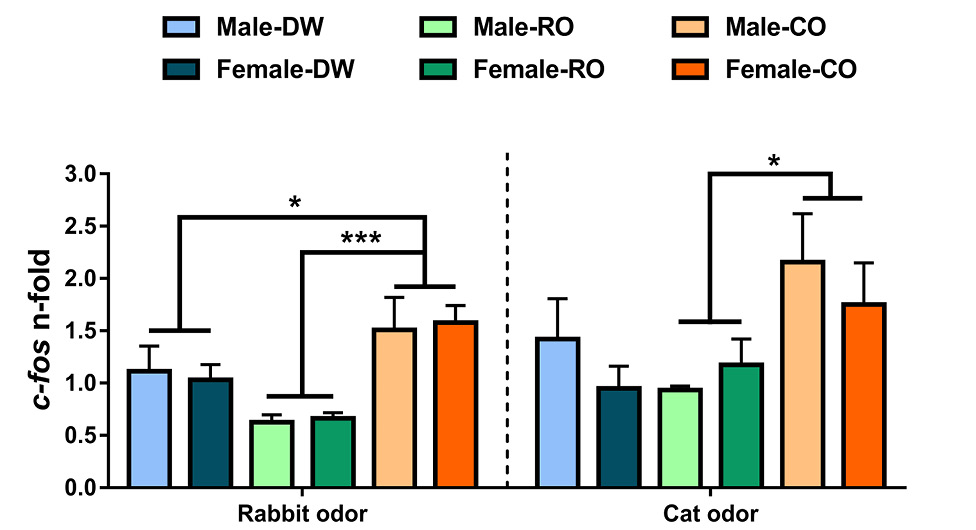
Expression of c-fos mRNA of vole offspring exposed to acute rabbit odor or cat odor from dams exposed to distilled water (DW), chronic rabbit urine odor (RO), and chronic cat urine odor (CO) while pregnant. Data are mean±SEM. Significant differences among vole offspring from different maternal treatments are indicated as follows: *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.