Earth Worms and Vermicomposting: A Review on the Story of Black Gold
Earth Worms and Vermicomposting: A Review on the Story of Black Gold
Ali Ahmad1*, Zubair Aslam1, Korkmaz Bellitürk2, Naeem Iqbal3, Muhammad Idrees3, Muhammad Nawaz4, Muhammad Yasir Nawaz5, Muhammad Kashif Munir6, Ahmad Kamal1, Ehsan Ullah1, Muhammad Ahsan Jamil1, Yousuf Akram1, Tanveer Abbas1 and Muhammad Mohsin Aziz1
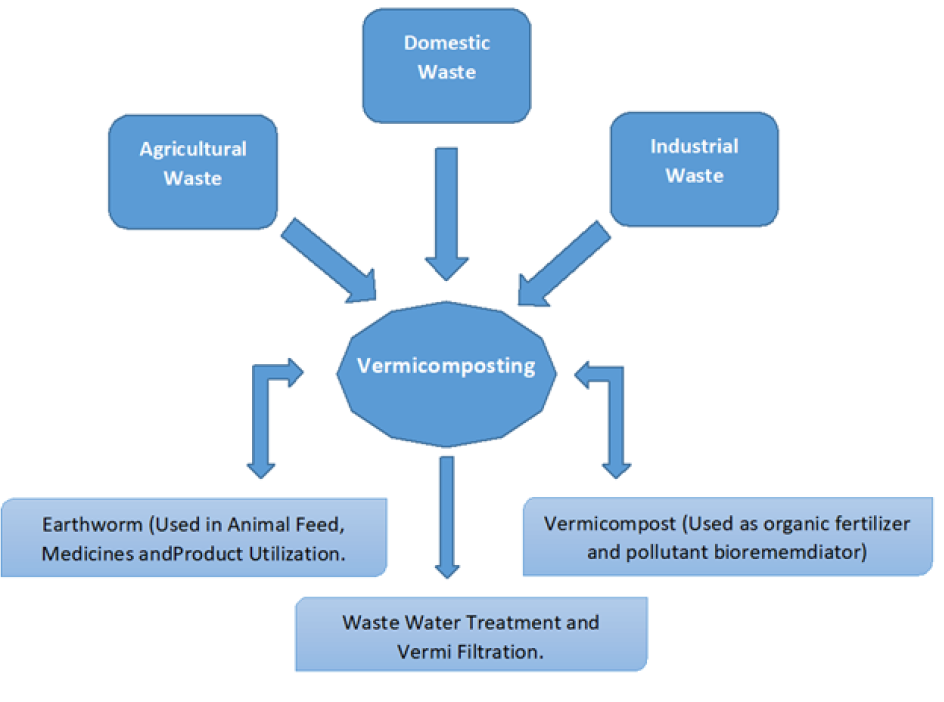
Vermi-technology.
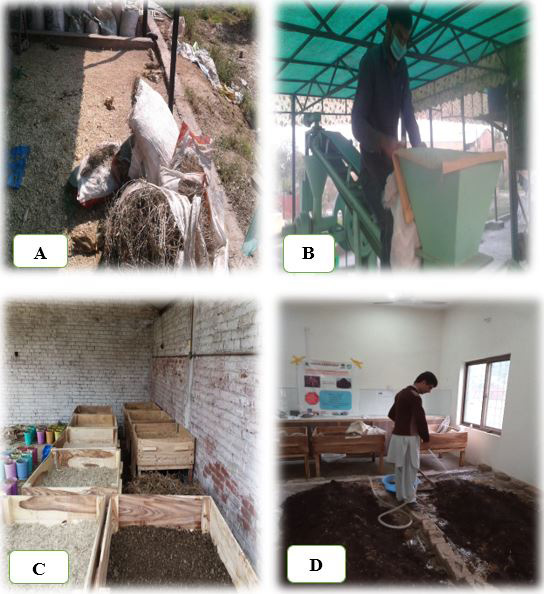
Vermicomposting procedures (A) Collection of Materials, (B) Crushing of materials, (C) Pre-composting, (D) Watering.
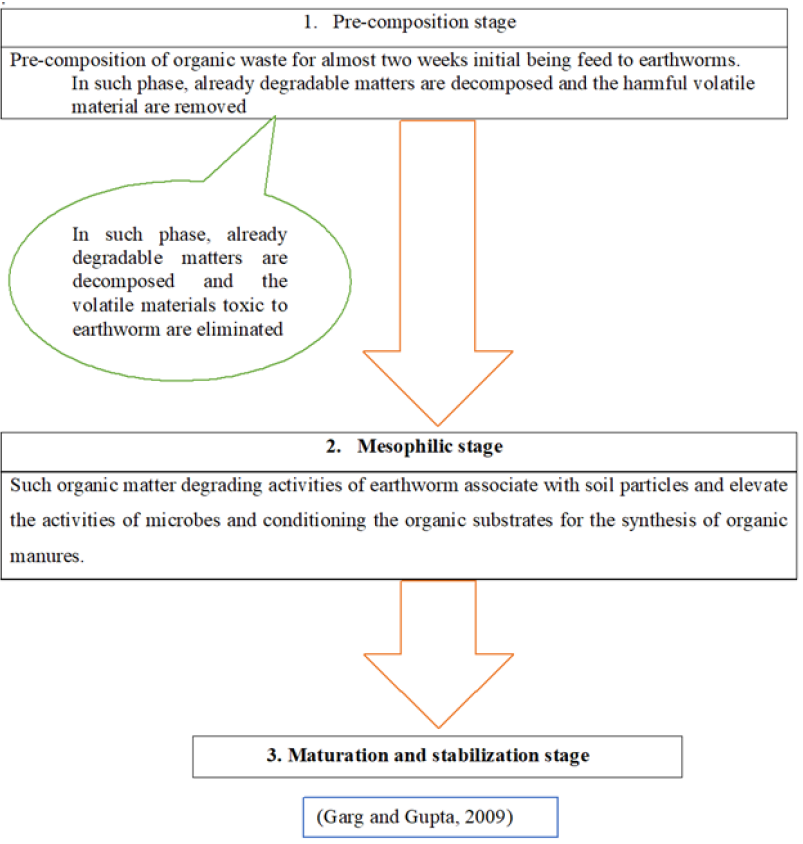
Illustrate the vermcomposting process.
Vermicompost Chemical analysis, (A) Streaking of bacteria’s, (B) Cellulose degrading bacerias collected from earth worm’s gut, (C) Inoculation of bacteria in vermicompost, (D) Dilution of vermicompost in water, (E) pH measurement, (F) Ec. Measurement.
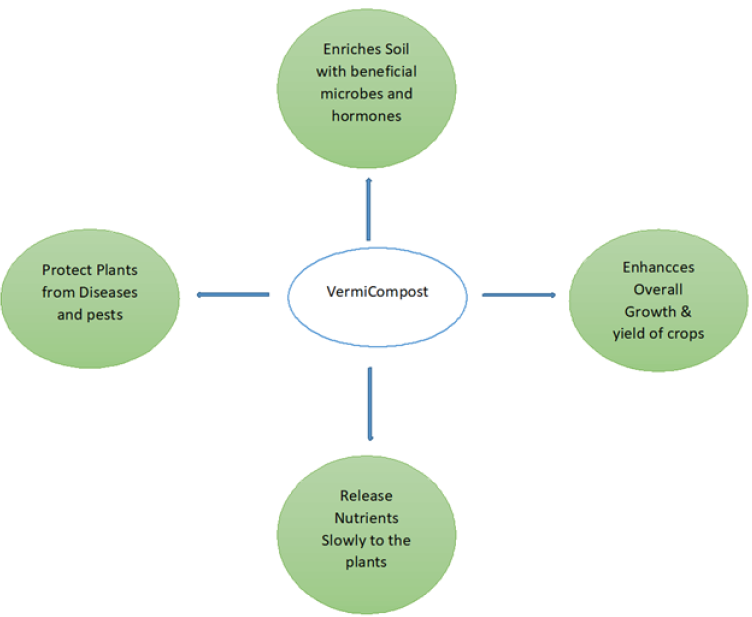
Vermicomposting benefits.
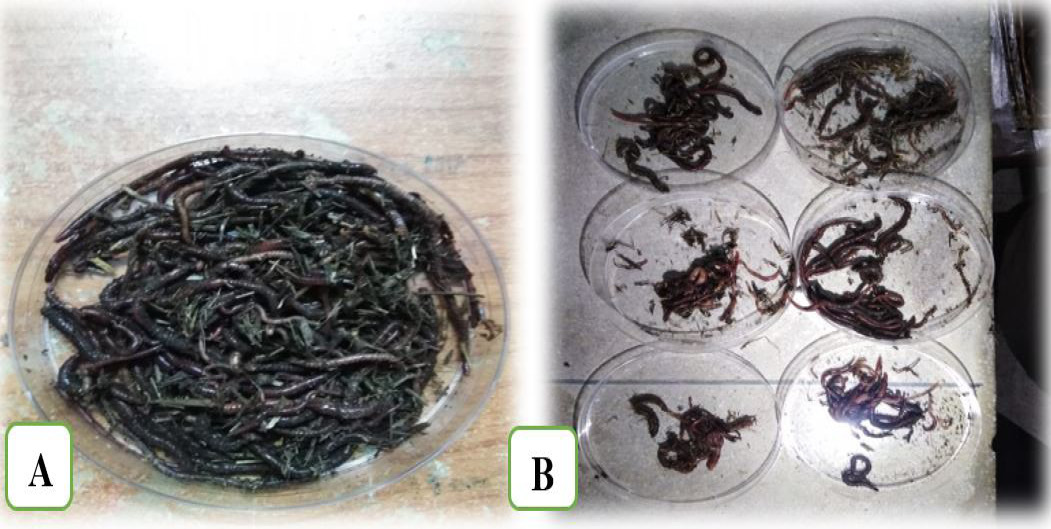
Eisenia Fetida in (A) Rice straw, (B) Wheat straw.