Diets High in Energy, Protein, Zinc, Iron and Vitamin A and Their Effects on Body Weight in Patients with Tuberculosis
Diets High in Energy, Protein, Zinc, Iron and Vitamin A and Their Effects on Body Weight in Patients with Tuberculosis
Muhammad Ashfaq ur Rahman1*, Saleem Khan1, Aurang Zeb1, Zia ud Din1 and Zafar Iqbal3
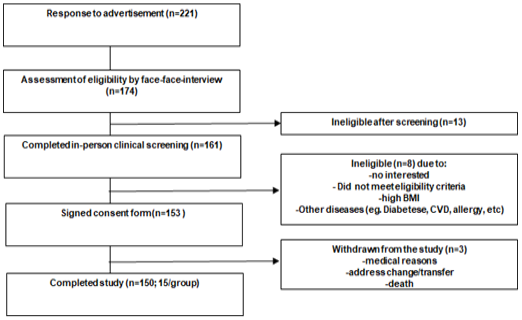
Patients who participated in the trial, provided informed consent, and underwent screening are shown in the CONSORT diagram. ITT (Intent-to-treat, from the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials, or CONSORT).
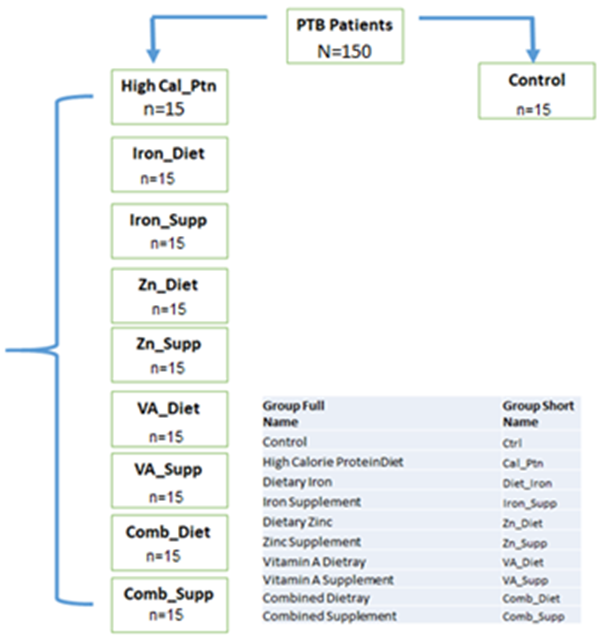
Schematic representation of patient classification.
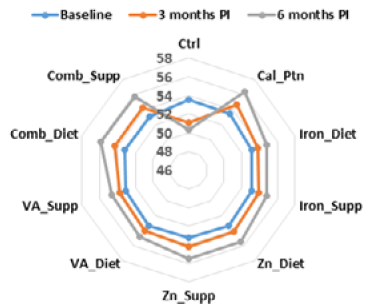
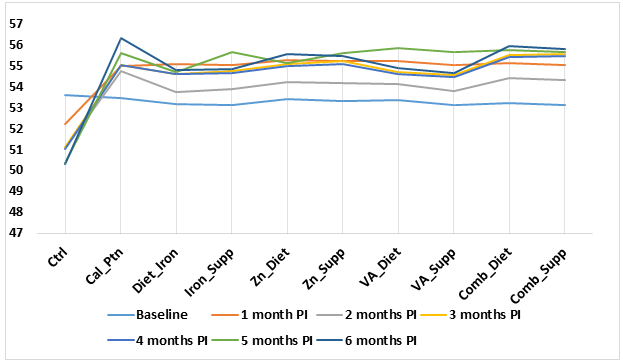
Average patient weight among the 9 nutrition intervention groups and the control group.
Progress images showing weight changes at 3, 6, and 12 months PI.
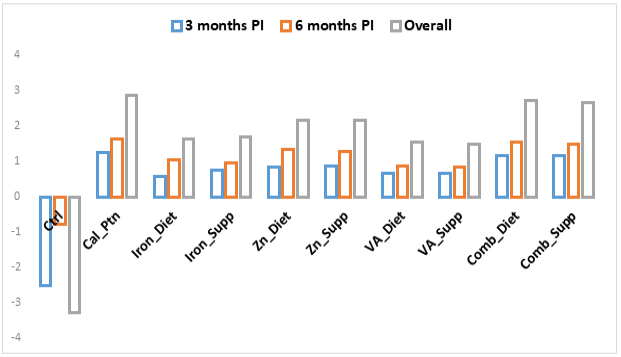
Monthly PTB patients’ weight gain or loss.