Chia Seeds Oil Inhibits Hepatic Resistance to Doxorubicin Via Suppressing Cyp3-A4 and Mrp-1 in Male Albino Rats
Chia Seeds Oil Inhibits Hepatic Resistance to Doxorubicin Via Suppressing Cyp3-A4 and Mrp-1 in Male Albino Rats
Shaimaa A.Tawfik2,3, EL S.T. Awad1*, Hoda O.Abu Bakr1, Amira M.Gamal-Eldeen4, Esmat Ashour2, Ismail M.Ahmed1
Effect of CSO on liver GSH (a) CAT (b) and MDA (c) concentration in different rat groups. Activity of ALT (d) and Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (e) enzymes in serum of different rat groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. Treated Groups showed a significance as compared to a control and b compared to DOX (*P<0.05)
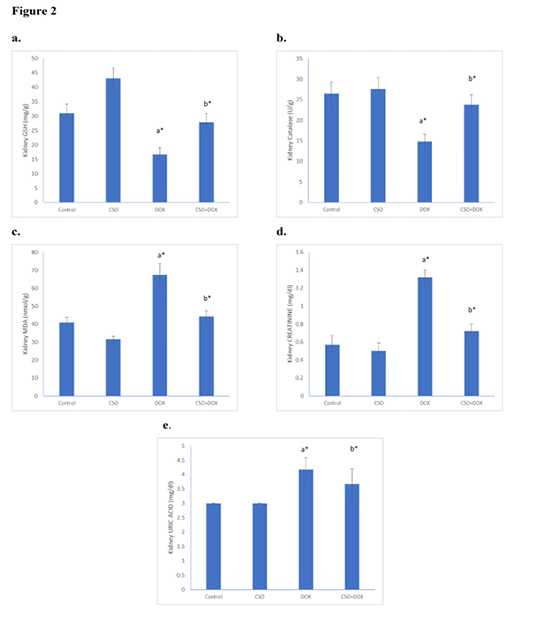
Effect of CSO on kidney GSH (a) CAT (b) and MDA (c) in different rat groups, concentration of creatinine enzyme (d) and uric acid (e) in serum of different rat groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. Treated Groups showed a significance as compared to a control and b compared to DOX (*P<0.05).
Effect of CSO on heart GSH (a), CAT (b) and MDA in different rat groups, Activity of LDH (d) and AST (e) enzymes in serum of different rat groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. Treated Groups showed a significance as compared to a control and b compared to DOX (*P<0.05).
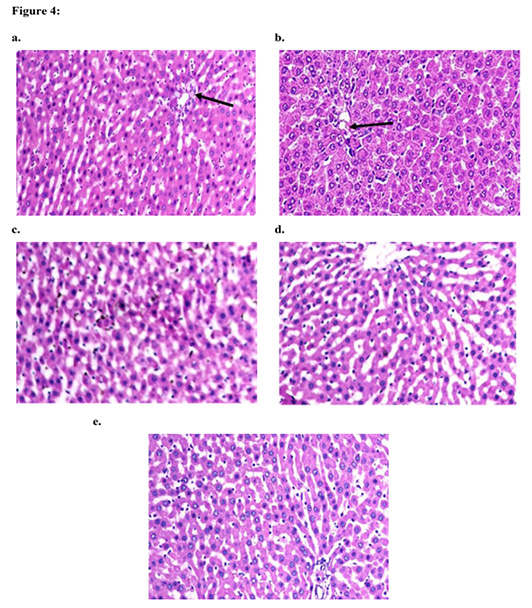
Histopathological examination of rat liver tissues by hematoxylin and eosin: a. control rats and b.CSO-administrated rat are showing normal histological structure in portal area (arrow) and hepatic cells. c. DOX-treated rat showing marked thickening of the hepatic (Glisson’s) capsule with edema and few inflammatory cells infiltration, necrosis and degeneration of the subcapsular hepatocytes.d.CSO/DOX-treated rat showing few inflammatory cells infiltrating the portal areas and mild degeneration of the hepatic cells. e. CSO/DOX-treated rat showing good restoration of the hepatic cells with only mild degeneration of the hepatic cells, (X200).
Histopathological examination of rat kidney tissues by hematoxylin and eosin: a. control rats and b. CSO-administrated rat administrated rats are showing normal histological structure of renal glomeruli (RG) and real tubules (RT). c. DOX-treated rats showed mild focal interstitial inflammatory cells infiltration , diffuse moderate tubular epithelial linings degeneration, necrosis d. DOX-treated rat showing degeneration (arrow), necrosis, few apoptosis (dashed arrow) and desquamation (short arrow) of the renal tubular linings with cast formation (thin arrow)in the tubular lumens. e. CSO/DOX-treated rat mild to moderate degree of necrobiotic changes of the renal tubular epithelium with cast formation in lumen of scattered tubules (arrow) (H&E, X100)
Histopathological examination of rat heart tissues by hematoxylin and eosin: a. control rats and b. CSO-administrated rat showed normal histological and orientation of the cardiac muscle fibers (MFs) with their centrally located nuclei (arrow). c. DOX-treated rats showed showing diffuse vacuolar degeneration of the cardiac muscle fibers, most of which showing signet ring appearance (arrow) and necrosis (dashed arrow), d. Dox-treated rats showing intermuscular edema (Ed), mild inflammatory cells infiltration (dashed arrow) e. CSO/DOX-treated rat showing good restoration of the cardiac muscle fibers with only mild vacuolar degeneration (arrow) and very few necrotic fibers
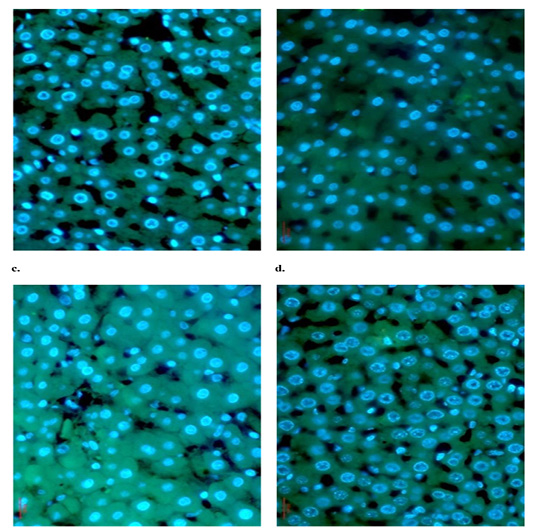
The immunohistochemical staining of CYP-3A4 in rat liver sections was implemented by FITC-conjugated IgG and CYP-3A4 antibody (green) and the nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Control group (a) and CSO-treated group (b) showed low concentration of CYP-3A4. Group treated with liposomal-doxorubicin (c) showed highly induced CYP-3A4 concentration. CSO/liposomal-doxorubicin group (d) showed highly suppressed CYP-3A4 compared to DOX-treated group. The sections were analyzed under fluorescence microscope (Magnification x400).
The immunohistochemical staining of MRP1 in rat liver sections was implemented by FITC-conjugated IgG and MRP1 antibody (green) and the nuclei were counterstaining with DAPI (blue). Control group (a) and CSO-treated group (b) showed low MRP1 concentration. The group that was treated with liposomal-doxorubicin (c) demonstrated highly induced MRP1 concentration compared to control group. CSO/liposomal-doxorubicin group (d) showed a highly decreased MRP1, compared to DOX-treated group. The sections were analyzed under fluorescence microscope (Magnification x200).
The immunohistochemical staining of c-MYC was implemented by FITC-conjugated IgG and c-MYC antibody (green). Control group (a) and CSO-treated group (b) showed high c-MYC concentration. Liposomal-doxorubicin-treated group (c) indicated low c-MYC concentration compared to control. The analysis of CSO/liposomal-doxorubicin group (d) showed increased c-MYC content than DOX-treated group. The sections were analyzed under fluorescence microscope (Magnification x100).
qRT-PCR analysis of the relative expression of miR-122 (a) and let-7a (b). in liver tissues of different groups. Data are expressed as mean ± SE. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p< 0.001, and **** p< 0.0001, a compared to the corresponding control, b compared to DOX-treated group