Toxicity Assessment Due to Chronic Exposure to Manganese in Male Wistar Rat
Toxicity Assessment Due to Chronic Exposure to Manganese in Male Wistar Rat
Hala Harifi*, Mouloud Lamtai*, Siham Ait Salhi, Fatima-Zahra Azzaoui, Omar Akhouayri, Abdelhalem Mesfioui, Leila Bikjdaouene
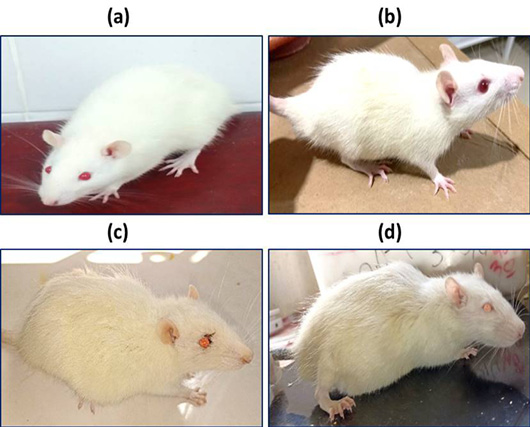
Hunched back with flattened limbs in control group (a), rat treated with 6 mg/kg (b), rat treated with 25 mg/kg (c), rat treated with 30 mg/kg (d).
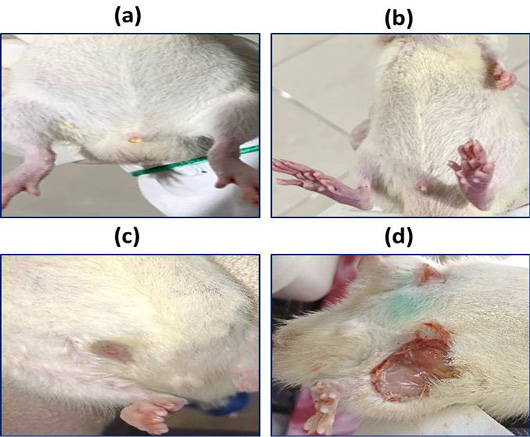
Abdominal lesions in control group (a), rat treated with 6 mg/kg (b), rat treated with 25 mg/kg (c), rat treated with 30 mg/kg (d).
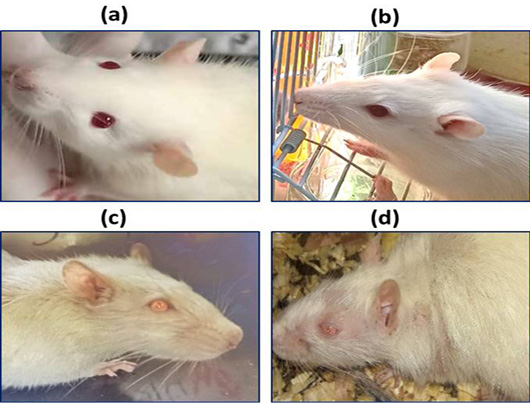
Hair color, piloerection, hair loss, and eyes color and paleness of the mucous membranes of the eyes in control group (a), rat treated with 6 mg/kg (b), rat treated with 25 mg/kg (c), and rat treated with 30 mg/kg (d).
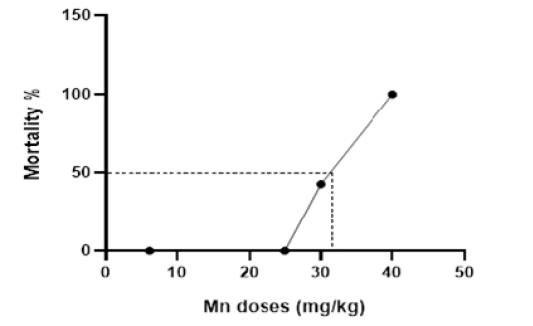
Dose-lethality curve after intraperitoneal injection of Mn at different doses.
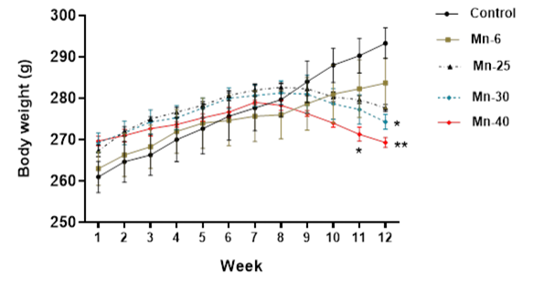
Mean body weight (Mean ± S.E.M) of male rats treated with Mn repeated intraperitoneal doses (6, 25, 30, and 40 mg/kg) for 12 weeks. Significantly different from vehicle control: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, respectively.
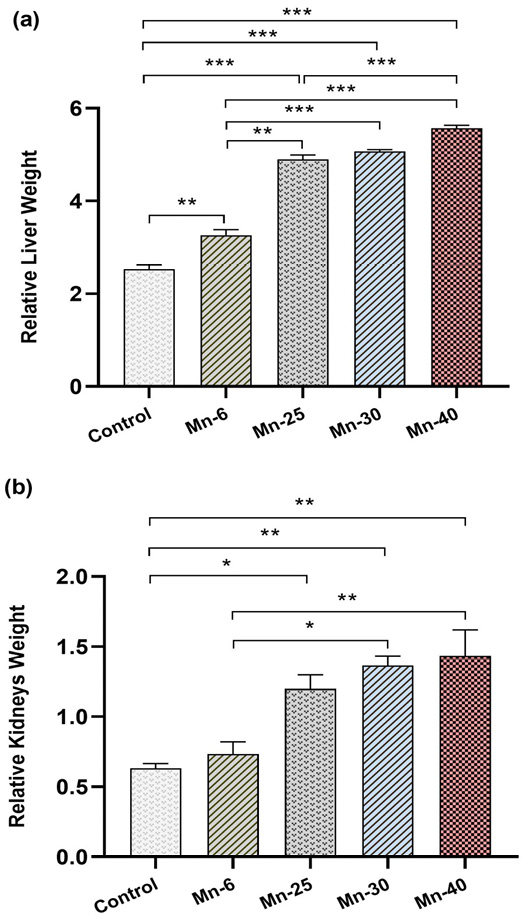
Relative weights of liver and kidneys (Mean ± SEM) of male rats treated with Mn repeated intraperitoneal doses (6, 25, 30, and 40 mg/kg) for 12 weeks. Significantly different from vehicle control: *p < 0.05.