The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of a Rare Cavefish (Sinocyclocheilus cyphotergous) and Comparative Genomic Analyses in Sinocyclocheilus
The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of a Rare Cavefish (Sinocyclocheilus cyphotergous) and Comparative Genomic Analyses in Sinocyclocheilus
Xiaoping Gao1, Yanping Li2*, Renyi Zhang3, Yunyun Lv2, Yongming Wang2, Jinrong Shi2, Jiang Xie2, Chiping Kong1 and Lekang Li1
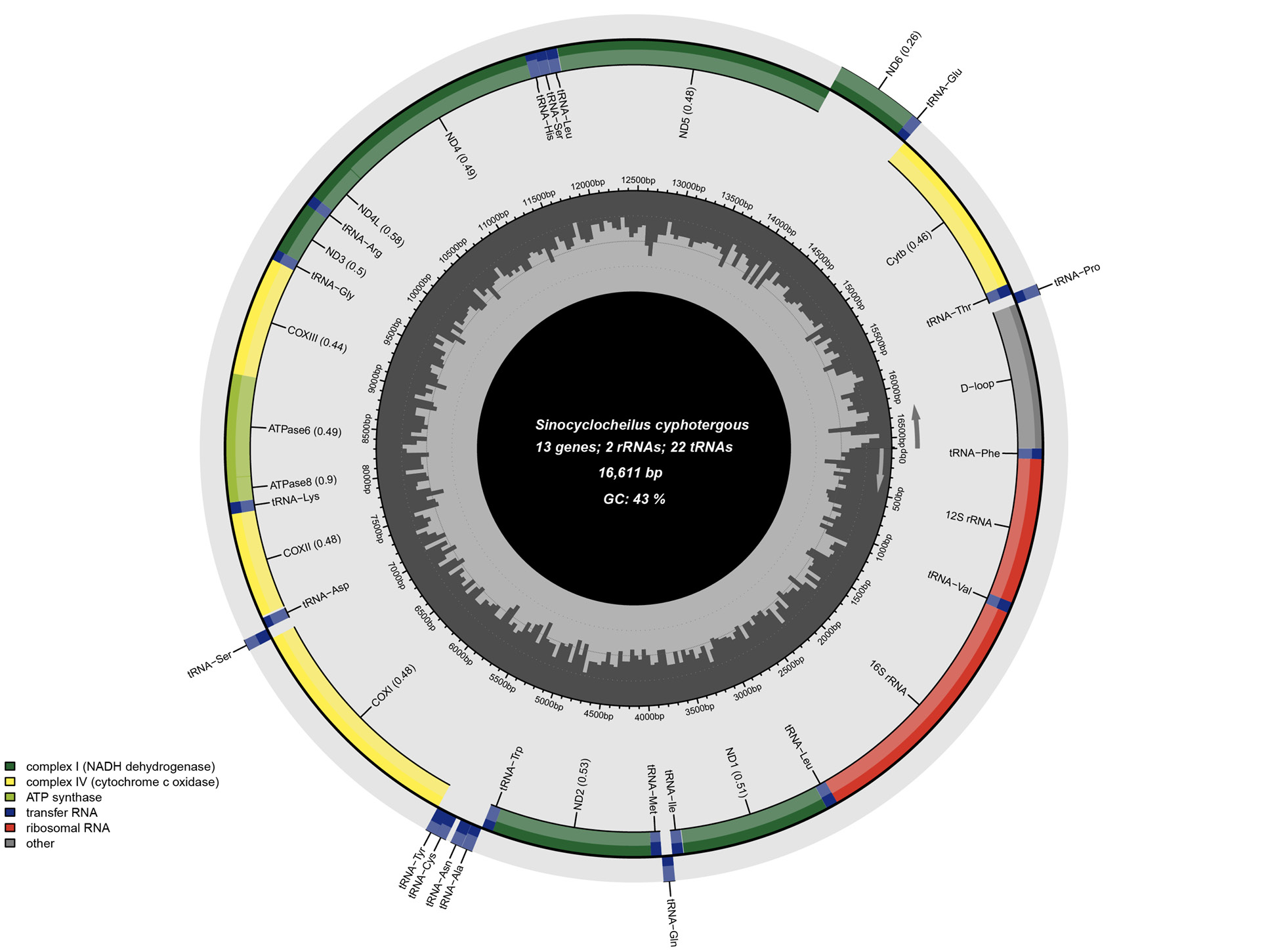
Circular map of the complete mitochondrial genome of S. cyphotergous. Genes encoded on the H-strand and L-strand are shown inside and outside the circular map of the mitogenome. Protein-coding genes of NADH dehydrogenase were colored in green, cytochrome c oxidases were colored in yellow, and ATP synthases were colored in light green. Blue and red colour represented transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA, respectively. Control region of D-loop was colored in gray.
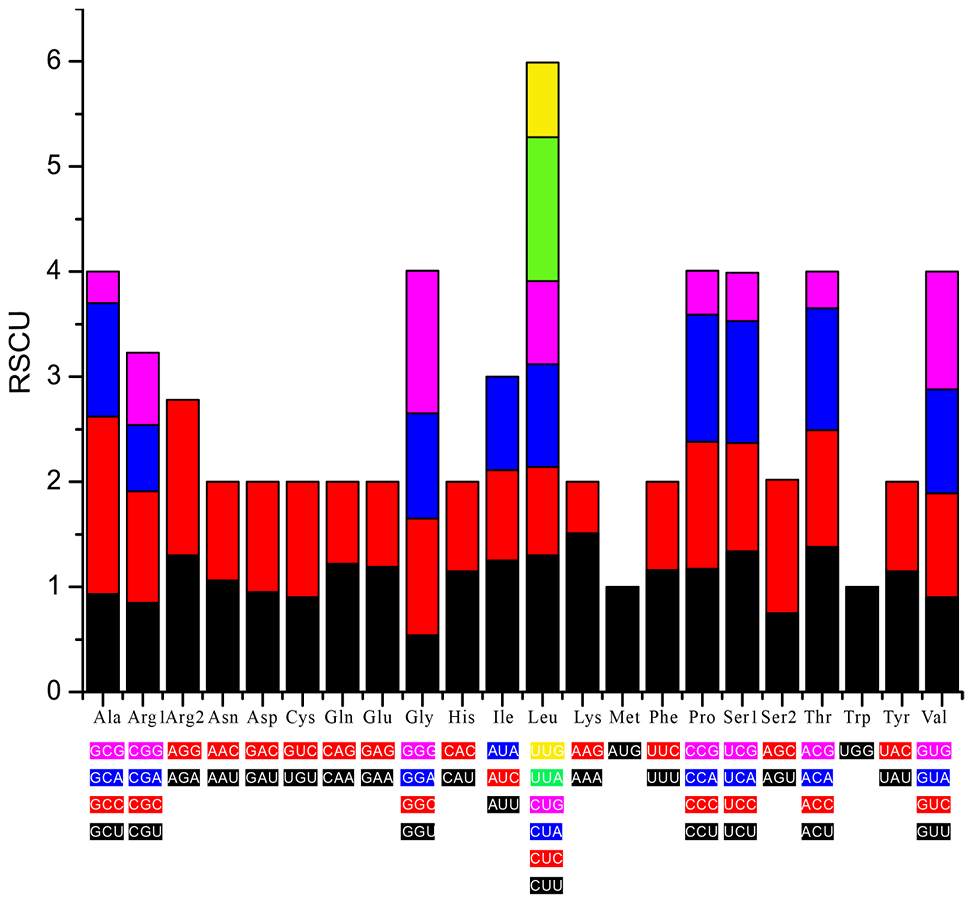
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) in the S. cyphotergous mitogenome. X axis shows the Condon family, and Y axis shows the RSCU values.
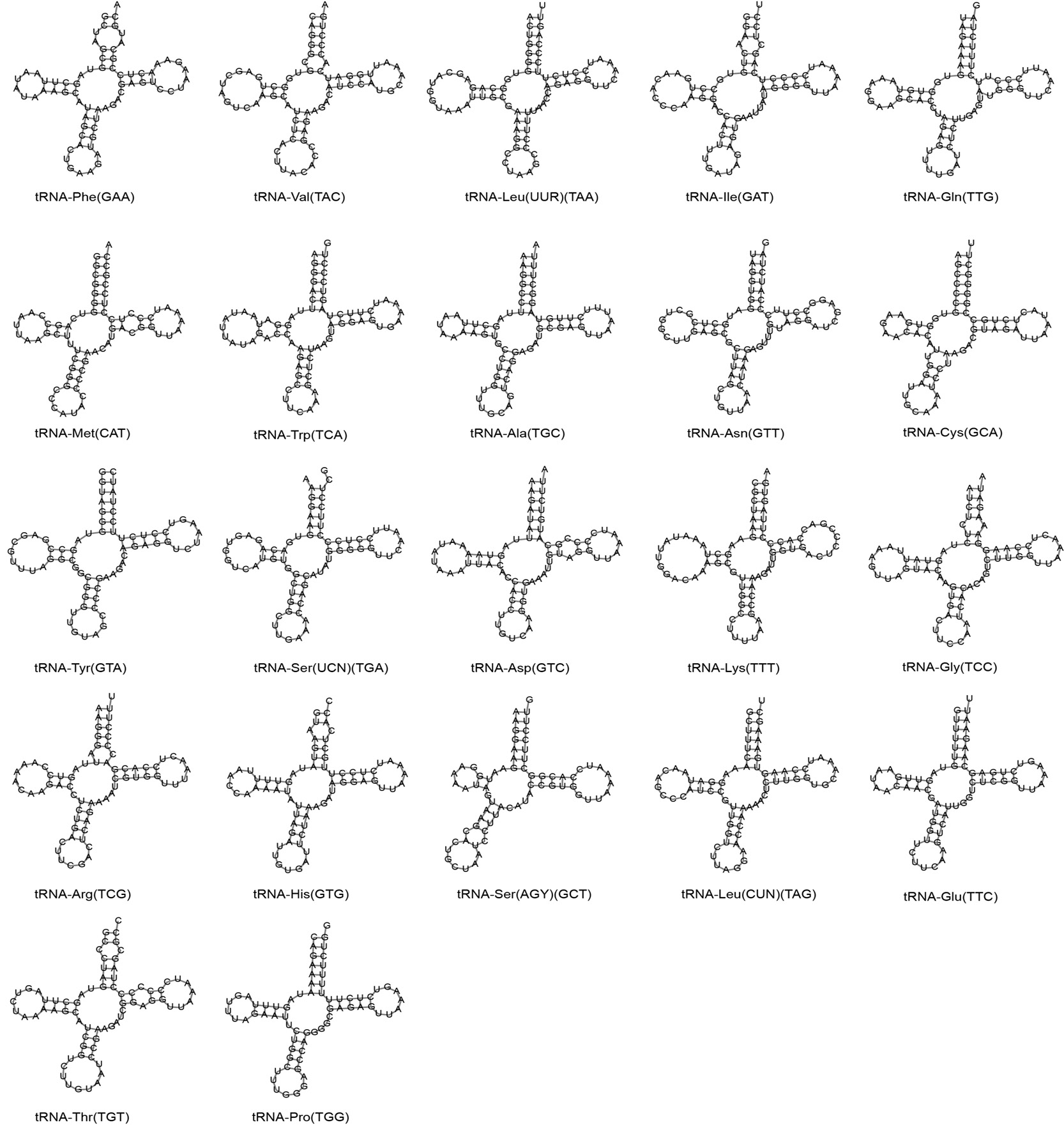
Putative secondary structures of the 22 tRNA genes identified in the mitochondrial genome of S. cyphotergous. The tRNAs are labelled with abbreviations of their corresponding amino acid. The orders based on clockwise from top are amino acid acceptor arm, the TΨC arm, the anticodon arm, and the dihydrouridine arm.
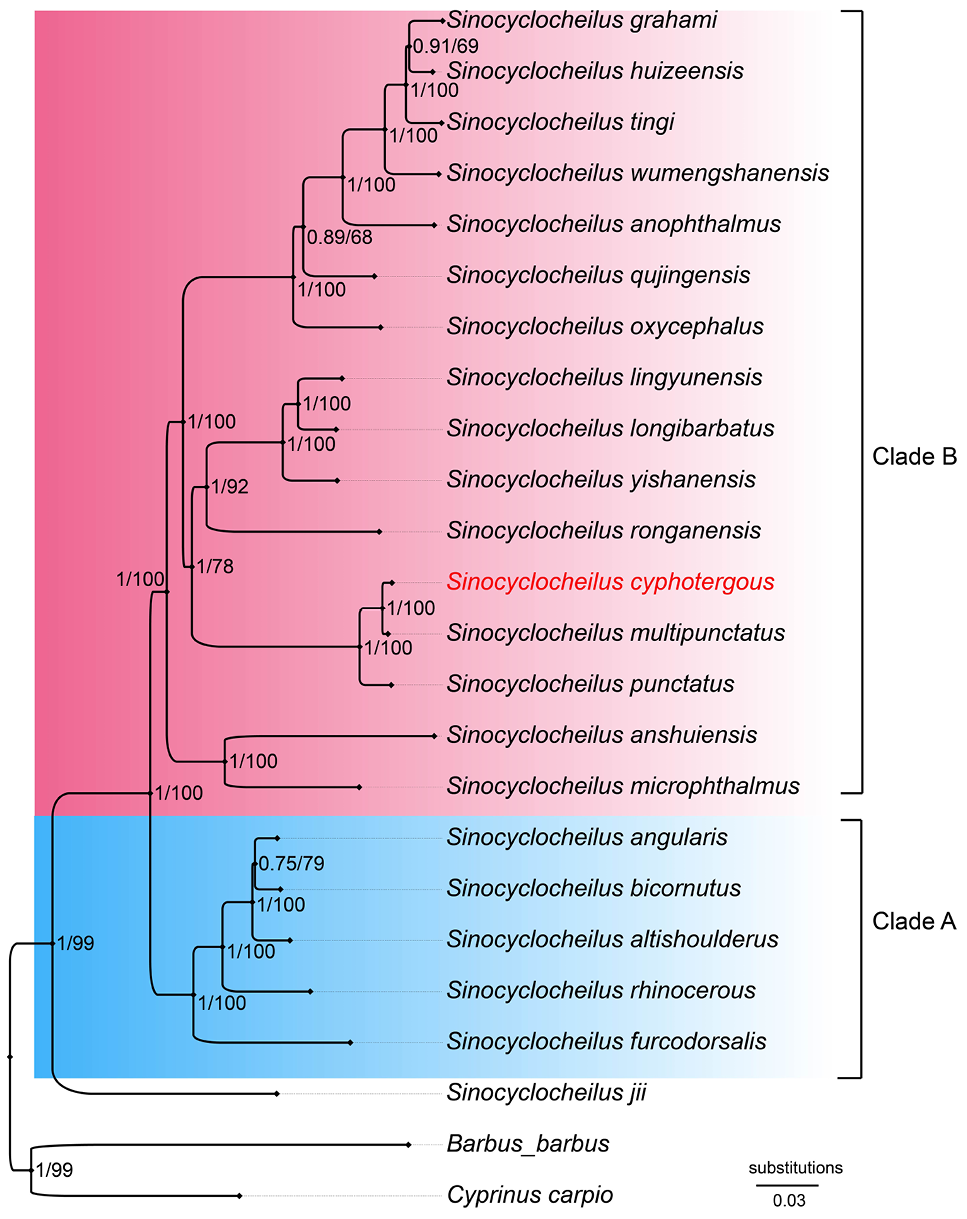
Phylogenetic relationships of species in genus Sinocyclocheilus inferred by Bayesian Inference and Maximum Likelihood analyses, based on the mitochondrial genome. Numbers on the branches from left to right are Bayesian posterior probabilities obtained by BI and ML bootstrap values, respectively.
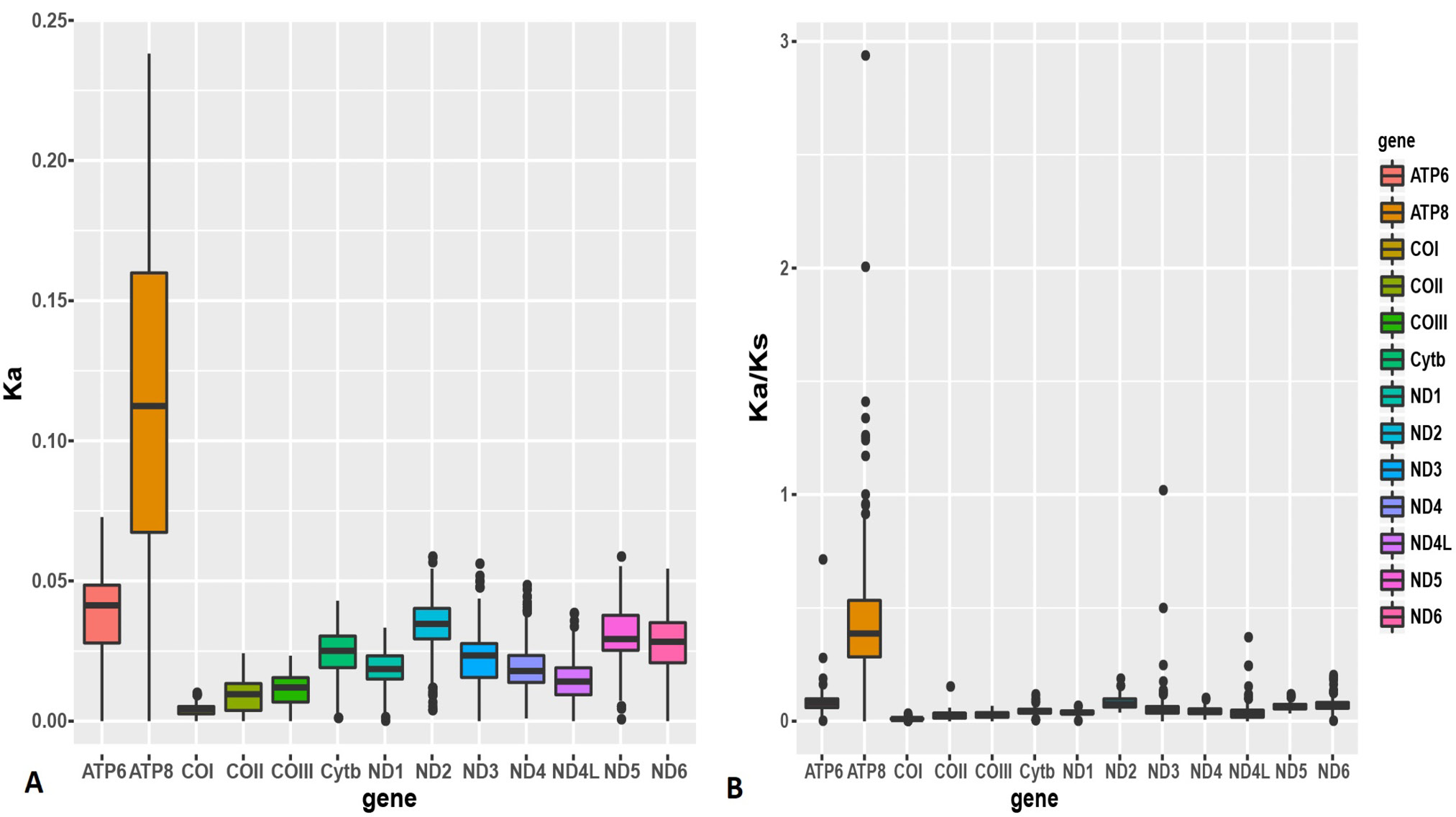
Boxplots of (a) Ka and (b) Ka/Ks for the 13 mitochondrial protein-coding genes of the 21 Sinocyclocheilus mitogenomes examined. The average Ka and Ka/Ks were greatest in ATP8.