Phylogenetic Relationship of Locally Isolated Paramecium Species Inferred from Histone H4 Genes
Phylogenetic Relationship of Locally Isolated Paramecium Species Inferred from Histone H4 Genes
Fareeda Tasneem1, Farah Rauf Shakoori1 and Abdul Rauf Shakoori2,*
Multiple alignment of sequences of the studied histone H4 gene in 10 strains along with 24 species from the GenBank Data. Differences in nucleotides of sequences are highlighted in pink.
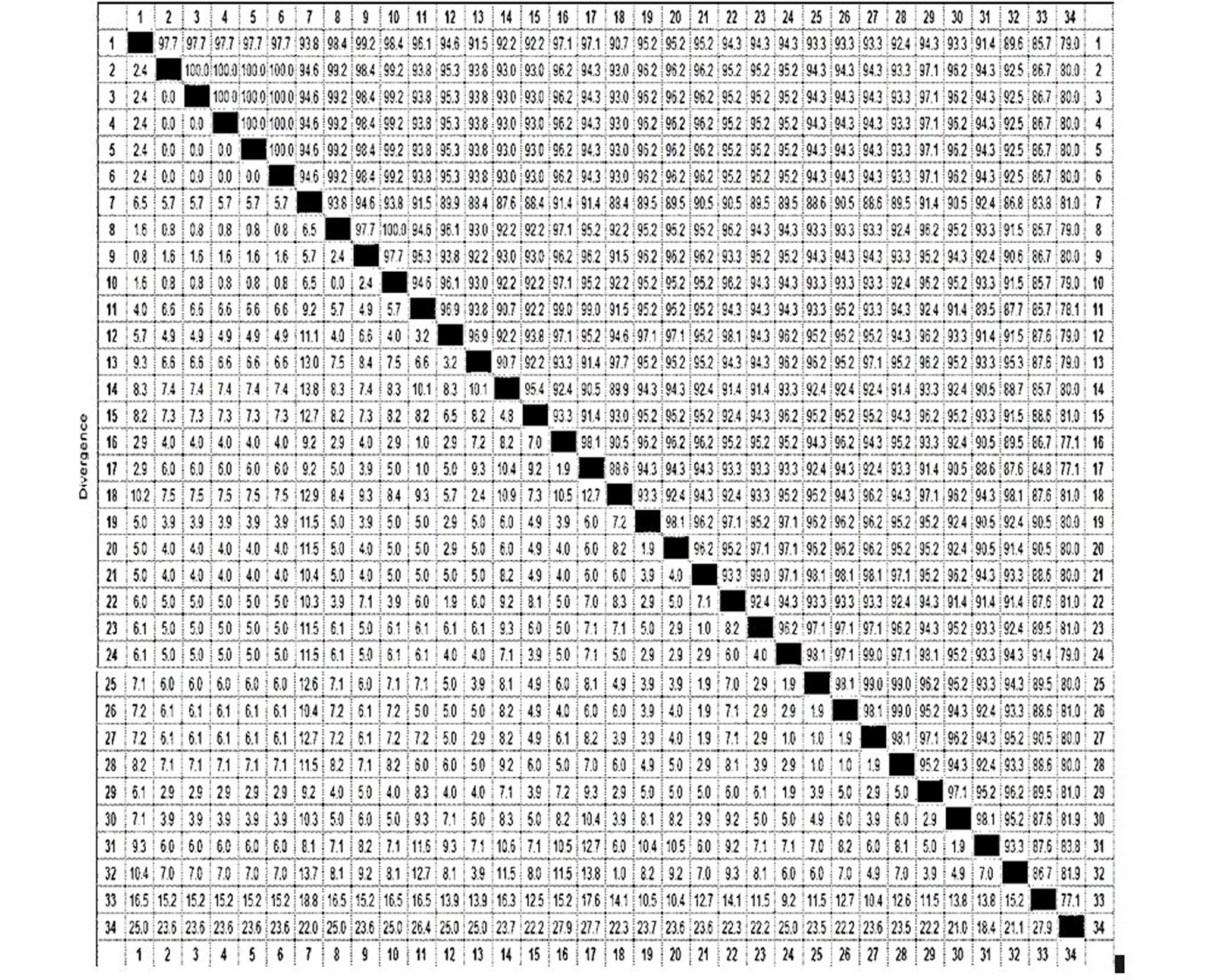
Percentage identity and divergance matrix of 10 strains of locally isolated Paramecium species from 1 to 10 (FT2.1-FT11.1 respectively) and 24 sequences from GenBank data based on the histone H4 gene fragment. From 11-15 are P. tetraurelia species (XM001425872, XM001455606, XM001452606, XM001452073, XM001459068 respectively). 16 is P. decaurelia (DQ067622), 17 and 18 again representing P.tetraurelia (AJ004699, XM001442554), 19 P.tredecaurelia (DQ067629), 20 P. pentaurelia (DQ067623), 21 is P. primaurelia (DQ067620), 22 P. quadecuarelia (DQ0676630), 23 P. decaurelia (DQ067626). 24 to 29 are P. jenningsi (DQ001056, DQ001064, DQ001062, DQ001059, DQ001061, DQ001057 respectively). 30 P. undecaurelia (DQ067627), 31 P. septaurelia (DQ067624), 32 P. tertraurelia (AJ004700), 33 P. caudatum (AB670962) and 34 P. bursaria (AJ004702).
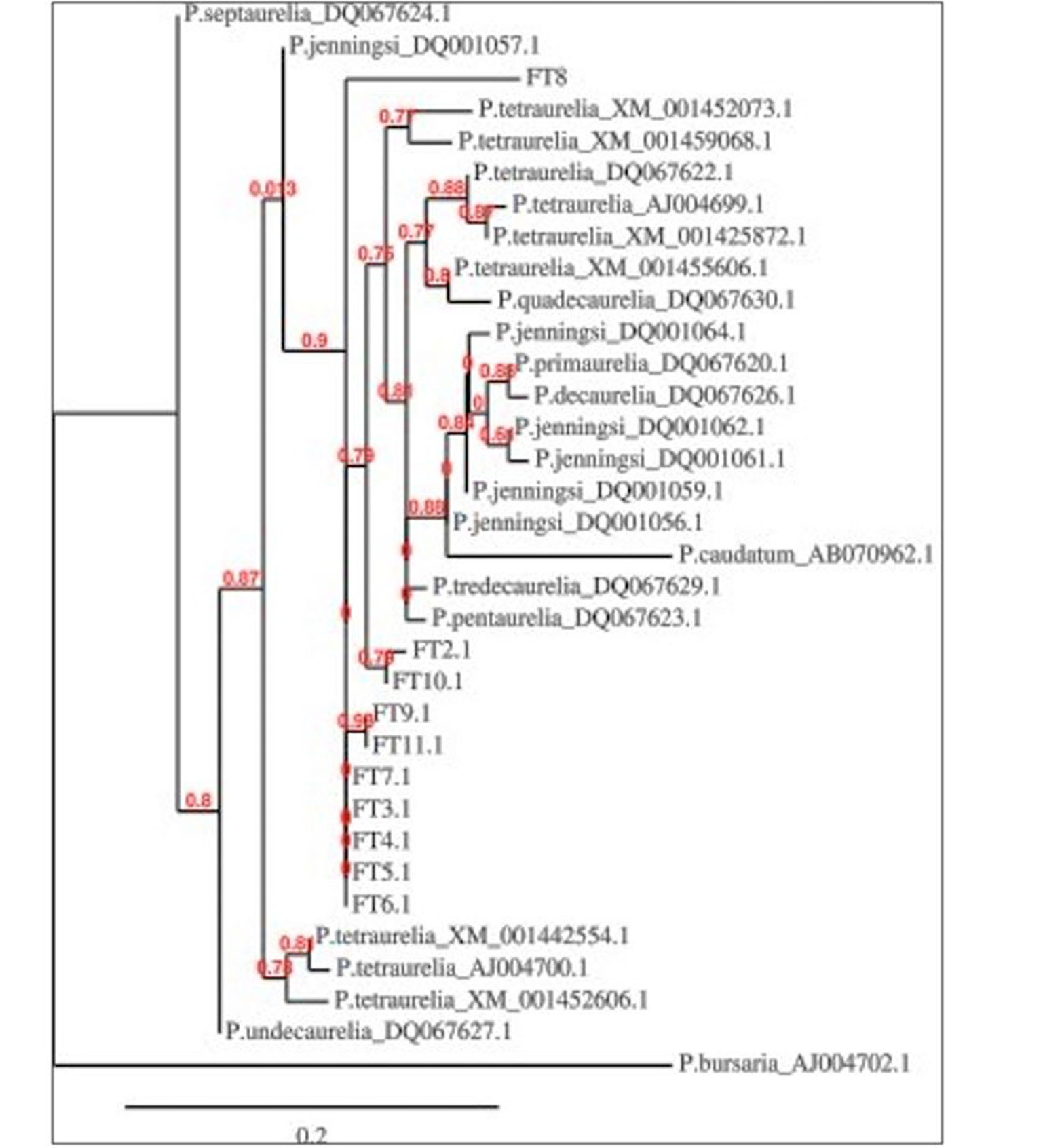
Phylogenetic tree of 10 strains of locally isolated Paramecium species (FT2.1-FT11.1) based on comparison of sequences of the histone H4 gene fragment with the application of maximum likelihood correction method. Bootstrap values are presented as percentages from 1000 comparisons. Sequence of Paramecium bursaria is representing as an out group.