Pelagic Larval Dispersal Habits Shape the Weak Population Structure of Thais clavigera in the Coastal Areas of China Sea
Pelagic Larval Dispersal Habits Shape the Weak Population Structure of Thais clavigera in the Coastal Areas of China Sea
Chengrui Yan1, Jing Miao1, Jiantong Feng1, Liping Xia1, Yingying Ye1,2*, Jiji Li1 and Baoying Guo1,2
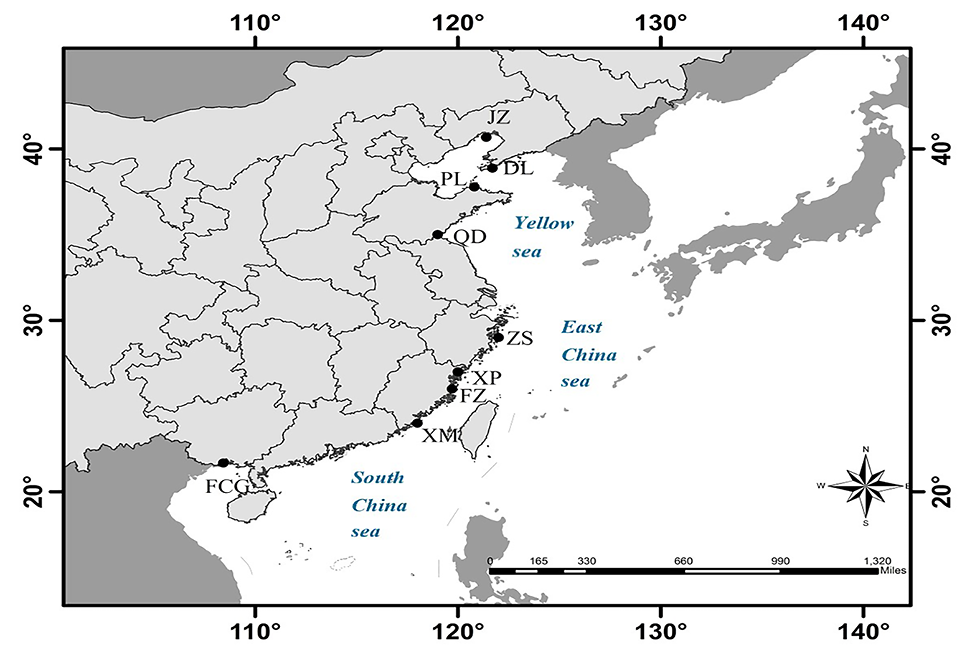
Map showing the sampling locations along the coast of China.
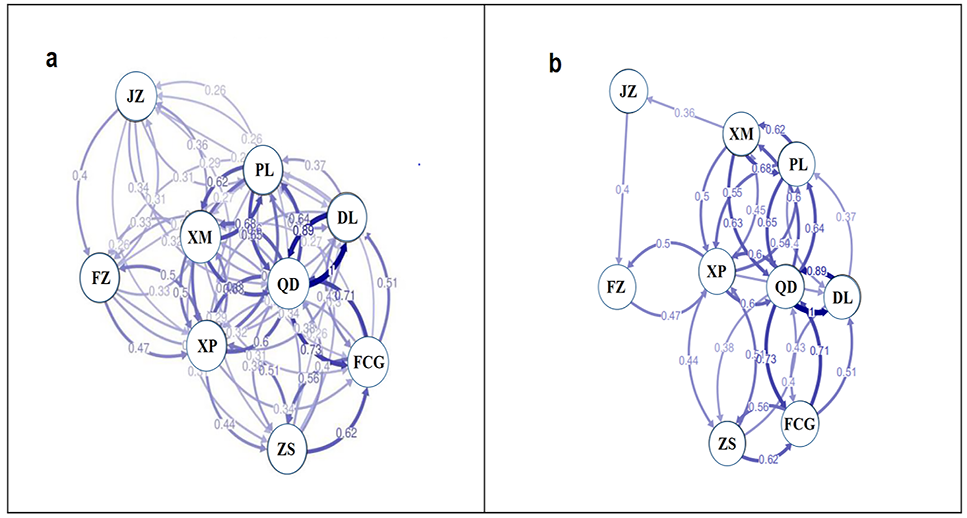
Directional relative migration networks of T. clavigera populations constructed with divMigrate using FST Values above 0.25 (a) and 0.35 (b) are shown.
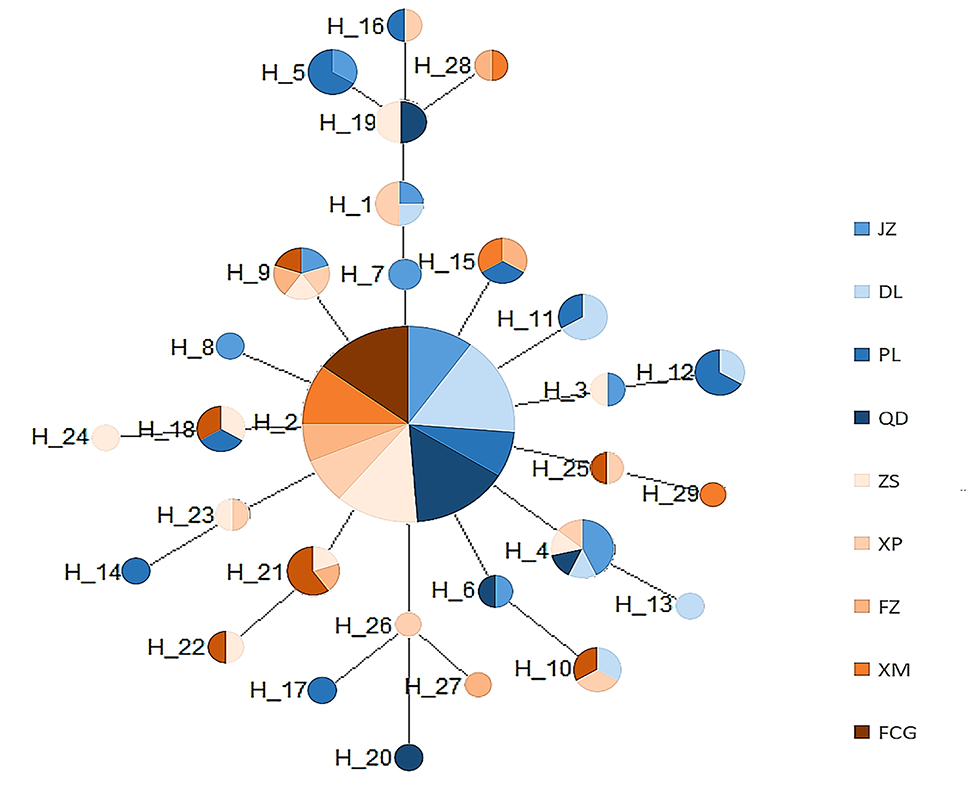
Networks of T. clavigera developed using COI data. Color representation is showing the population frequency. Numbers are representing the haplotype numbers.
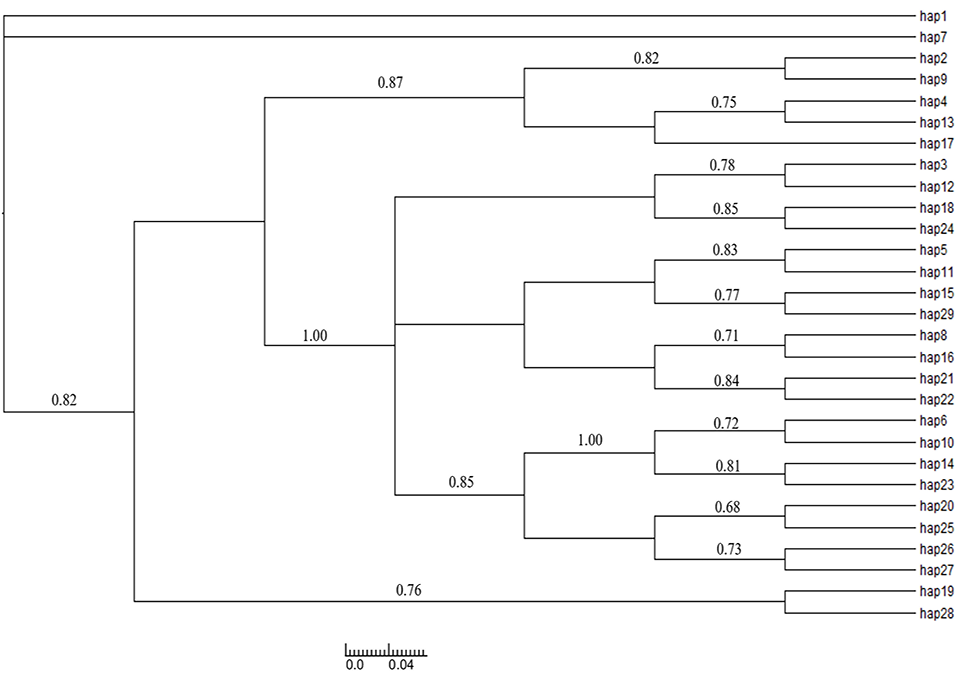
Bayes haplotype evolutionary tree based on COI gene.
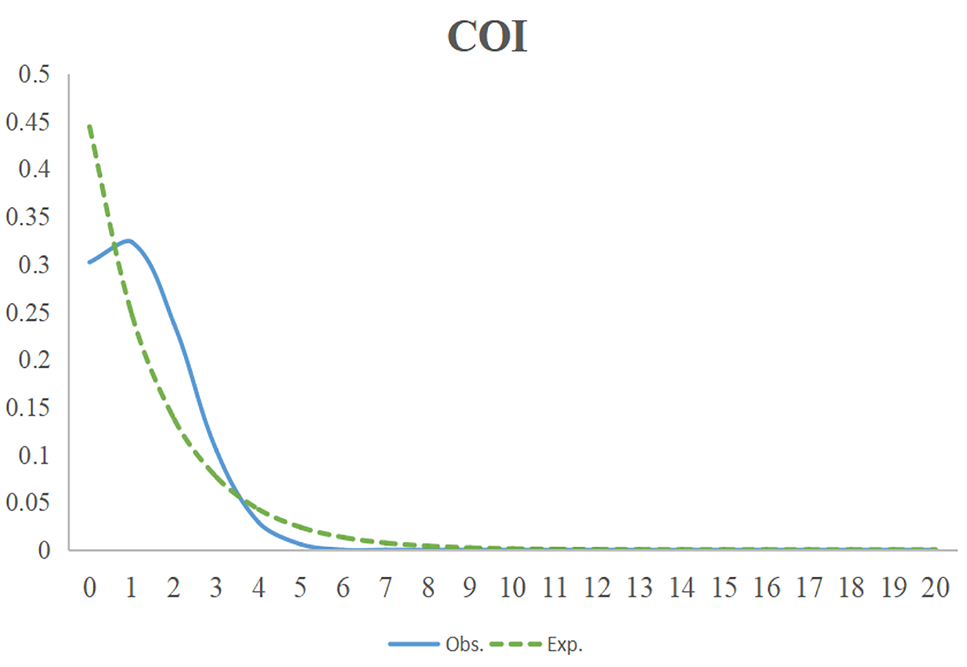
Mismatch histogram-line composite graph based on COI gene.
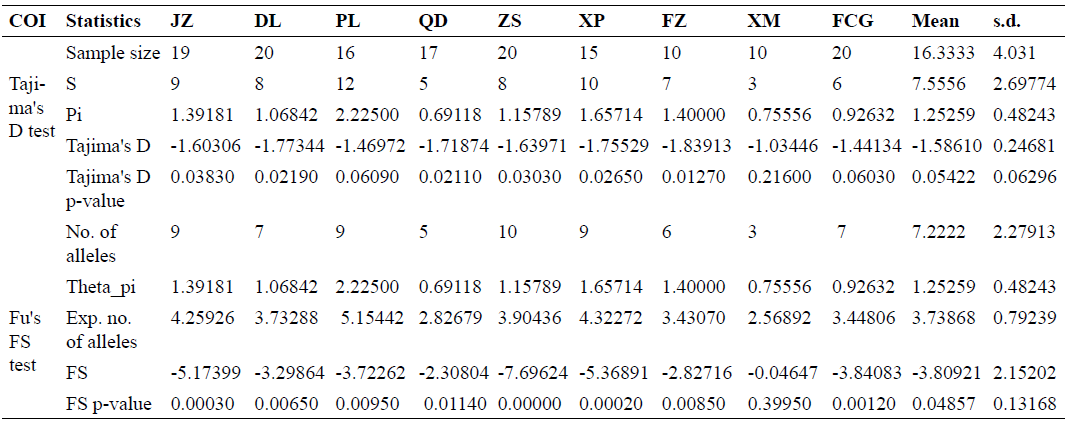
Based on the sequences of COI, the neutral test was conducted for the 9 populations of T. clavigera.