Pathological Studies on Contagious Ecthyma in Naturally Infected Small Ruminants
Pathological Studies on Contagious Ecthyma in Naturally Infected Small Ruminants
Muhammad Usman Ghani1*, Muti Ur Rehaman Khan1, Asim Aslam1, Zubair Shabbir2, Li Bo3 and Naveed Anwar4
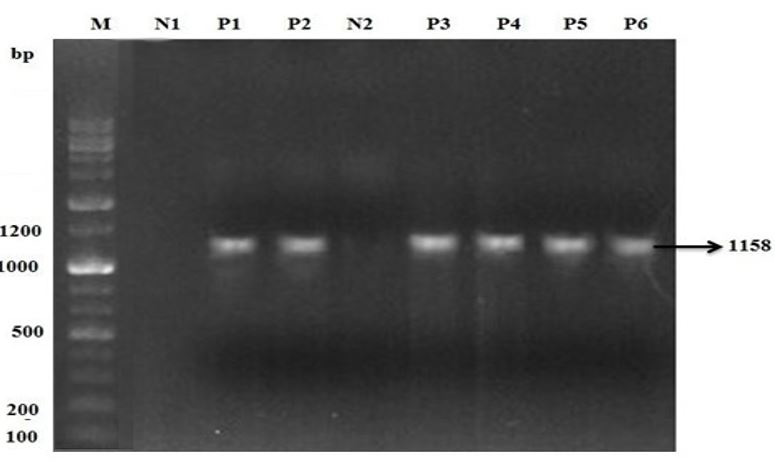
Agrose gell electrophoresis of PCR product of Orf. M is 2 kb (+) DNA ladder marker. N1 is negative control. P1 and P2 are positive sample of sheep. N2 is negative control used for goat samples. P3, P4, P5 and P6 are positive sample of goats for Orf infection.
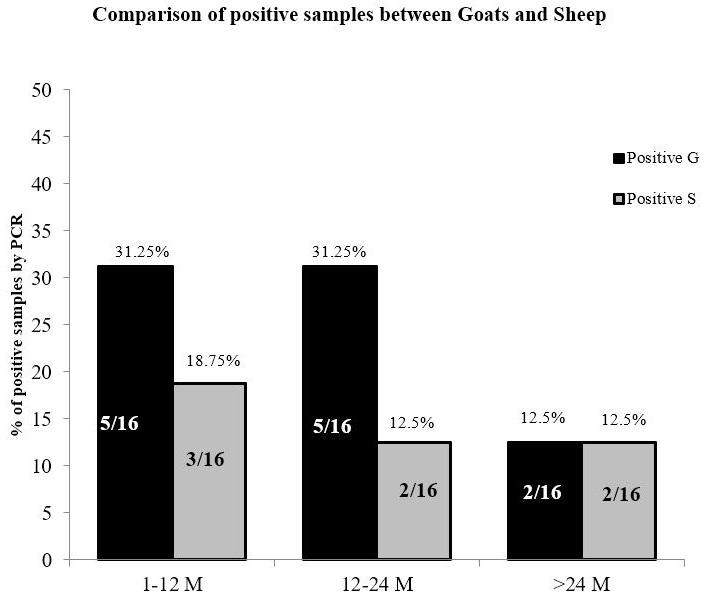
Comparison of PCR positive sheep and goats with Bar chart.
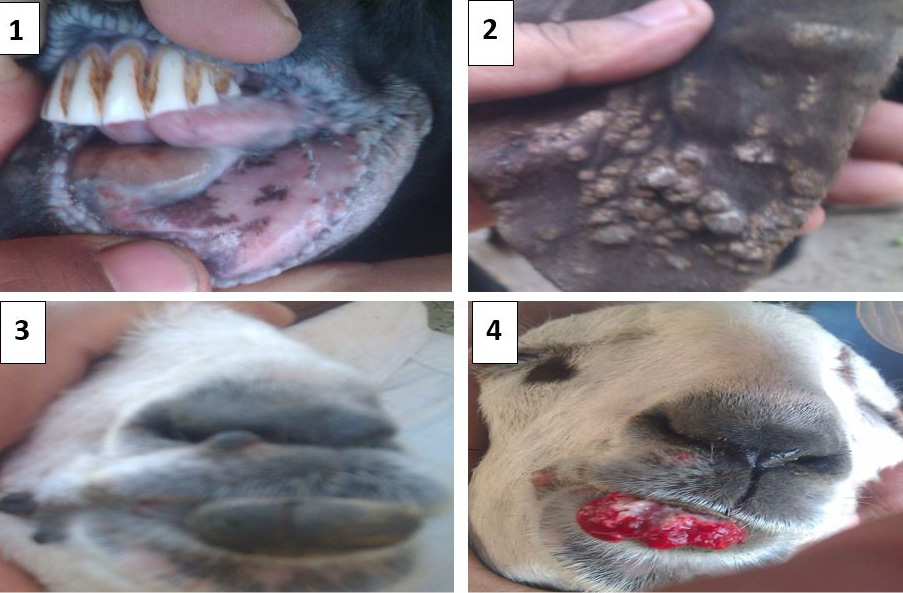
Gross pathological lesions in sheep and goats. (1) Ulceration and hemorrhages on soft tissues of oral cavity. (2) Nodules formation on ear pinnae of external ear of sheep. (3) Warts on lower lip and commissure of goat. (4) Oozing of blood and ulceration upon removal of warts.
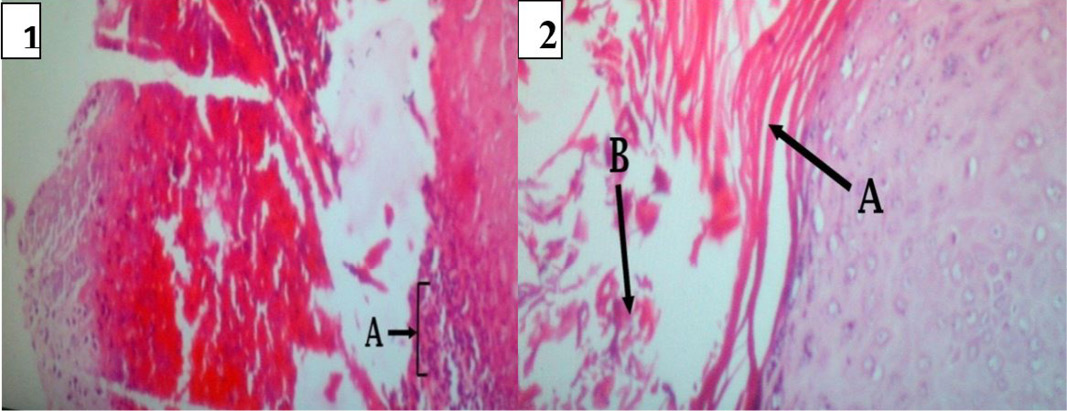
Lesion development in soft tissue of oral cavity. In (1): Necrotic dermatitis with zone of dead and dying neutrophils in soft tissue of oral cavity (A) Abscess formation; (2): (A) Acanthosis of stratum spinosum. (B) Hyperkeratosis of epidermis.