Molecular Characterization of Recent Field Isolate of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus Compared to the Vaccinal Strains
Molecular Characterization of Recent Field Isolate of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus Compared to the Vaccinal Strains
Akram A. Salama1, Moustafa A. Zaghloul2*, Ahmed A. Zaghawa1, Mohamed A. Nayel1, Ahmed M. Elsafey1, Mohamed F. Azooz2, Hanem S. Harb1 and Walid S. Mousa1
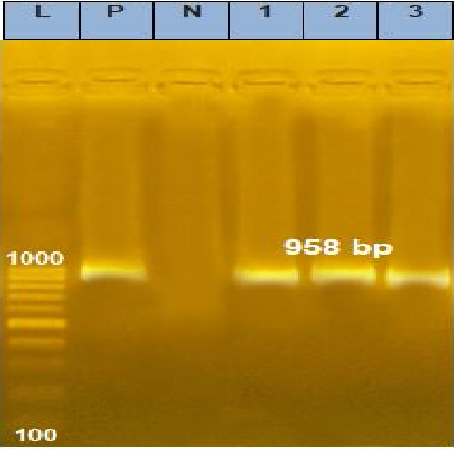
Agarose gel electrophoresis picture of PCR product showing the amplification of fragment of EEV gene at 958 bp. P: Control positive; L: DNA ladder; N: Negative fragment of LSDV in samples; Lane 1: Positive fragment of LSDV from skin nodules; Lane 2: Positive fragment of LSDV in samples taken from vaccine as positive control; Lane 3: Positive fragment of LSDV in samples taken from vaccine as positive control.
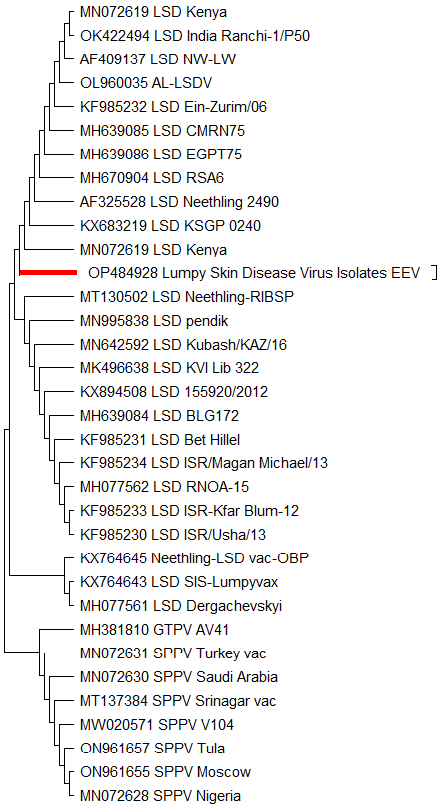
Neighbor joining Phylogenetic tree of based LSDV isolate (OP484928) and vaccinal strains based on nucleotide sequences of EEV gene and drawn by MEGA 11.
Deduced amino acids multiple sequence alignments of the EEV gene. The Egyptian LSDV (Accession No. OP484928) isolate were aligned with representative LSDV sequences retrieved from GenBank, Lumpy skin disease virus strain Neethling-LSD vaccine-OBP (Accession. No. KX764645.1), Lumpy skin disease virus strains SIS-Lumpyvax vaccine (Accesion No. KX 764643.1). The dots indicate the identical nucleotides in the alignment and digit detect the changes between sequences.
Pair wise nucleotide sequence alignment. LSDV (Query) aligned against Lumpy skin disease virus strain Neethling-LSD vaccine-OBP (acc. KX764645.1) (Subject).