Hepatotoxicity Induced by the therapeutic dose of Chlorpromazine and Ameliorative for Saussurea Costus Roots Extract and Effect of Physiological and Histological Liver of Albino Rats
Hepatotoxicity Induced by the therapeutic dose of Chlorpromazine and Ameliorative for Saussurea Costus Roots Extract and Effect of Physiological and Histological Liver of Albino Rats
Nbaa Mutea Abid AL-Alh1, Nuha Hatem Khalaf1, Nagam Khudhair1*, Ahmed Khalid2
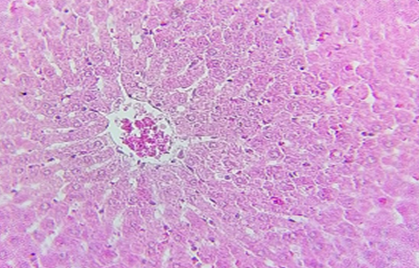
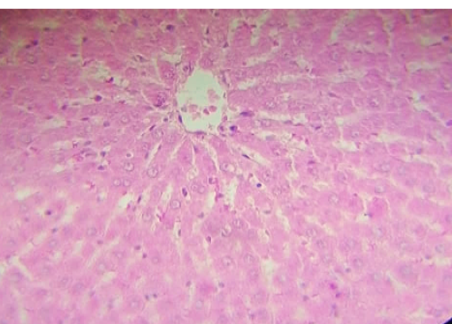
Histophotograph of the liver of control group screening hepatic architecture, central vein hepatocyte and blood sinusoids H and E400X.
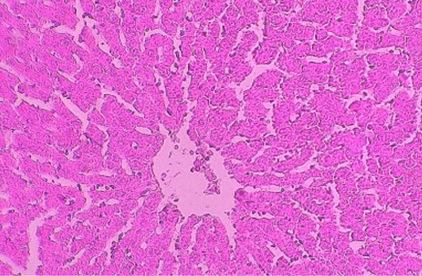
Histophotograph of liver treated with CPZ showing hepatocyte suffering from acute cell swelling. H and E X400.
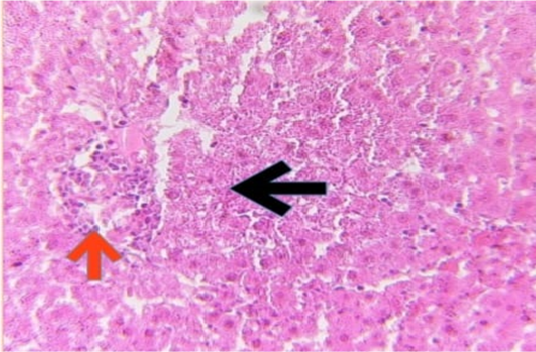
Histophotograph of liver treated with CPZ showing necrotizing hepatocyte (black arrow) and inflammatory cells infiltration (red arrow). H and E X400.
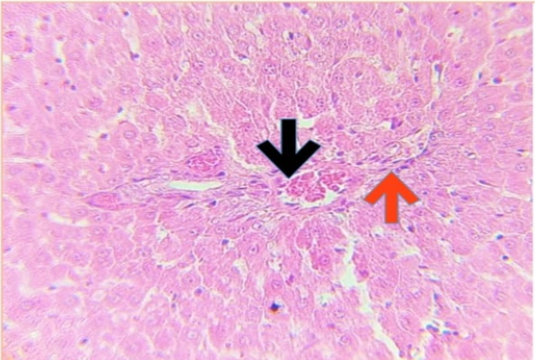
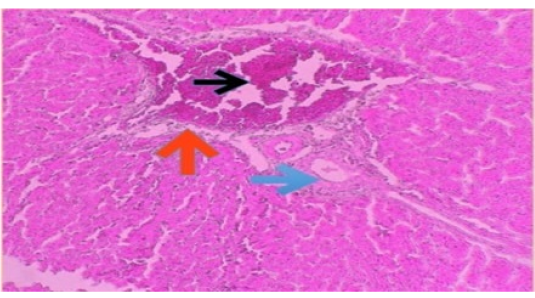
Histophotograph of liver treated with CPZ showing blood vessels congestion (black arrow) and perivascular inflammatory cells infiltration (red arrow). H and E X400.
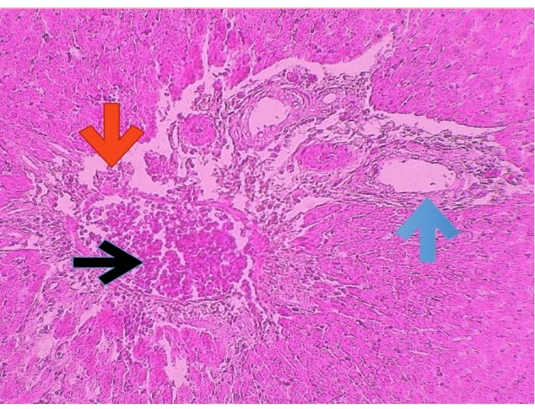
Histophotography of liver treated with CPZ, showing portal vein dilation (black arrow) with perivascular edema (red arrow) and bile ducts epithelial hyperplasia (blue arrow). H and E X100.
Histophotography of liver treated with CPZ, showing portal vein dilation (black arrow) with perivascular edema (red arrow), bile ducts epithelial hyperplasia (blue arrow) and hemosiderin deposition (blue arrow) H and E X100.
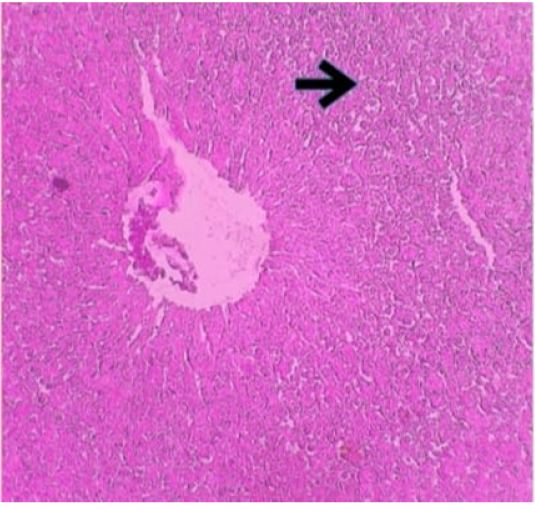
Histophotograph of liver showing peri central area of Hydropic Degeneration(arrow). H and E X 100.
Histophotograph showing the improvement of liver histology by prophylactic group treated with alcoholic extract of S.costus (5 ml) H and E 400X.