Growth Arrest Specific Gene 6 Improved in vitro Maturation of Oocytes and the Development Potential of Porcine Embryo after Parthenogenetic Activation
Growth Arrest Specific Gene 6 Improved in vitro Maturation of Oocytes and the Development Potential of Porcine Embryo after Parthenogenetic Activation
Zhi-Peng Li, Laiba Shafique, Saif ur Rehman, Kui-Qing Cui, Xiao-Can Lei, Xing-Rong Lu, De-Shun Shi* and Qing-You Liu*
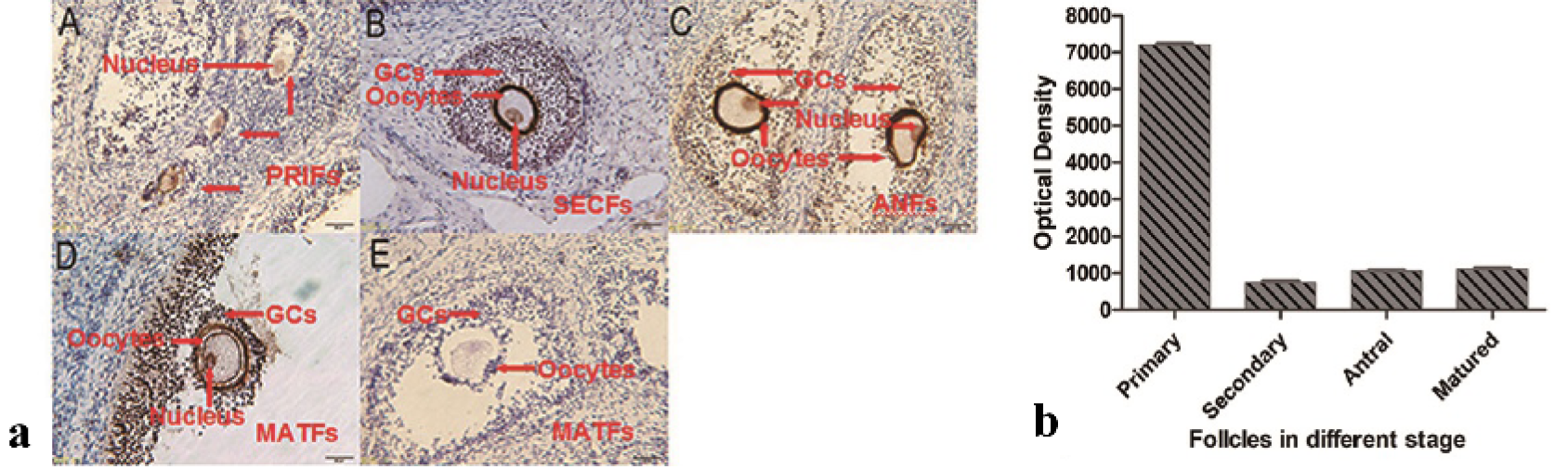
Immunohistochemistry analysis of Gas6 in the ovaries of porcine. a) Gas6 protein were staining brown by immunostaining using anti-Gas6 antibody (A, B, C and D), pre-immune serum instead of anti-Gas6 antibody was used as negative control (E). PRIFs, primary follicles; SECFs, secondary follicles; ANFs, antral follicles; MATFs, mature follicles. Scale bars=100 μm. b) The optical density of oocytes in different stage was analyzed by image-pro plus 6.0 software. The results are presented as mean ± SEM. GCs, granule cells.
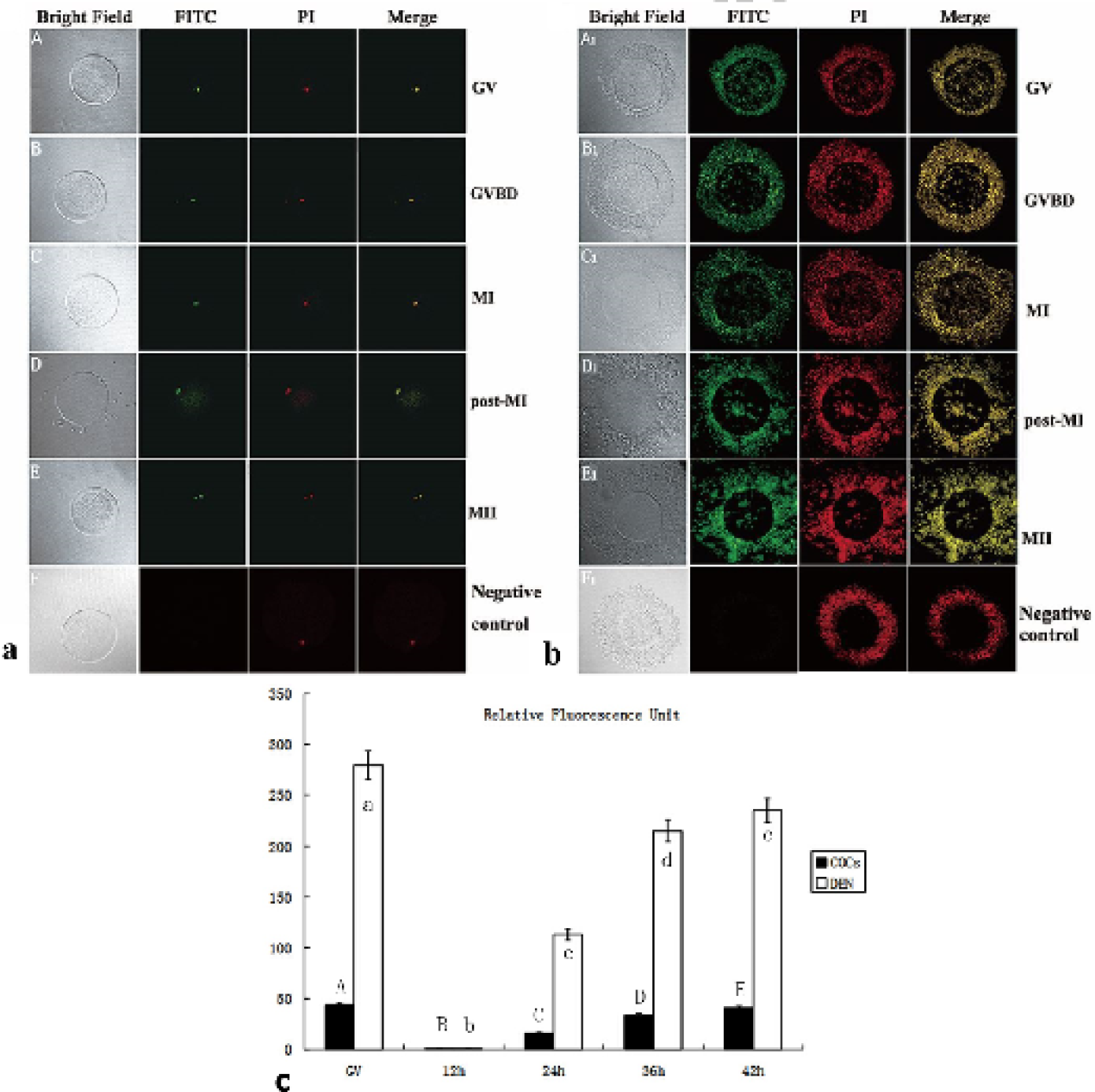
Immunofluorescence analysis of the Gas6 in oocytes in vitro maturing. a and b, Identification of Gas6 in oocytes and COCs. The green staining indicates a FITC signal and the red stain indicates counterstaining with propidium iodide (PI). C, Relative fluorescence unit during the oocyte maturation was analyzed by image-pro plus 6.0 software. COCs, Cumulus-oocyte complexes. GV, germinal vesicle; GVBD, germinal vesicle broken down; MI, metaphase I; MII, metaphase II; COCs, cumulus-oocyte complexes; DEN, denuded oocytes. The results are presented as mean ± SEM.
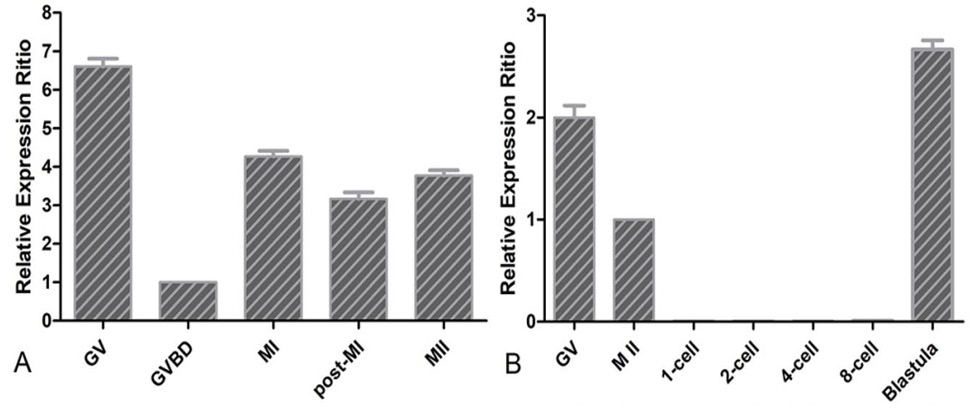
QRT-PCR analysis of Gas6 in the process of oocytes maturation (A) and embryo development (B). The relative gene expression was calculated using the 2-△△Ct method with 18S as the reference gene, and the expression ratio was calculated against Gas6 expression in the GV oocyte. Experiments were repeated 4 times, and data were presented as mean ± SEM.
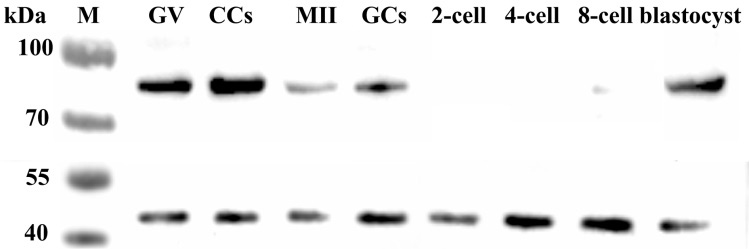
Western blot analysis of Gas6 expressed in the oocytes and early embryos. GV, Germinal vesicle; CCS, Cumulus oocyte complexes; MII, Metaphase II stage oocytes; GCS, Granulosa cells.