Genetic Diversity and its Impact on Post Translational Modifications of PKC and bml-Beta Tubulin Homolog Proteins in Different Species and Strains of Sordaria
Genetic Diversity and its Impact on Post Translational Modifications of PKC and bml-Beta Tubulin Homolog Proteins in Different Species and Strains of Sordaria
Ayesha Ahsan1, Rabia Arif2*, Samina Nazir1, Muhammad Saleem2 and Memunna G. Shahid1
Multiple sequence alignment of different strains of S. fimicola with reference sequence of S. fimicola to observe genetic variations for tubulin gene. Highlighted area indicating polymorphic sites while (*) symbol indicating conserved regions.
Multiple sequence alignment of different strains of S. fimicola with reference sequence of S. fimicola to observe genetic variations for PKC gene. Highlighted area indicating polymorphic sites while (*) symbol indicating conserved regions.
Multiple sequence alignment of different species of Sordaria and N. crassa to observe conserved regions of Beta tubulin homolog bml protein.
Multiple sequence alignment of different species of Sordaria and N. crassa to observe conserved regions of PKC protein.
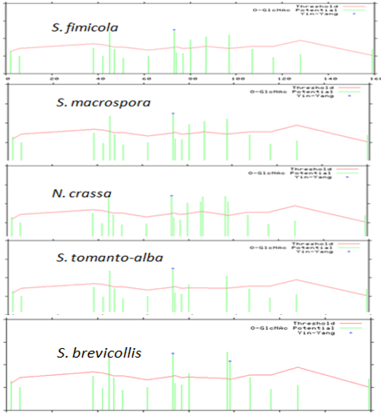
Comparison of O-glycosylation and YinOYang sites in different species of Sordaria and N. crassa for BML protein.