Exposure of Pregnant Mice to Hexavalent Chromium Causes Fetal Defects
Exposure of Pregnant Mice to Hexavalent Chromium Causes Fetal Defects
Madeeha Arshad1, Naveed Ahmad2,*, Muhammad Khalid3, Asmatullah1, Mohammad Tahir2, Khadija Naveed1 and Asia Iqbal4
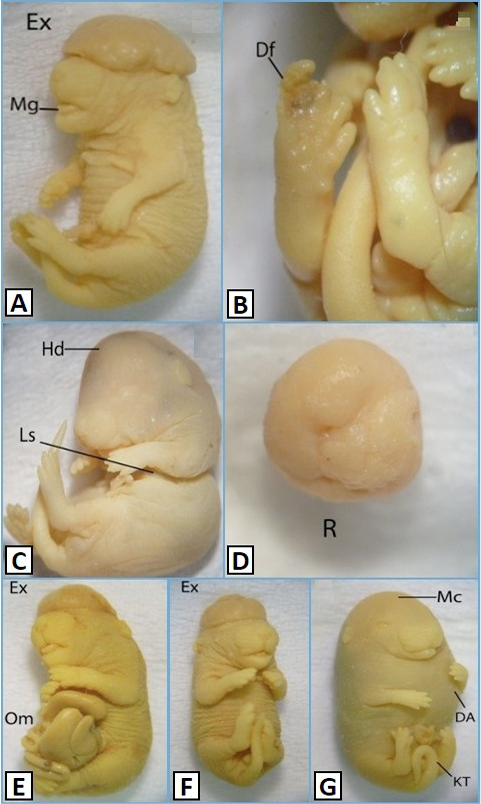
Morphological features of 18 days oldfetuses of mice administration with K2Cr2O7 at a dose of 22µg/g B.W. (A, B), and 11µg/g B.W. (C-G) Control, Vehicle control (VC); Df, deformed; Hd, hydrocephaly; Ls, laproschisis; Mg, macroglossia; R, resorption. DA, dilated abdomen; Ex, exencephaly; KT, kinked tail; Mc, Microcephaly; Om, Omphalocoel. Magnificaton: A=10X, B&D=25X, C, E&G=8X, F=9X
Morphological features of 18 days old fetuses of mice, administered with K2Cr2O7 at a dose of 44µg/g B.W. A, Control; B, VC, vehicle control; AO, anophthalmia; AT, abnormal tail; Cl, clinodactyly; DW, drooped wrist; Ex, exencephaly; FD, fused digits; Hm, hemorrhage; KT, kinked tail; MR, malrotation. Magnification: A=7X, B&C=8X, D=25X, E=20X, F=10X, F=9X.
Histological transverse sections of Control (A), Vehicle control (B) of different dose groups (44,22,11µg/g B.W) (C-H), 18 days old fetus from brain, Ex: exencephaly, M Vent: misshapen ventricle, HB: hind brain, MB, mandibular gland; FP, fused pinna, M sub corticle region: misshapen sub corticle region; Co, cortex; RA, right atrium; LA, left atrium; RA, right atrium; M Sc, misshapen spinal cord; SB, spina bifida; Om, Omphalocoel; NC, nasal cavity; Sg, serous gland; IRS, intra retinal space; RLV, right lateral ventricle, MB, mandibular gland; CA, cerebral aquaduct; LLV, left lateral ventricle; HC, hyaloid cavity; NS, nasal septum; FV, follicles of vibrissae; L, lens; FB, primordium of 1frontal bone; NLR, neural layer of retina; PM, pre molar.
Skeletons of control (A) and vehicle control (B), and selected sections from different dose groups (11,22,44µg/g B.W) (C-E). Simple arrows show less degree ossification while bold arrows show no ossification in three different dose groups. F, Frontal; N, Nasal; Pm, Pre Maxila; Z, Zygomatic; Md, Mandible; C, Clavicle; H, Humerus; R, Radius; U, Ulna; Ri, Ribs; Ti, Tibia; Fi, Fibula; I, Ilium; Fe, Femur; Sq, Squamosal; A, Atlas; Eo, Exocipital; So, Supraocipiltal; Ip, Interperitonial; P, Parietal.