Exploring the Effect of Phenotypic Variability on Genetic gain in Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Yield under Semi Drought Conditions
Exploring the Effect of Phenotypic Variability on Genetic gain in Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Yield under Semi Drought Conditions
Shiguftah Khalid1, Muhammad Jahanzaib2*, Haris Khurshid2, Rabia Khalid3, Sundas Waqar3, Faiza Siddique3, Fazal Yazdan Saleem Marwat3 and Zahid Akram1
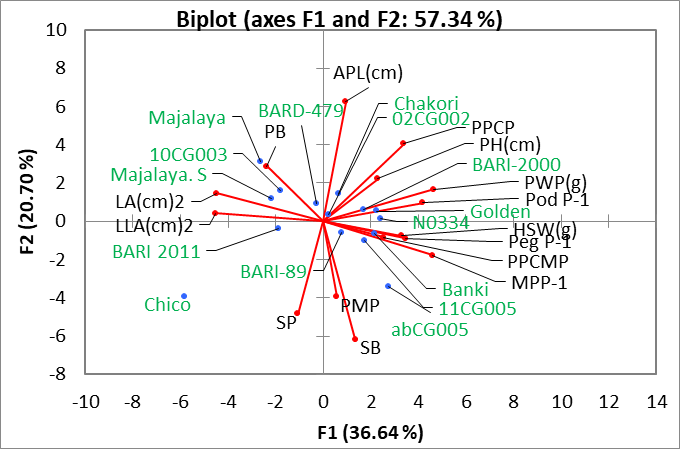
Biplot (Principal component analysis) indicating overall variability in 15 genotypes for traits variables, LA (Leaf Area), LLA (Leaflet Area), PB (Primary Branches), SB (Secondary Branches), PH (Plant Height), PPCP (Percentage of Pegs Converted into Pods), MPP-1 (Mature Pods per Plant), PPCMP (Percentage of Pegs Converted into Mature Pods), PMP (Percentage of Mature Pods), PWP (Pods Weight per Plant), SP (Shelling Percentage), APL (Average Pod Length) and HSW (Hundred Seed Weight).
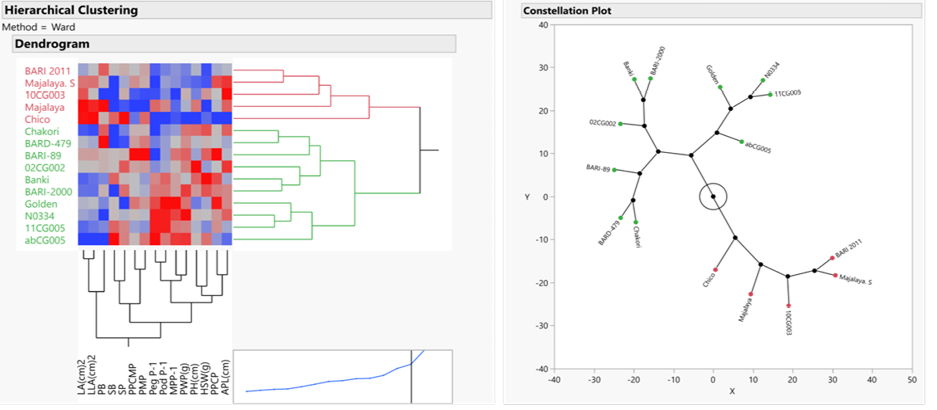
Cluster analysis indicates the degree of genetic diversity. Cluster diagram using WARD’s method revealed three clusters. Cluster I comprise of five genotypes, cluster II contains six genotypes and cluster III contains four genotypes.
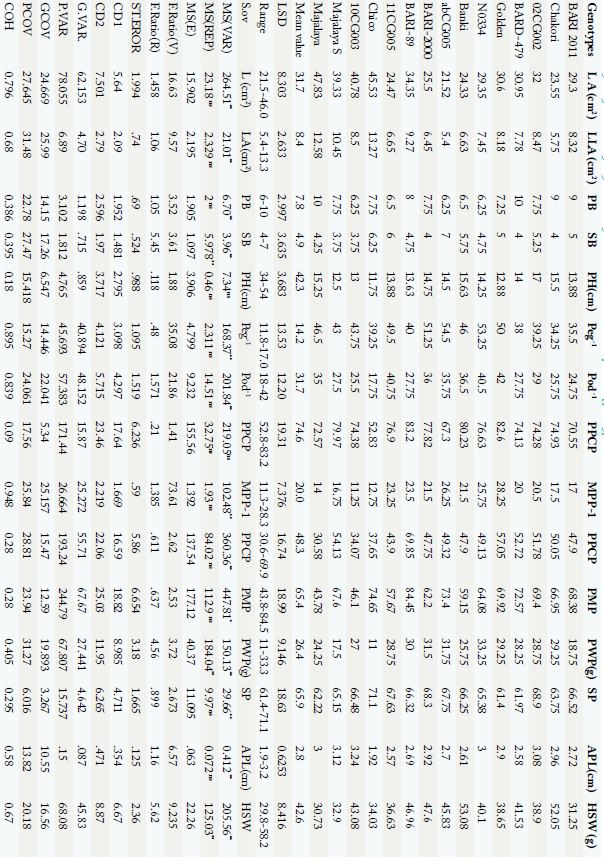
Analysis of variance for yield and yield related traits in 15 peanut genotypes.
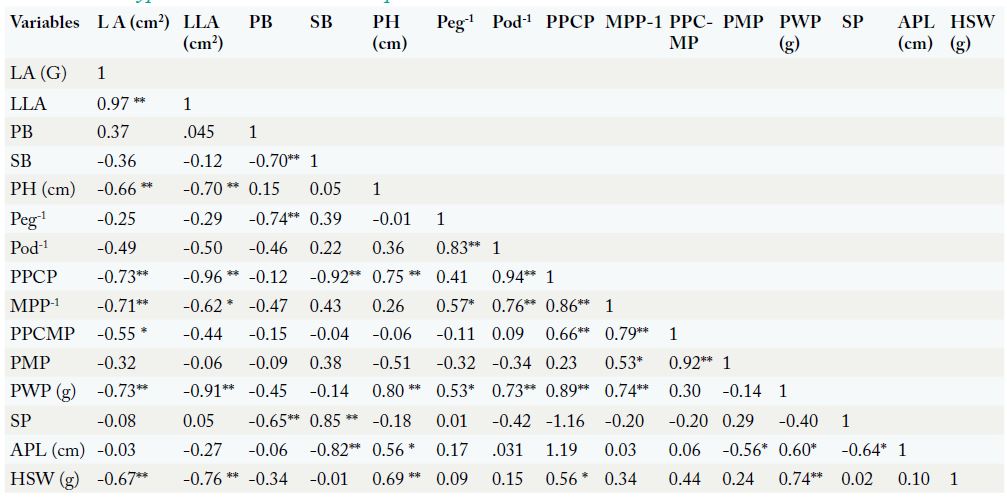
Genotypic Correlation between 15 peanut traits.
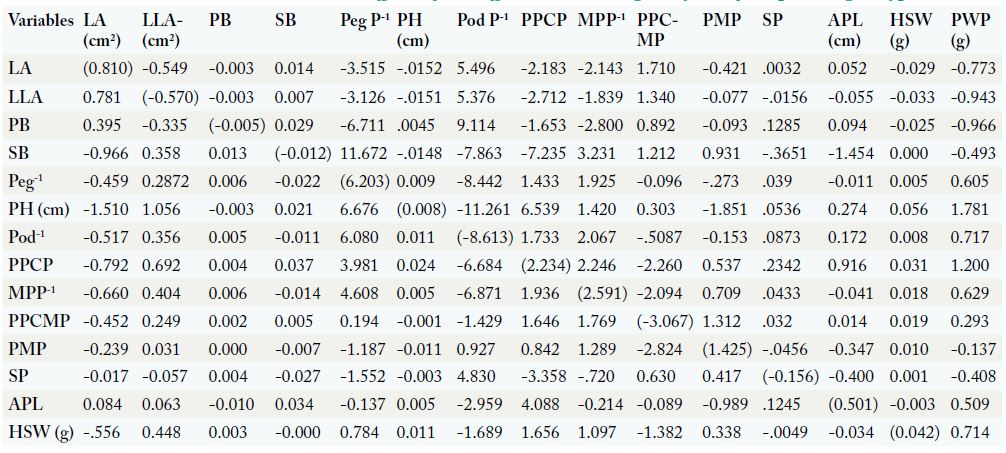
Direct (Parenthesis) and Indirect effects of 14 different traits on grain yield of 15 peanut genotypes.
LA (Leaf Area), LLA (Leaflet Area), PB (Primary Branches), SB (Secondary Branches), PH (Plant Height), PPCP (Percentage of Pegs Converted into Pods), MPP-1 (Mature Pods per Plant), PPCMP (Percentage of Pegs Converted into Mature Pods), PMP (Percentage of Mature Pods), PWP (Pods Weight per Plant), SP (Shelling Percentage), APL (Average Pod Length), HSW (Hundred Seed Weight).