Evalution of Antibacterial Activity of Portulaca oleracea against Escherichia Coli in vitro
Evalution of Antibacterial Activity of Portulaca oleracea against Escherichia Coli in vitro
Ahmed M. Manthoor, Ali H. Saliem*
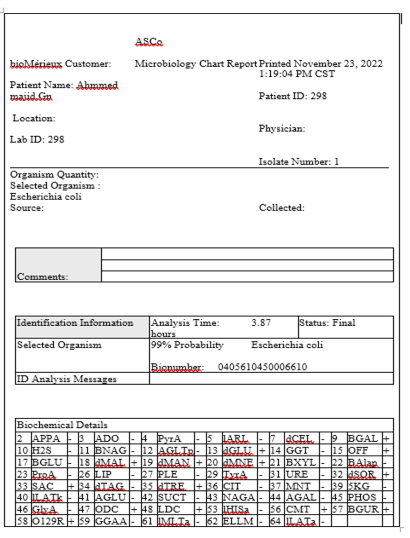
Report of Identification of E. coli by VITEK ®2 System.
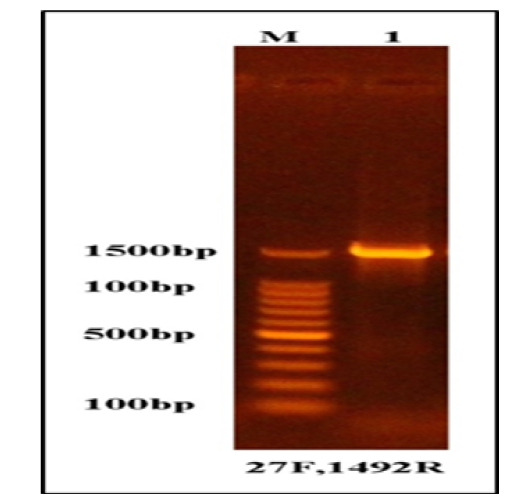
Results of the amplification of 16s RNA gene of the bacteria were fractionated on 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis stained with Eth.Br. M: 100bp ladder marker. Lanes 1 resemble 1500bp PCR products.
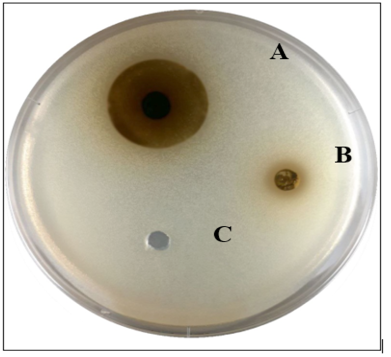
Susceptibility of E. coli to different concentrations of the extract in comparison with distilled water A (128 mg/ ml), B (32 mg/ ml) and C (D.W).
Susceptibility of E. coli to different concentrations of ciprofloxacin, in comparison with distilled water A (800µg/ml), B (50µg/ml) and C (D.W).
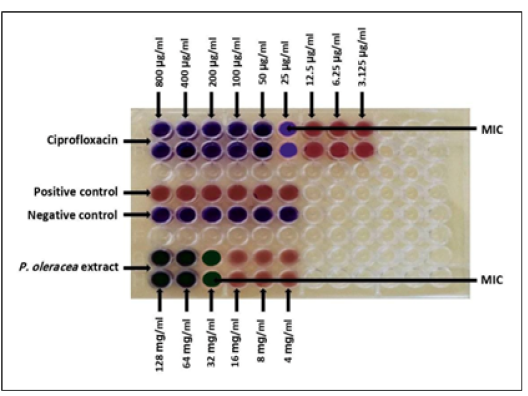
Checkerboard assay for minimum inhibitory concentration of the extract and ciprofloxacin against E. coli (Blue: no growth, red: growth).
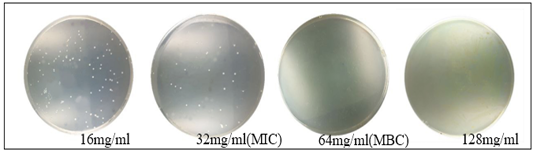
Minimum bactericidal concentrations of the extract against E. coli (64mg/ml).
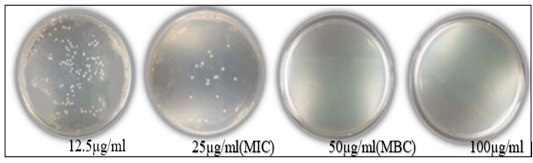
Minimum bactericidal concentrations of ciprofloxacin against E. coli (50µg/ml).
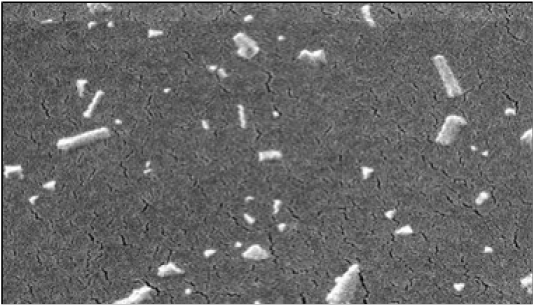
Identify mechanism of action of P. oleracea methanolic extract by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM). Destruction of cell and alteration in the shape of the bacterial cells, shrinkage, and mass accumulation of cell debris.