Emergence of Pathogenic Strains of Staphylococcus aureus in Goat Milk and Their Comparative Response to Antibiotics
Emergence of Pathogenic Strains of Staphylococcus aureus in Goat Milk and Their Comparative Response to Antibiotics
Iqra Muzammil1, Muhammad Ijaz Saleem1, Amjad Islam Aqib2,*, Ambreen Ashar3, Syed Ashar Mahfooz1, Sajjad ur Rahman4, Muhammad Shoaib4, Muhammad Aamir Naseer1, Imran Khan Sohrani1, Javeed Ahmad1, Razaullah Saqi1, Fizzah Laeeq Lodhi1 and
Qaisar Tanveer5
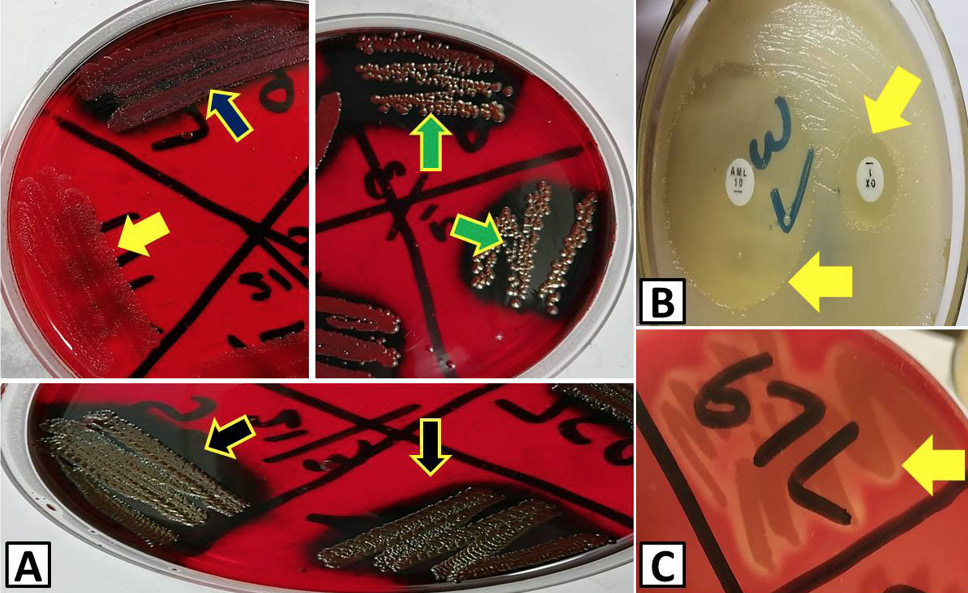
Biofilm producing strains, response of S. aureus against antibiotics and haemolytic strains. A, arrows point out different kinds of biofilm: yellow arrow, no biofilm; blue arrow, weak biofilm; green arrows, moderate biofilm; black arrow, strong biofilm. B, zone of inhibitions produced by antibiotics against S. aureus (yellow arrows, zones of inhibition). C, haemolysis on blood agar produced by S. aureus (yellow arrow, partial haemolysis).
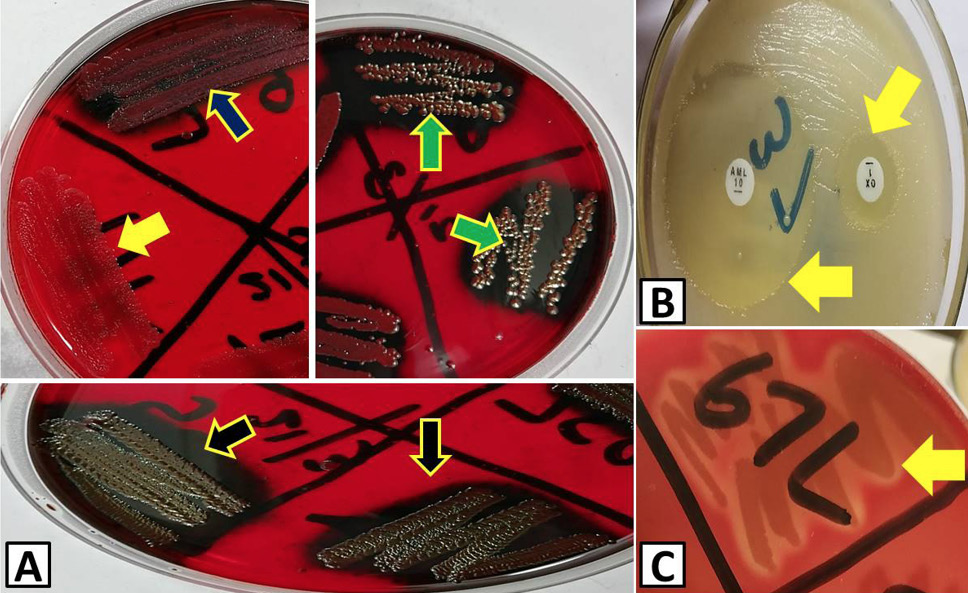
Biofilm producing strains, response of S. aureus against antibiotics and haemolytic strains. A, arrows point out different kinds of biofilm: yellow arrow, no biofilm; blue arrow, weak biofilm; green arrows, moderate biofilm; black arrow, strong biofilm. B, zone of inhibitions produced by antibiotics against S. aureus (yellow arrows, zones of inhibition). C, haemolysis on blood agar produced by S. aureus (yellow arrow, partial haemolysis).