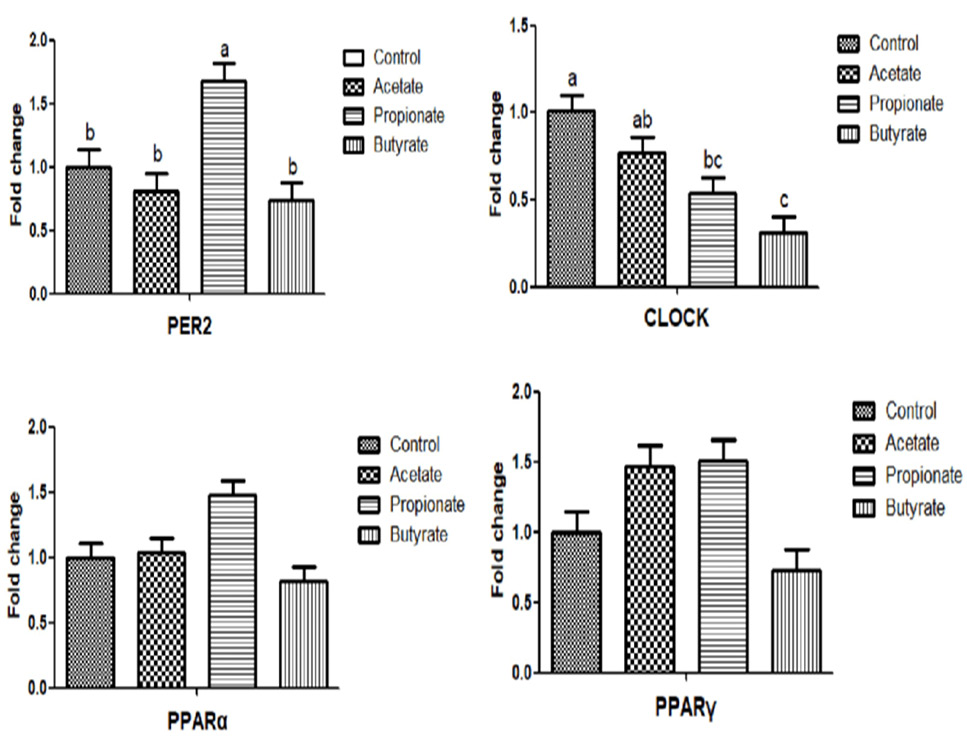
Fig. 1.
Effect of different VFAs on relative gene expression of CLOCK and PPARs family in ruminal epithelial tissue.
Note: PER, period circadian clock; CLOCK, clock circadian regulator; PPARα, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Values with different superscripts on the bars differ significantly (P<0.05), and values with the same superscripts on the bars have no significance (P>0.05).
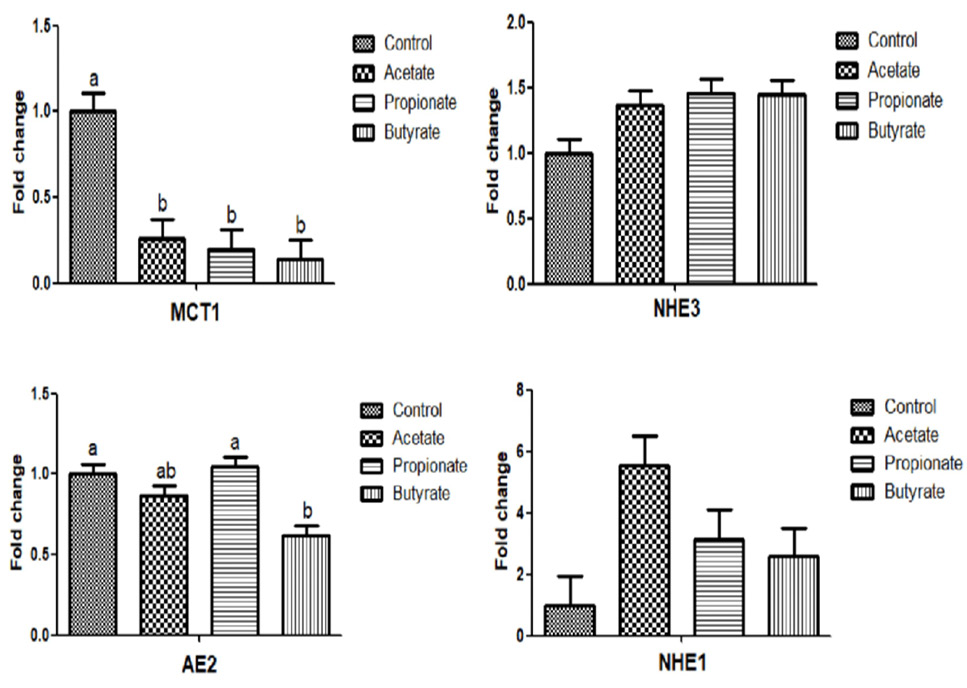
Fig. 2.
Effect of different VFAs on relative gene expression of VFA transport and absorption in rumen epithelial tissues.
Note: NHE, Na+/H+ exchange; AE2, anion exchanger 2; MCT1, monocarboxylic acid transporter 1. Values with different superscripts on the bars differ significantly (P<0.05), and values with the same superscripts on the bars have no significance (P>0.05).
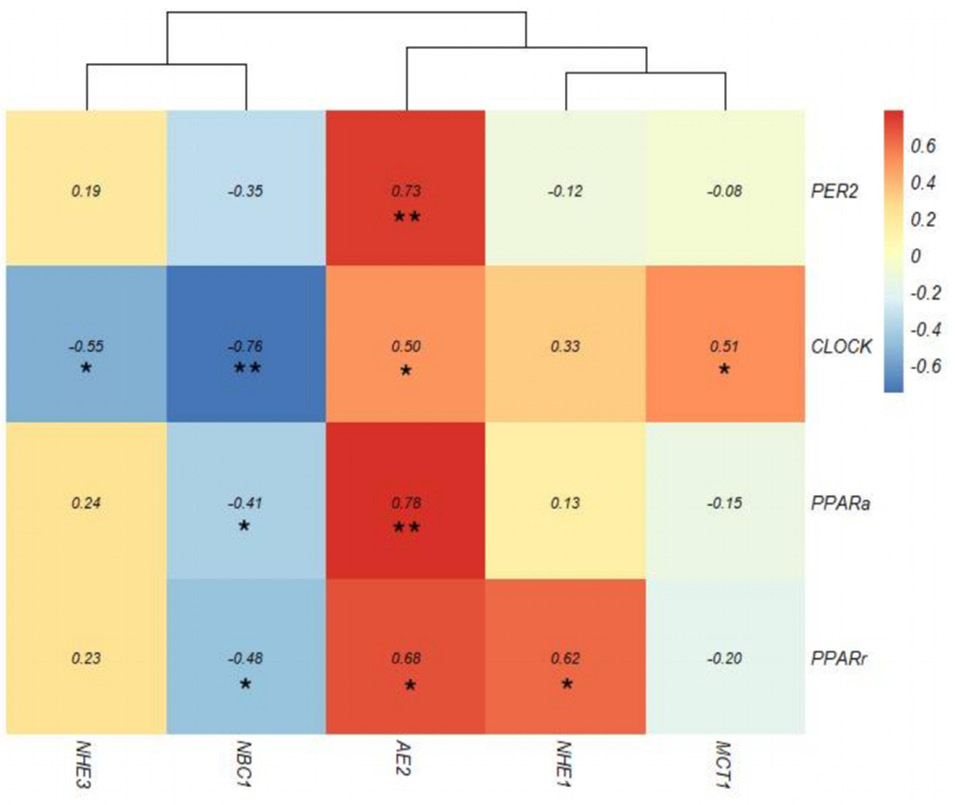
Fig. 3.
Effect of different VFAs on relative gene expression of VFA transport and absorption in rumen epithelial tissues.
Note: NHE, Na+/H+ exchange; AE2, Anion exchanger 2; MCT1, Monocarboxylic acid transporter 1. Values with different superscripts on the bars differ significantly (P<0.05), and values with the same superscripts on the bars have no significance (P>0.05).
Featuring
-
The Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Saurogobio punctatus (Cypriniformes: Cyprinidae: Gobioninae)
Juan Guo, Yu Zeng, Jin Li, Ling Mao and Yu Shuang Zhao
Pakistan J. Zool., Vol. 57, Iss. 3, pp. 1099-1105
-
Implications for Primate Population Management and the Occupational Safety of Primate Handlers: A Natural, Zoos and Captive Environment Comparative Study in China
Yong Zhu, Xingxing Yang, Ruisong Tao and Qixin Zhang
Pakistan J. Zool., Vol. 57, Iss. 3, pp. 1091-1097
-
Drug Resistance of Bloodstream Infection with Klebsiella pneumoniae and Detection of drug resistance Genes
Jinru Li and Xuemei Zhang
Pakistan J. Zool., Vol. 57, Iss. 3, pp. 1083-1090
-
Grafted Larval Age as a Factor Affecting Honeybee (Apis mellifera) Queen Cell Acceptance and Morphometric Characteristics
Muhammad Akbar Lashari, Agha Mushtaque Ahmed, Dalal M. Aljedani, Fahad Nazir Khoso, Rashid Mahmood, Muhammad Khalid Rafique, Hamed A. Ghramh, Waseem Akram, Saboor Ahmad, Sabir Hussain and Khalid Ali Khan
Pakistan J. Zool., Vol. 57, Iss. 3, pp. 1073-1081
Subscribe Today
Receive free updates on new articles, opportunities and benefits

© 2025 ResearchersLinks. All rights Reserved. ResearchersLinks is a member of CrossRef, CrossMark, iThenticate.