Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Either Zinc Oxide or Nano-Zinc Oxide on Growth Performance, some Serum Biochemical Parameters, Androgen Receptor Gene Expression and Microscopical Structure of the Testis in Growing V-Line Male Rabbits
Effect of Dietary Supplementation of Either Zinc Oxide or Nano-Zinc Oxide on Growth Performance, some Serum Biochemical Parameters, Androgen Receptor Gene Expression and Microscopical Structure of the Testis in Growing V-Line Male Rabbits
Ahmed H. El-Anwar, Eid A. Mabrouk, Khaled M. Ali, Nermeen A. Helmy, Rehab M. Reda*
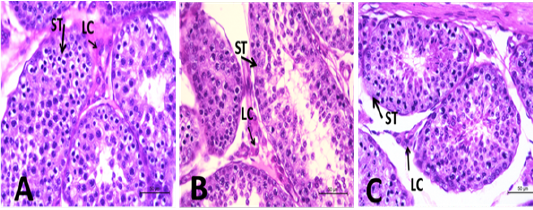
(A): Seminiferous tubules (ST) of the control group shows normal histological structure in which spermatogonial cells show mitotic activity, incomplete spermatogonial cycle (immature), and Leydig cells (LC) are dispersed in between (X 400). (B): ST of the ZnO group shows mitotic activity, immature spermatogonial cycle, and LC are dispersed in between. Few ST tubules show a limited number of spermatozoa most of which are attached to Sertoli cells (early maturation) (X 400). (C): ST of the n-ZnO group shows spermatogenic activity including spermatid and spermatozoa in high density (X 400).