Determinants of Grooming Behavior in Captive Langurs under Human Disturbance: A Case Study from the Central Zoo, Kathmandu, Nepal
Determinants of Grooming Behavior in Captive Langurs under Human Disturbance: A Case Study from the Central Zoo, Kathmandu, Nepal
Shailendra Sharma, Smriti Shrestha, Naresh Pandey and Laxman Khanal*
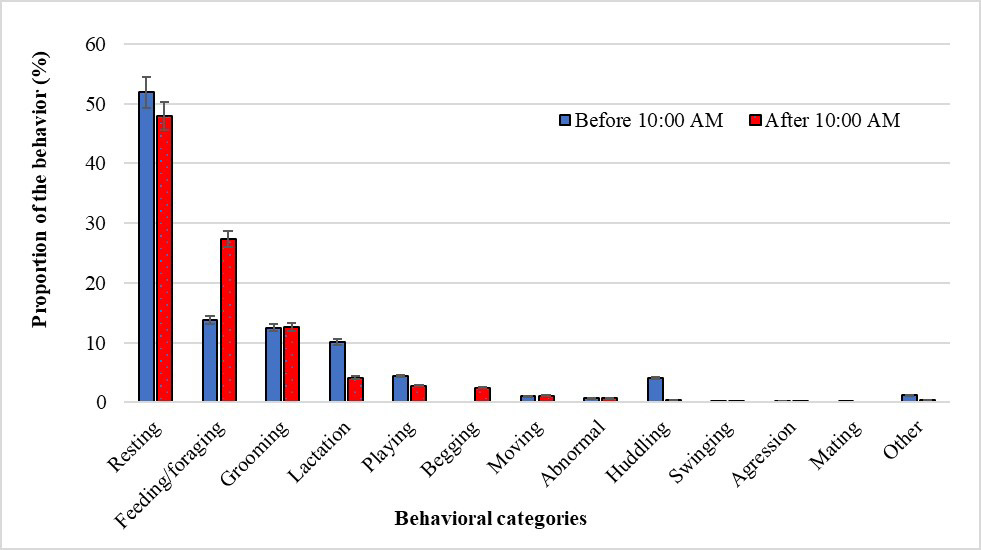
Overall activity proportion of captive langurs before and after 10:00 AM.
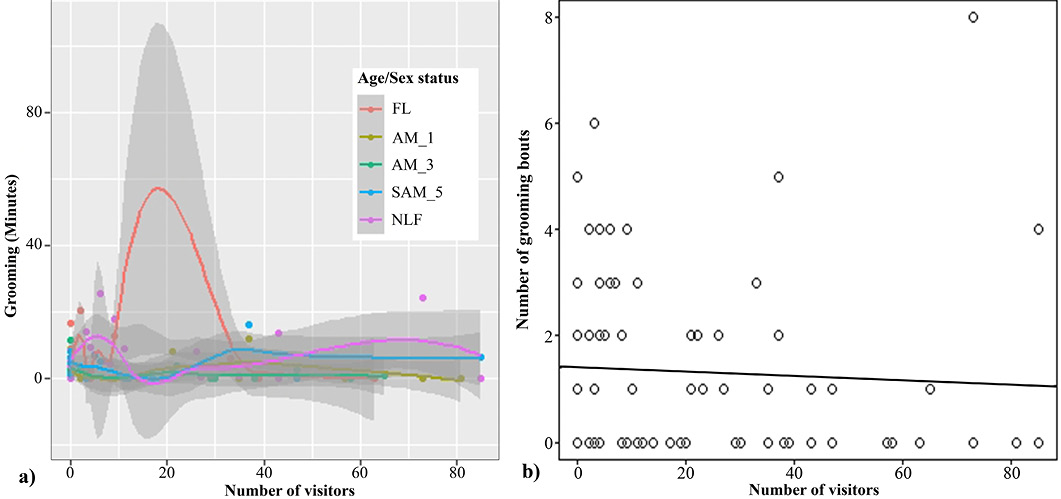
Grooming behavior by langurs in response to the number of visitors near the cage; (a) Age/sex-wise variation in time invested on grooming, (b) number of grooming bouts by the langurs (FL- lactating female, NLF- non lactating female, AM_1- adult male_1, AM_3- adult male_3, SAM_5- sub adult male_5).
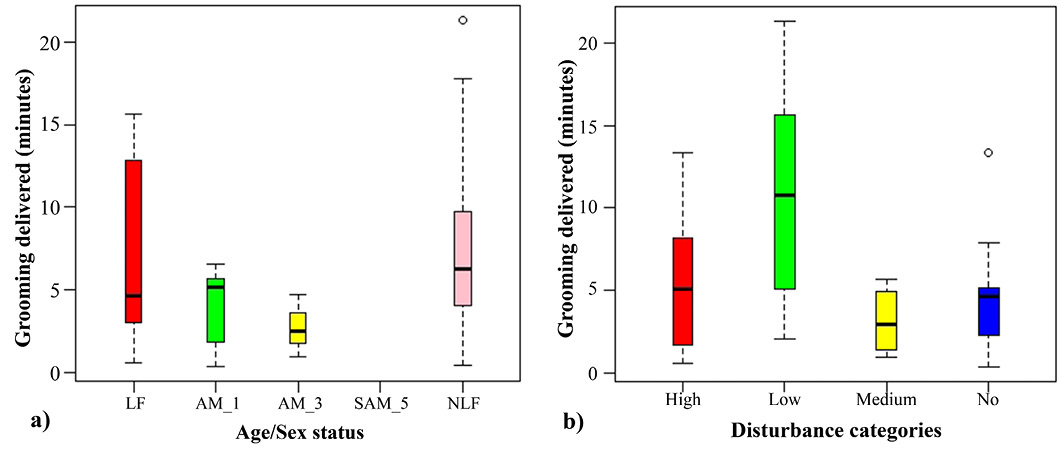
Boxplot representing mean time of grooming delivered based on- (a) age/sex status of the animal, and (b) level of disturbance from visitors.
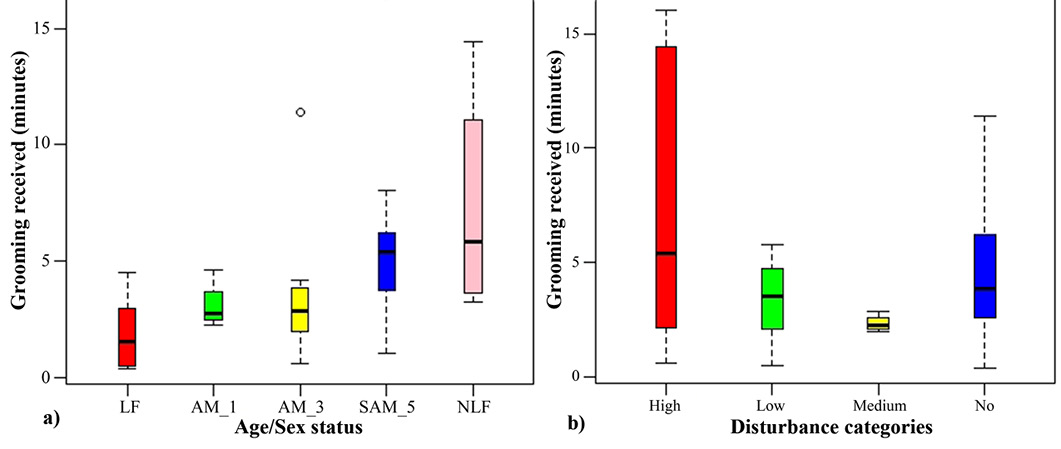
Boxplots representing mean time of grooming received based on- (a) age/sex status of the animal, and (b) level of disturbance from visitors.