Characterization of Unusual Human Group A Rotavirus VP4 Genotype Detected in Moroccan Children Fully Vaccinated with Rotarix™
Characterization of Unusual Human Group A Rotavirus VP4 Genotype Detected in Moroccan Children Fully Vaccinated with Rotarix™
Hassan Boulahyaoui1,2*, Sanaa Alaoui Amine1,3, Marouane Melloul4, Farida Hilali5, Elmostafa El-Fahime1,3, Saad Mrani1,2 and Nadia Touil1,5*
Phylogenetic analysis based on the VP4 gene nucleotide sequences of Moroccan P[14] strains, and sequences from the Genbank database. Moroccan strains obtained from vaccinated children are marked with a filled circle. Moroccan strains isolated from goat and bovine are marked with a filled and an empty triangle respectively. The lineages appeared at the right. Numbers at the nodes indicate bootstrap values (values <60% are not shown).
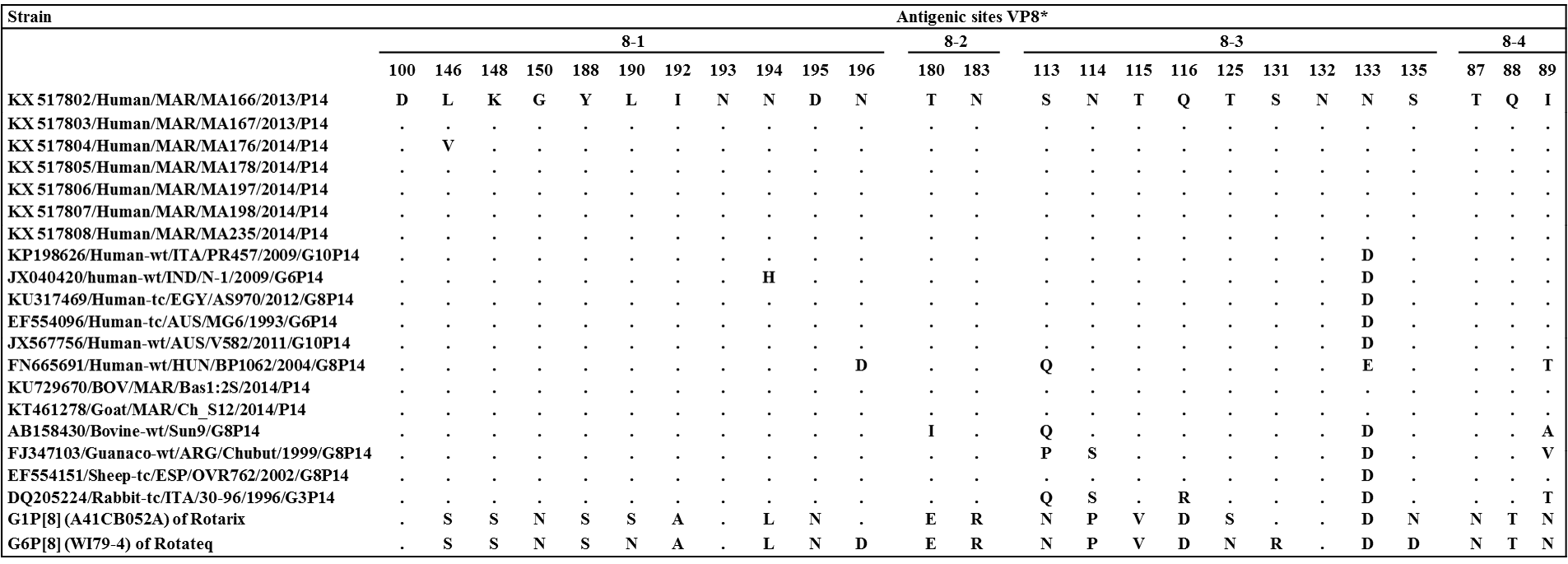
Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences inside antigenic epitopes of VP8* proteins of Moroccan P[14] stains analyzed and compared with vaccines and field P[14] strains retrieved from GenBank database.