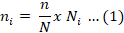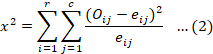Adoption of Agricultural Innovations: Does the Awareness Raising through Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) is Functional
Research Article
Adoption of Agricultural Innovations: Does the Awareness Raising through Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) is Functional
Faisal Khurshid1*, Asad Ullah1 and Sana Manan2
1Department of Rural Sociology, Faculty of Rural Social Sciences, The University of Agriculture Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; 2Department of Agricultural and Applied Economics, Faculty of Rural Social Sciences, The University of Agriculture, Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
Abstract | This study aims to assess the effectiveness of Agricultural Innovations Information Communication Technologies (ICTs) in adoption of agricultural innovations among the farmers community. The data were collected by using stratified random sampling technique. A sample size of 322 farmers was selected randomly from three villages namely Palosai, Badizai and Shahi Bala of the District Peshawar, Pakistan. The conceptual framework of the study comprised of an independent variable (knowledge of innovations) and dependent variable (adoption of agricultural innovations). Chi-square test was applied to ascertain the association among the study variables. It was found that adoption of agricultural innovations was significantly associated with knowledge of ICTs, (P=0.002), mobile/Applications as the most popular media of agriculture innovations and way of acquiring information (P=0.009), mobile play vital role in the transfer of knowledge of agricultural innovations (P=0.001), information provided through mobile application are accurate about weather updates, market subsidies, fertilizers, etc. (P=0.014), and mobile application/information enabled direct interaction with agriculture experts in getting required knowledge about innovates (P=0.006). It is concluded from the study that access to information communication technology facilitated its adopters in timely awareness of market information and government subsidies to boost their motivational level and let them persuade a favourable attitude towards agricultural innovations. Awareness raising among farmers for efficient use of ICTs for accessing innovation technological and encasing subsidies hired by the government alongside other information updates were the main recommendation in light of the study.
Received | January 04, 2022; Accepted | October 27, 2022; Published | December 26, 2022
*Correspondence | Faisal Khurshid, Department of Rural Sociology, Faculty of Rural Social Sciences, The University of Agriculture Peshawar, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan; Email: khurshidfaisal5@gmail.com
Citation | Khurshid, F., A. Ullah and S. Manan. 2022. Adoption of agricultural innovations: Does the awareness raising through information communication technologies (ICTs) is functional. Sarhad Journal of Agriculture, 38(5): 335-340.
DOI | https://dx.doi.org/10.17582/journal.sja/2022/38.5.335.340
Keywords | Information communication technologies (ICTs), Knowledge of innovations, Mobile/Applications, Government subsidies, Awareness of market information
Copyright: 2022 by the authors. Licensee ResearchersLinks Ltd, England, UK.
This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Introduction
The ICTs have an important and effective role in transferring knowledge in different agricultural technologies as it is accepted phenomena around the globe. Moreover, this has been adopted very widely and has a very broad audience to follow. There are fewer shreds of evidence that are in the support of the statement that ICTs are helping the farmers in their decisions. The research of Sey and Fellows (2009) shows that very little work have been done in this regard which shows the importance of structural process of ICT-driven models. But they feel worried about the time research in the sector knowing less impact of the said purpose (Ali and Kumar, 2011). The use of ICTs plays an important role in the knowledge of the farmers, through this channel farmers can adopt new technologies and they can obtain satisfactory results in their farming. ICT is not just a tool but a bridge between the farmers and the authorities providing them instructions on the new farming techniques which is surely the example of good communication and cooperation, through which their problems are solved lifelong (Afshari et al., 2009). In province of the initiative of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa agriculture department to start use of ICTs for diffusion of innovative ideas, practices and technologies among farming communities, this research study is designed to assess the effectiveness of ICTs in awareness raising of farmers about innovative technologies for its adoption.
Materials and Methods
The present study was conducted in three selected villages (Palosai, Shahi Bala and Badizai) of District Peshawar respectively, because of the adoption level of the new mobile technology, from the population of 713 adopters a sample size of 322 was sufficient as per Senker (1995) criteria. The study respondents included the households head from each selected households. Additionally, the sample size was proportionally distributed to each village using proportional allocation method.
Formula for proportional allocation is given in Equation 1.
Where; ni = required sample for each village; n= Total sample size; N = total population; Ni = Population of each village.
|
S. No |
Independent variable |
Dependent variable |
|
1. |
knowledge of innovations |
Adoption of agricultural innovations |
A conceptual framework was design with one independent variable (knowledge of innovations) and one dependent variable (adoption of agricultural innovations) as shown in the Table 1. Furthermore, Uni-variate analysis was applied through percentage and frequency distribution and reflected in the tables. To test the associations between independent variables (knowledge of innovations) with dependent variable (adoption of agricultural innovations) chi-square statistics were used (Kothari, 2004). Chi-square values were calculated by using the formula given in Equation 2 and explained below (Maccall, 1975).
Results and Discussion
Knowledge of innovations
Knowledge of agricultural innovations refer to exposure of individual or group of farmers to the messages related to existence or working of innovations. In the innovation diffusion model the knowledge is first stage to start with diffusion process Perception of personal experiences of the farmers with respect to agricultural innovations were determined by asking certain questions, results of which are given in Table 2.
Results in Table 2 show that majority of 76.7% respondents agreed that they had the knowledge of agriculture related innovative technologies, like seeds, fertilizers, chemicals, machinery, irrigation etc. Similarly, 76.7% respondents had the knowhow of using mobile phones to access agricultural related innovative technologies. Moreover, majority of 81.7% respondents were versant to mobile application to access agriculture experts or acquire different set of information like weather updates and market subsidies. The knowledge phase of the diffusion of innovation process is characterized with the dissemination of
Table 2: Knowledge of innovations.
|
S. No. |
Statement |
Agree |
Disagree |
Uncertain |
Total |
|
1 |
You have the knowledge of new technologies (seed, fertilizer, chemicals, machinery, irrigation etc.) in agriculture |
247(76.7%) |
36(11.2%) |
39(12.1%) |
322(100%) |
|
2 |
You have the knowhow about using of mobile to access knowledge related to new agricultural technologies |
247(76.7%) |
36(11.2%) |
39(12.1%) |
322(100%) |
|
3 |
You have the knowledge of mobile application to reach the agriculture experts in acquiring of different information such as (weather updates, market subsidies etc.) |
263(81.7%) |
25(7.8%) |
34(10.6) |
322(100%) |
|
4 |
You think that mobile and mobile apps in Pakistan are most popular media of agriculture innovations and way of acquiring information? |
256(79.5%) |
26(8.1%) |
40(12.4%) |
322(100%) |
|
5 |
You think that mobile have an important role in the transferring of knowledge of innovations in agriculture |
257(79.8%) |
24(7.5%) |
41(12.7%) |
322(100%) |
|
6 |
You agree that the information provided through mobile application is accurate about weather updates, market subsidies, fertilizer etc. |
286(88.8%) |
19(5.9%) |
17(5.3%) |
322(100%) |
|
7 |
You follow the instructions regarding new farming techniques such as three layer farming |
223(69.3%) |
19(5.9%) |
17(5.3%) |
322(100%) |
|
8 |
You agree that mobile application have an important role comparatively to face to face interaction with the experts in getting knowledge of innovations in agriculture interaction with the in getting knowledge of innovations in agriculture |
231(71.7%) |
61(18.9%) |
30(9.3%) |
322(100%) |
* Number in table represent frequencies and number in parenthesis represent percentage proportion of respondents.
innovation related knowledge through appropriate communication channels. The significance of mass media is justified in awareness related campaigns. The usage of mobile phone for awareness rising in the farmers for adoption of innovative agricultural technologies is quite necessary to enable them for right decision in time. Hall and Andriani (2002) also signified the importance of mobile phone use in disseminating agricultural innovations knowledge related to the farmers, so as to enable them to make right decision at right time.
Moreover, majority of 79.5% respondents described mobile phone applications as the most popular medium for acquiring agricultural information, 79.8% of respondents thought that the mobile phone played important role in knowledge transfer to the farmers and 88.8% respondents were satisfied that the information provides through mobile application were accurate. The mobile phone applications are developed for dissemination of specific information in an efficient and timely manner. It is evident from the above results that the farmers were quite satisfied in using of the mobile application for accurate and timely disseminated information related to agricultural innovations, weather forecast or other associated subsidies. Consequently, the mobile phone applications are gaining popularity among the farmers due to its desirable results. These results are similar to the findings of Conesa et al. (2005) who reported that the interpersonal communication channels can be established and strengthened through mobile application that can help in rapid diffusion information related to innovative technologies.
Results further show that 69.3% respondents followed the technical instructions provided by the experts related to modern technologies such as (three layer farming) and 71.1% respondents were of the opinion that uses of phone application were more efficient in technological information dissemination then the interpersonal communication channels. In the modern agricultural information mobile applications are designed to cover multiple aspects of understanding and learning from the messages by the farmers. For this purpose the applications are supported with audio, video and pictorial messages that are easily understandable to a range of farmers from all literacy and socioeconomic classes. That’s why the mobile applications are gaining popularity in use among the farmers.
Moreover, the information communicated are better understood and implemented by the farmers. In addition, Gracia (2015) described that use of mobile phones technologies is making great breakthrough in agriculture extension system. The mobile phones due to its accessibility updated knowledge and multipurpose use are extensively use by the farmers for getting access to innovative technologies and its practical utility in the field.
Association between knowledge of innovation and adoption of agricultural innovation
The 21st century has started with the boom of scientific and technological innovations and its regular updating. The scientific innovations are regularly upgraded and replaced with new technologies and its related knowledge. Consequently, the communication signs have been signified in its importance is disseminating scientific information innovative technologies. The adoption of agricultural innovations is also influenced by appropriate communication methods in different parts of world. Association between knowledge of agriculture innovations and its adoption is given in Table 3 and explained below.
A significant association was found between adoption of agricultural innovations and knowledge of new technologies (seed, fertilizers, chemicals, machinery and irrigation etc) in agriculture (P=0.002). Similarly, popularity of mobile applications in the region for agriculture information acquisition had a significant association (P=0.009) with adoption of agriculture innovations. Knowledge is the first phase of innovation decision process. In this stage, the potential adopters like farming community, come across such messages through which they get the knowledge of existence of an innovations or its use. The above results clearly show that the mobile applications were efficient tools for disseminating agricultural innovations related knowledge to the farmers that helped them in making appropriate adoption or rejection related decision as depicted from significant P values of above results. The Von Krogh et al. (2000) also reported the significance
Table 3: Association between knowledge of innovation and adoption of agricultural innovation.
|
Statement |
Attributes |
Adoption of agricultural innovation |
Statistics |
|||
|
Highly satisfaction level of adoption |
Moderate satisfaction level of adoption |
Low satisfaction level of adoption |
Total |
|||
|
You have the knowledge of new technologies (seed, fertilizer, chemicals, machinery, irrigation etc.) in agriculture |
Agree |
147(64.5) |
49(21) |
32(14.0) |
228(100) |
x2=17.1 P=0.002 |
|
Disagree |
33(49.3) |
17(25.4) |
17(25.4) |
67(100) |
||
|
uncertain |
8(29.6) |
9(33.3) |
10(37.0) |
27(100) |
||
|
You have the knowhow about using of mobile to access knowledge related to new agricultural technologies |
Agree |
146(59.1) |
57(23.1) |
44(17.8) |
247(100) |
x2 =0.825 P=0.93 |
|
Disagree |
19(52.8) |
10(27.8) |
7(19.4) |
36(100) |
||
|
uncertain |
23(59.0) |
8(20.5) |
8(20.5) |
39(100) |
||
|
You have the knowledge of mobile application to reach the agriculture experts in acquiring of different information such as (weather updates, market subsidies etc.) |
Agree |
164(62.4) |
53(20.5) |
45(17.1) |
263(100) |
x2 =11.98 P=0.24 |
|
Disagree |
12(48.0) |
7(28.0) |
6(24.0) |
25(100) |
||
|
Uncertain |
12(35.3) |
14(41.2) |
8(23.5) |
34(100) |
||
|
You think that mobile and mobile apps in Pakistan are most popular media of agriculture innovations and way of acquiring information |
Agree |
159(62.1) |
55(21.5) |
42(16.4) |
256(100) |
x2 =7.81 P=0.09 |
|
Disagree |
10(38.5) |
9(34.6) |
7(26.9) |
26(100) |
||
|
uncertain |
19(47.5) |
11(27.5) |
10(25) |
40(100) |
||
|
You think that mobile have an important role in the transferring of knowledge of innovations in agriculture |
Agree |
158(61.5) |
53(20.6) |
46(17.9) |
257(100) |
x2 =7.58 P= 0.10 |
|
Disagree |
12(50) |
9(37.5) |
3(12.5) |
24(100.0) |
||
|
uncertain |
18(43.9) |
13(31.7) |
10(24.4) |
41(100) |
||
|
You agree that the information provided through mobile application is accurate about weather updates, market subsidies, fertilizer etc. |
Agree |
168(58.7) |
68(23.8) |
50(17.5) |
286(100) |
x2 = 6.80 P= 0.14 |
|
Disagree |
6(73.7) |
5(10.5) |
6(15.8) |
17(100.0) |
||
|
uncertain |
6(35.3) |
5(29.4) |
6(35.3) |
17(100) |
||
|
You follow the instructions regarding new farming techniques such as three layer farming |
Agree |
139(62.3) |
42(18.8) |
42(18.8) |
223(100) |
x2 = 9.51 P= 0.049 |
|
Disagree |
31(52.5) |
20(33.9) |
8(13.6) |
59(100.0) |
||
|
uncertain |
18(52.5) |
13(33.9) |
9(3.6) |
40(100.0) |
||
|
You agree that mobile application have an important role comparatively to face to face interaction with the experts in getting knowledge of innovations in agriculture |
Agree |
146(63.2) |
46(19.9) |
39(16.9) |
231(100.0) |
x2 = 8.78 P= 0.06 |
|
Disagree |
29(47.5) |
18(29.5) |
14(23.0) |
61(100.0) |
||
|
uncertain |
13(43.3) |
11(36.7) |
6(20.0) |
30(100.0) |
||
* Values in table represent frequencies and values in parenthesis represent percentage proportion of respondents.
of mobile technologies and software applications for dissemination of innovative knowledge to the potential farming communities. Consequently, such potential adopters were in better position to get awareness of existence of modern technologies and appropriate way of its applications in the field. An efficient communication of these innovative technologies streamlined adoption of some modern tools and practices by the farmers to enhance their agriculture production.
Furthermore, following instructions regarding new farming techniques such as three layer farming exhibited significant association (P=0.049) with adoption of agricultural innovations. The communication experts disseminating appropriate knowledge with in a social system that touches the majority of potential adopters due to interconnected social structures of the farming communities. Therefore, a better informed farmer is more compulsive to think and practice the innovative technologies that lead to its subsequent adoption. Sneeker (1995) also reported that formulation and dissemination of agriculture knowledge to the farmers in an appropriate fashion is stimulating to the farmers to think upon these technologies its practicing and later on complete adoption.
However, adoption of agricultural innovations had a non-significant association with knowledge of mobile use to access the agriculture technologies (P=0.93), use of mobile to access agricultural experts (P=0.024), important role of mobile application in knowledge transfer (P=0.40), accuracy of information provided by mobile application (P=0.14) and comparatively high advantages of mobile applications over face to face interaction (P=0.06). Despite of the significance of mobile phone technology and its associated applications the use of mobile phones is not optimal among farmers due to which the full benefits of this important source of knowledge dissemination couldn’t be achieved as shown by the non-significant association in the above results.
Knowledge of innovations provides foundation for adoption of innovative technologies among farmers. The mobile phone application is important source of disseminating agriculture innovations related information like seed, fertilizers, chemicals, machinery and irrigation etc to the farmers that facilitate farmers in understanding and follow the instructions for use of these innovative technologies for its full fledge adoption. However, the complications in accessing and interpreting of these mobile application based information is difficult for farmers due to which they faced difficulties in gaining information, querying about their questions and remained partially informed due to which the adoption of agriculture innovations was obstructed.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The results help to conclude that mobile phone applications and internet services are emerging as tools for disseminating agriculture related innovations knowledge and knowhow to use several technologies. The selected respondents (being the leading farmers of the society) were facilitated through information communication technologies in getting awareness and knowledge about seed, fertilizers, chemicals, machinery and irrigation etc. These farmers acted as opinion leader in disseminating not only the agriculture innovations among their fellow farmers but also motivated them to adopt information communication technologies for updating their knowledge base. However, the low literacy level of the farmers, their low income standing and difficulties in use of information communication technologies constraints farmers for its full fledge adoption and use in communication of agriculture related problems and solutions.
Creating awareness among farmers regarding information communication technologies and its use for accessing information related to innovative technologies and its practical applications in fields, weather forecast, government subsidies and market information with convenience are the major recommendations in light of study findings.
Novelty Statement
This research study is first of its kind to relate effectiveness of ICT use in shaping farmer’s adoption related behavior in the study area.
Author’s Contribution
Faisal Khurshid: Conceived the idea, collected the data and drafted the manuscript.
Asad Ullah: Supervised the research, fixed the parameters and analysed thedata.
Sana Manan: Processed the data and edited the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
References
Afshari, M., K.A. Bakar, W.S. Luan, B.A. Samah and F.S. Fooi. 2009. Factors affecting teachers use of information and communication technology. Int. J. Instr., 2: 77-104.
Aldosari, F., M.S. Al-Shunaifi, M.A. Ullah, M. Muddassir and M.A. Noor. 2019. Farmers perceptions regarding the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Northern Pakistan. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci., 18(2): 211-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2017.05.004
Ali, J., and S. Kumar. 2011. Information and communication technologies (ICTs) and farmers decision-making across the agricultural supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manage., 31(2): 149-159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2010.07.008
Conesa, A., S. Götz, J.M. García-Gómez, J. Terol, M. Talón and M. Robles. 2005. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics, 21(18): 3674-3676.
Dhraief, M.Z., S. Bedhiaf-Romdhania, B. Dhehibib, M. Oueslati-Zlaouia, O. Jebali and S. Ben-Youssef. 2018. Factors affecting the adoption of innovative technologies by livestock farmers in arid area of Tunisia. FARA Res. Rep., 3(5): 22. https://doi.org/10.30682/nm1904a
García-Álvarez, M.T., 2015. Analysis of the effects of ICTs in knowledge management and innovation: The case of Zara Group. Comput. Hum. Behav., 51: 994-1002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.10.007
Hall, R. and P. Andriani. 2002. Managing knowledge for innovation. Long Range Plan., 35(1): 29-48.
Kothari, C.R. 2004. Research methodology: Methods and techniques. New Age International.
Macharia, J.K. and T.G. Pelses. 2004. Key factors that influence the diffusion and infusion of information and communication technologies in Kenyan higher education. Stud. High. Edu., 39(4):695-709.
Moore, G.A., 1995. Crossing the chasm: Marketing and selling technology products to mainstream customers, 2nd ed., Capstone Publishing, Oxford.
Nonaka, I., 1991. The knowledge-creating company. In: Harvard business review, November–December, 96-104.
Sey, A. and M. Fellows. 2009. Literature review on the impact of public access to information and communication technologies. CIS working paper/Center for Information and Society, University of Washington; no. 6.
Senker, J., 1995. Tacit knowledge and models of innovation. Ind. Corp. Change, 4(2): 425-447. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/4.2.425
Von Krogh, K. Ichijo and I. Nonaka. 2000. Enabling knowledge creation: How to unlock the mystery of tacit knowledge and release the power of innovation. Oxford University Press on Demand.
To share on other social networks, click on any share button. What are these?