A Study on Differentially Expressed Genes in Reserve Mesenchyme of Male and Female Reindeer Antler Tip
A Study on Differentially Expressed Genes in Reserve Mesenchyme of Male and Female Reindeer Antler Tip
Jiancheng Zhai, Li Gao, Yanling Xia and Heping Li*
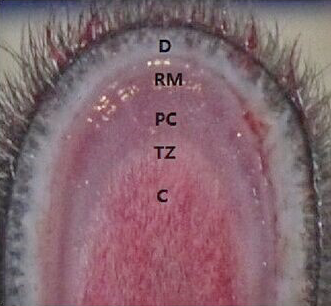
Layer identification of unstained proliferative zone in a growing reindeer antler tip. D, dermis; RM, reserve mesenchyme; PC, precartilage; TZ, transitional zone; C, cartilage.
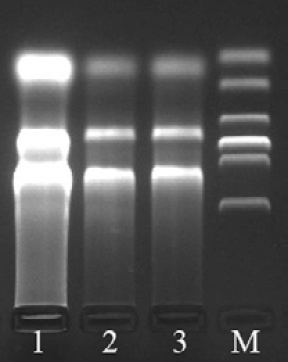
Electrophoresis of RNA of reindeer antler mesenchyme. 1, the male reindeer; 2 and 3, the female reindeer; M, 2000bp DNA marker.
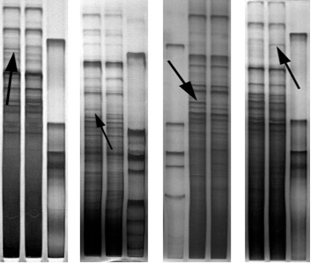
Electrophoresis of partial products of DDRT-PCR. The lanes represent the DDRT-PCR from reserve mesenchyme of male and female reindeer antler tip. The differentially expressed fragments are indicated by arrows.
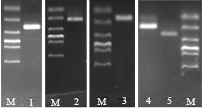
Electrophoresis of recovered differential fragments. 1 to 5 represented fragments Ci2, Ce1, Ae1, Af1 and Af3, respectively. M, 2000bp DNA marker.
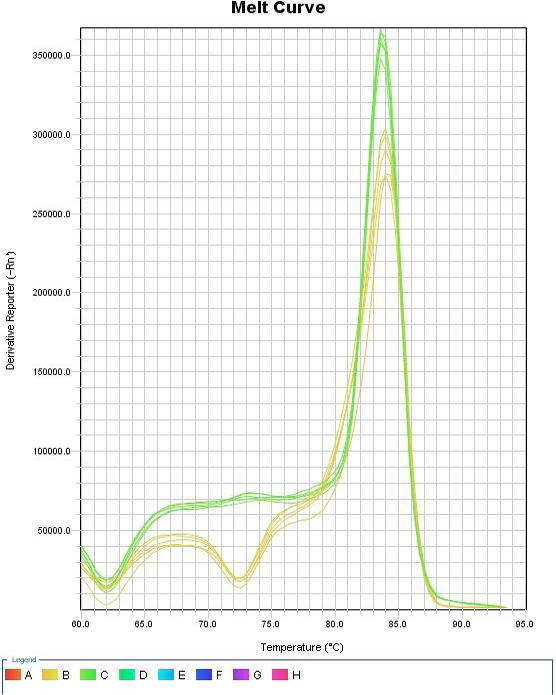
Melt curve of real-time PCR. Yellow, β-actin gene. Green, COL6A3 gene.
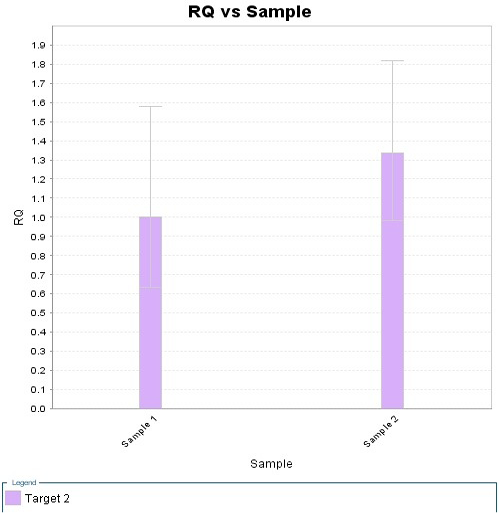
Relative quantitative of samples. The 1 and 2 mean the relative expression levels of the reserve mesenchyme of the male and the female reindeer antler tip, respectively.