Evolutionary Adaptation of Fermenting Strains in Wheat Straw Hydrolysate for Bioethanol and Lactic Acid Production
Evolutionary Adaptation of Fermenting Strains in Wheat Straw Hydrolysate for Bioethanol and Lactic Acid Production
Imrana Khushk1, Abdul Nabi Jatt2, Abdul Sattar Qureshi1*, Choudhary Haider Ali3, Muhammad Aqeel Bhutto1, Imran Ibrahim Khaskheli1, Sartar Iqbal Panhwer1
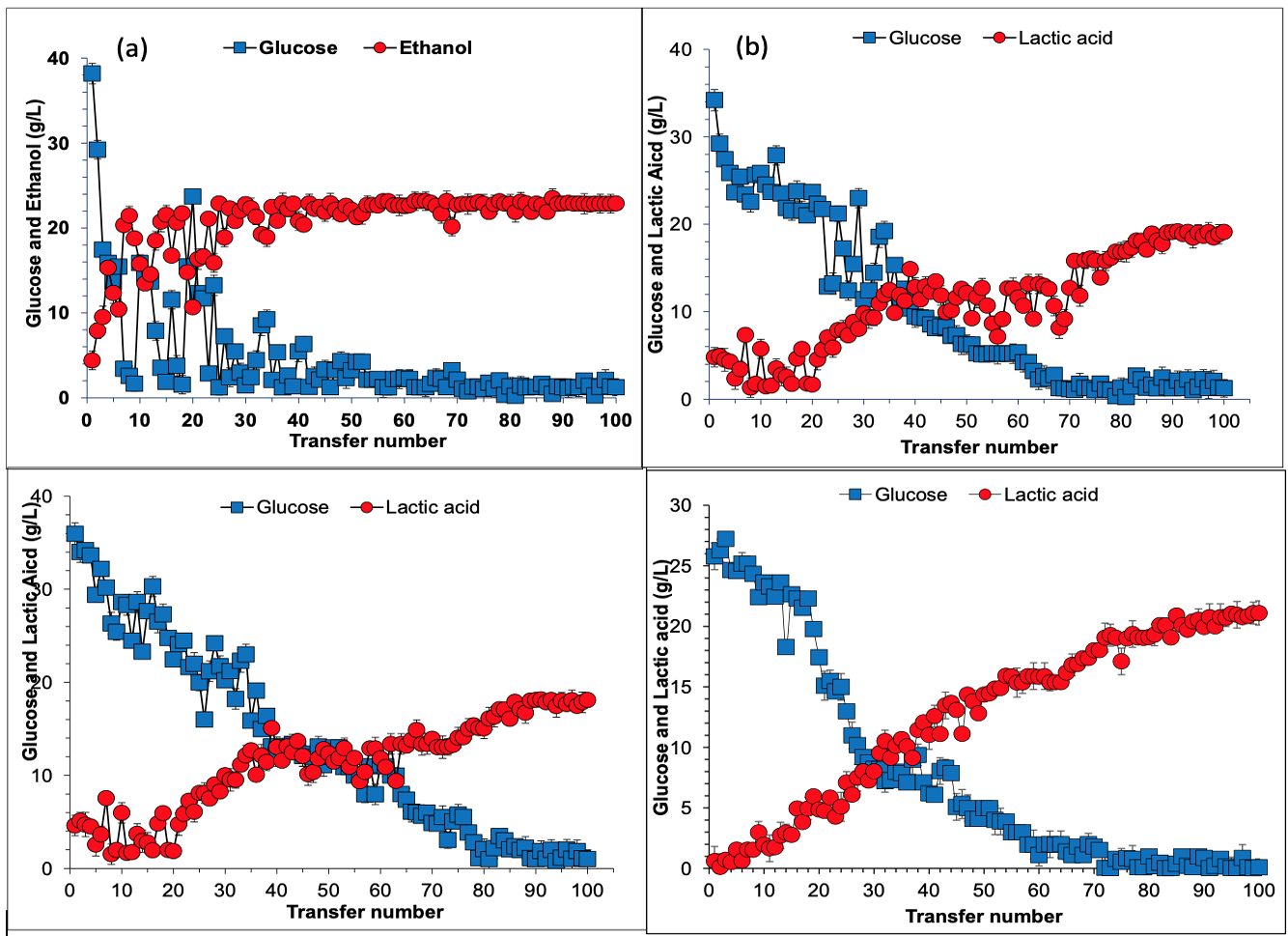
Evolutionary adaptation of ethanol and lactic acid fermenting strains. (a) Long term adaptation of S. cerevisiae Angel using hydrolysate prepared from 15 % w/w freshly pretreated wheat. Conditions: 20 ml wheat straw hydrolysate (100%) supplemented with (g/L) KH2PO4 2, MgSO4 1, NH4 (SO4)2 1, yeast extract 1, 37 °C, pH 5.5 and shaking at 150 rpm. Primarily, S. cerevisiae Angel was inoculated on synthetic medium for activation. In the next step, 10% v/v inoculum was sequentially transferred into fresh 100% wheat straw hydrolysate medium for 100 transfers; each transfer was carried out after 12h of fermentation. (b) Evolutionary adaptation of Pediococcus sp in wheat straw hydrolysate. Conditions: 20 mL of wheat straw hydrolysate (100%) supplemented with tryptone 10.0 g/L, yeast extract 10.0 g/L, MnSO4∙H2O 0.25 g/L, C6H14N2O7 2.0 g/L, MgSO4∙7H2O 0.58 g/L, K2HPO4 2.0 g/L, C6H12O6.∙H2O 22.0 g/L, CH3COONa 5.0 g/L. Strain was activated on MRS medium then 10% v/v of inoculum was transferred to wheat straw hydrolysate for 100 transfers, each transfer was carried out after 12 h of fermentation. (c) Evolutionary adaptation of Lactobacillus sp in wheat straw hydrolysate, where as other conditions were same as mentioned for Pediococcus sp. (d) Evolutionary adaptation of Bacillus coagulans in wheat straw hydrolysate, other conditions were same as mentioned for b.
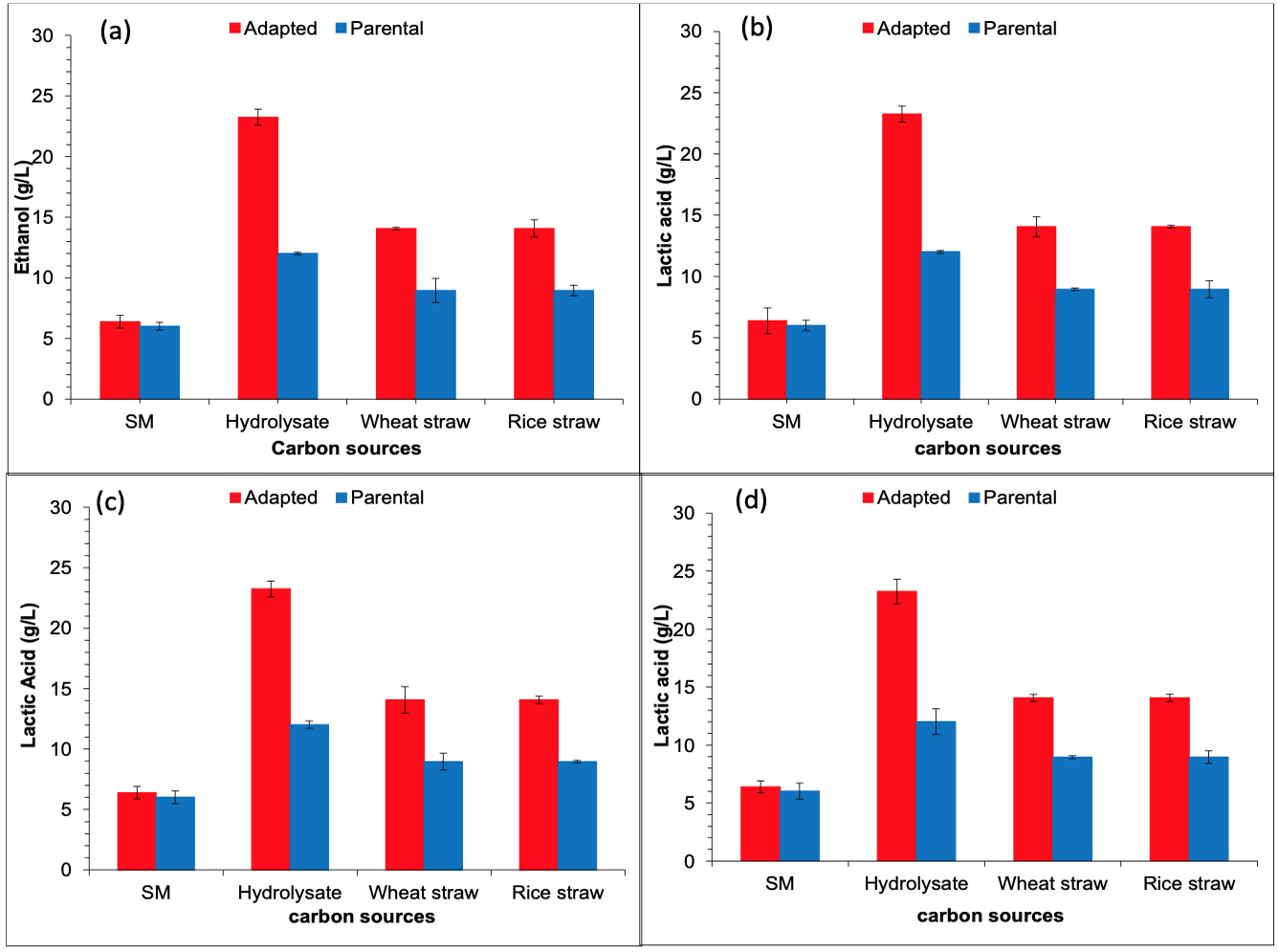
Ethanol and lactic acid fermentation of pure glucose (synthetic medium), wheat straw hydrolysate and freshly pretreated wheat straw and rice straw by parental and adapted strains. (a) S. cerevisiae Angel; conditions: ethanol fermentation was carried out for 12 h in each case at 37 °C in shaking condition, (b) Pediococcus sp., (c) Lactobacillus sp., (d) B. coagulans. Conditions: Lactic acid fermentation was carried out for 12 h in each case at 42 °C in shaking condition.
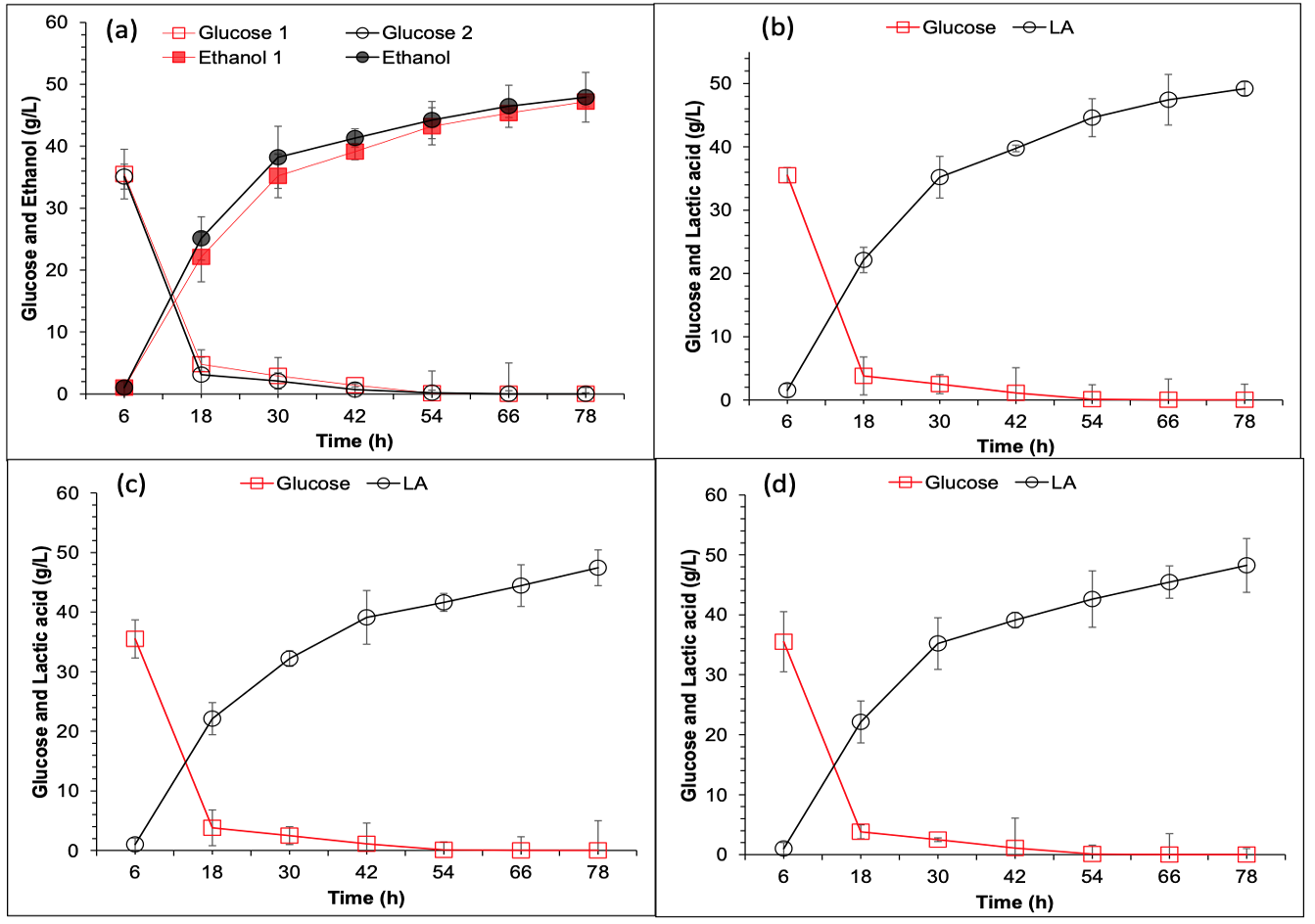
SSF of wheat straw by adapted ethanol and lactic acid fermenting strains. (a) Ethanol fermentation using freshly pretreated rice straw from S. cerevisiae Angel. Conditions: 20 % w/w solids loading, 15 FPU/g DM cellulase dosage (youtell#7 purchased enzyme) and onsite cellulase with same nutrients composition of SM except glucose. Prehydrolysis was performed for 6 h at 50 °C, pH 4.8, and 150 rpm. Solid seeds culture was inoculated in SSF system. Real SSF was performed for 72 h at 37 °C, pH 4.8, 150 rpm, (b) Lactic acid fermentation using freshly pretreated rice straw from Pediococcus sp. Conditions: 20 % w/w solids loading, 15 FPU/g DM cellulase dosage (onsite produced cellulase) with same nutrients composition of MRS except glucose. Prehydrolysis was performed for 6 h at 50°C, pH 4.8, and 150 rpm. Real SSF was performed for 72 h at 42 °C, pH 5.5, 150 rpm, (c). Lactic acid fermentation from Lactobacillus sp. other conditions were as mentioned for b., (d). Lactic acid fermentation using adapted B. coagulans other conditions were same as mentioned for b.