Unveiling the Mysteries of Oxidative Stress: An Insightful Review of Recent Studies
Unveiling the Mysteries of Oxidative Stress: An Insightful Review of Recent Studies
Baraa Najim Al-Okaily
Process of Fenton reaction (Babuponnusami and Muthukumar, 2014).
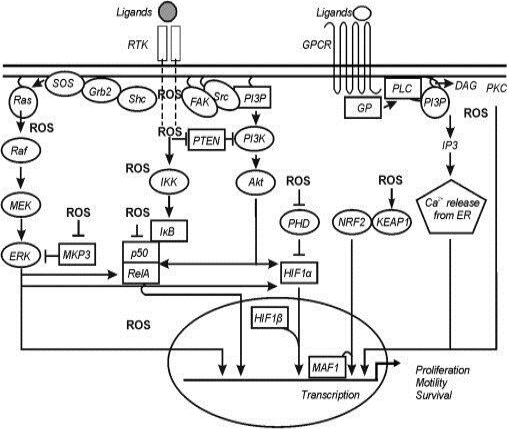
ROS-regulated signaling pathways. Simplified diagram representing major ROS regulated signaling pathways. ROS can influence the pathways either positively or negatively. ROS necessary for regulation of signaling pathways are mostly generated through specific enzymatic reactions as well as due to the changes in cellular metabolic activity leading to altered ROS production. DAG, diacylglycerol; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GP, G-protein; GPCR, G-protein coupled receptor; Grb2, growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; IKK, IκB kinase; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; MKP3, mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinasephosphatase/dual specificity protein phosphatase-6; PHD, prolyl hydroxylase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate; PKB/Akt, proteinkinase B; PKC, protein kinase C; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10; Raf, ras attachement factor; Ras, Rat sarcoma; RTK, receptor tyrosinekinase; SOS, son of sevenless; Shc, SHC-transforming protein; Src, sarcoma.ETC, electron transport chain; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NOX, NADPH oxidase subunit; PKC, protein kinase C; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; SOD,superoxide dismutase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid (Corlach et al., 2015).
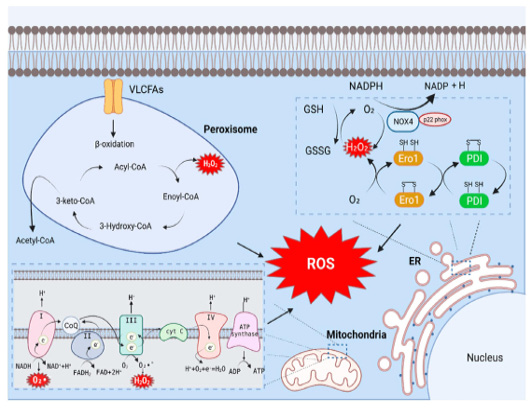
Major source of ROS production in Hepatic cell. The catalytic process of oxidoreductase Ero1 and NADPH oxidase (NOX) in the endoplasmic reticulum generates ROS. During cellular respiration, mitochondria transfer electrons to oxygen and generate ROS as a byproduct of oxidative oxidation. Mitochondrial ROS are mostly produced during oxidative phosphorylation of electron transport chains (ETCs) present in the inner mitochondrial membrane. The main cause of ROS generation in peroxisomes is peroxisomal β-oxidation. Acyl-CoA is converted to Enoyl-CoA by acyl-CoA oxidase containing FAD, which provides electrons directly to oxygen to produce H₂O₂ (Ma et al., 2022).
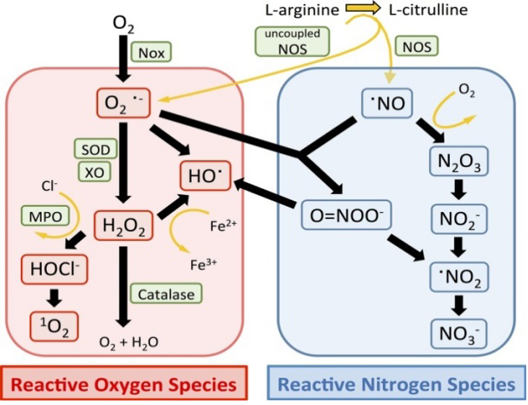
Illustrate the relationship between ROS and RNS in kidney cells (Ishimoto et al., 2018).