Ultrastructure of Antennal Sensilla of Scopula subpunctaria (Herrich-Schaeffer) (Lepidoptera: Geometridae)
Ultrastructure of Antennal Sensilla of Scopula subpunctaria (Herrich-Schaeffer) (Lepidoptera: Geometridae)
Fangmei Zhang1,2, Xiaocen Zhao1,2, Li Qiao1,2, Shibao Guo1,2, Li Zhang1,2,
Jian Yin1,2, Zhou Zhou1,2, Chuleui Jung3 and Shubao Geng1,2*
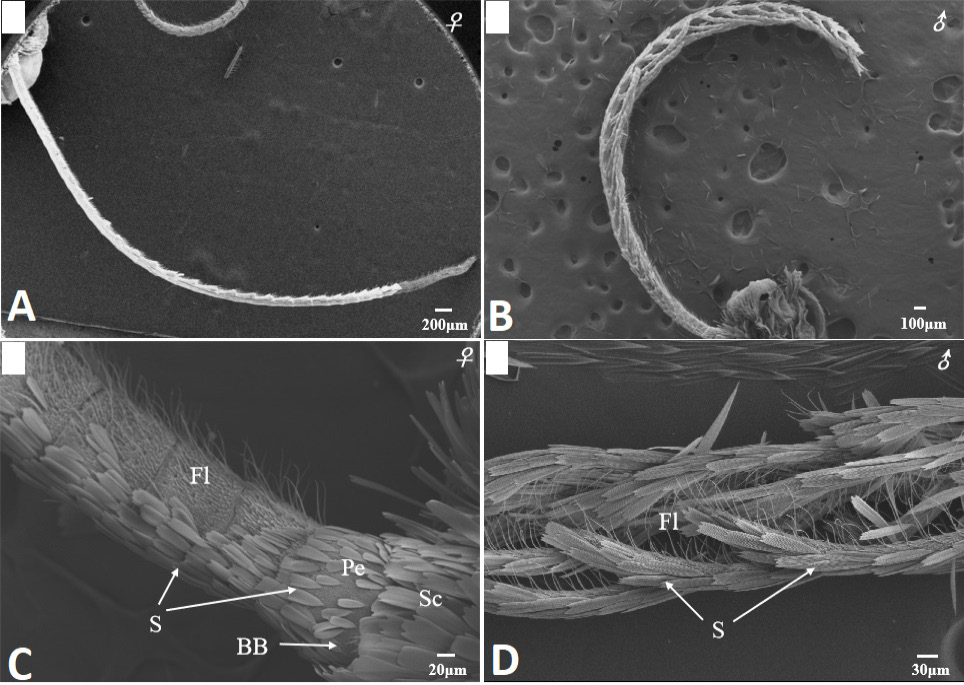
Scanning electron micrographs of the antennae in Scopula subpunctaria. (A) female filiform antenna; (B) male bipectinate antenna; (C) segments of flagellum (Fl), scape (Sc), pedicel (Pe) and Böhm bristles (BB) of female antenna; (D) segments of flagellum of male antenna.
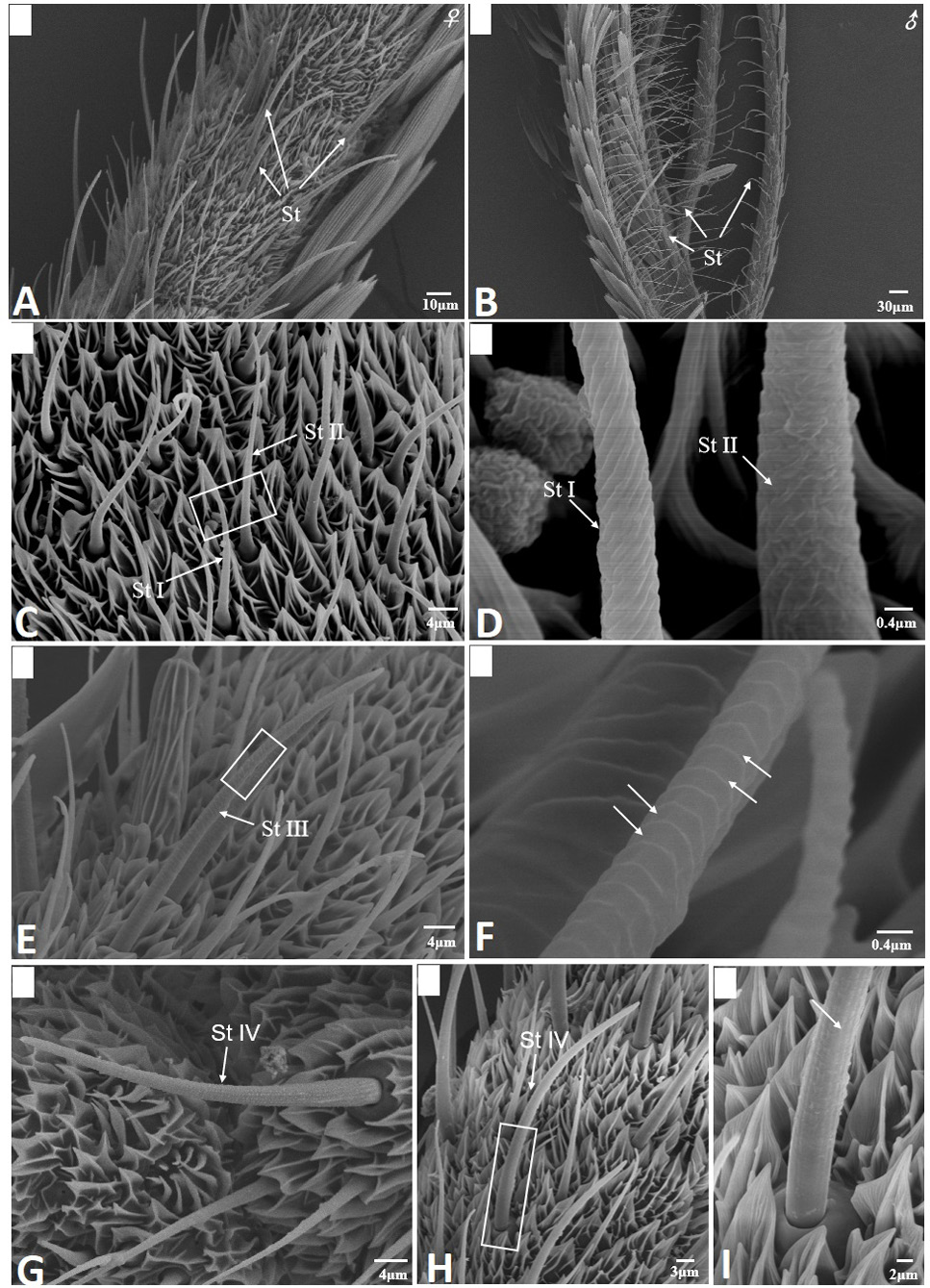
Scanning electron micrographs of sensilla trichodea in Scopula subpunctaria. (A) sensilla trichodea (St) on female antennae; (B) sensilla trichodea on male antennae; (C) St I and St II; (D) partial enlargement of St I and St II, showing helical deep grooves and wrinkle surface, respectively; (E) St III; (F) partial enlargement of St III, showing parallel horizontal deep grooves (arrows); (G-H) St IV; (I) partial enlargement on boxes of figure 2H, showing longitudinal grooves (arrows).
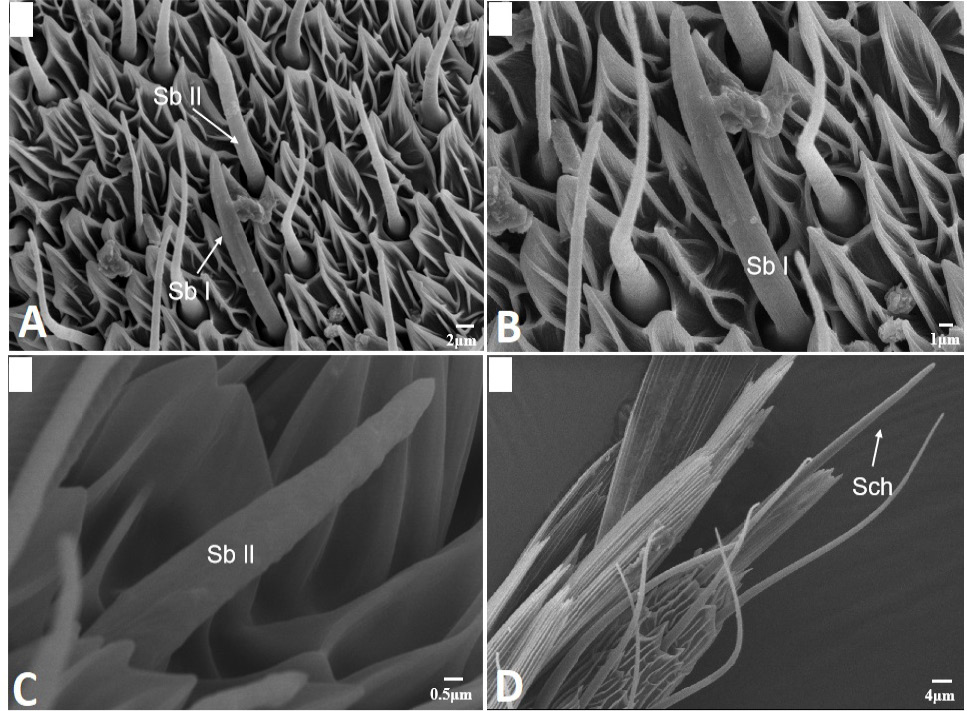
Scanning electron micrographs of sensilla basiconica and sensilla chaetica in Scopula subpunctaria. (A) sensilla basiconica I (Sb I) and sensilla basiconica II (Sb II); (B) sensilla basiconica I (Sb I); (C) sensilla basiconica II (Sb II); (D) sensilla chaetica (Sch).
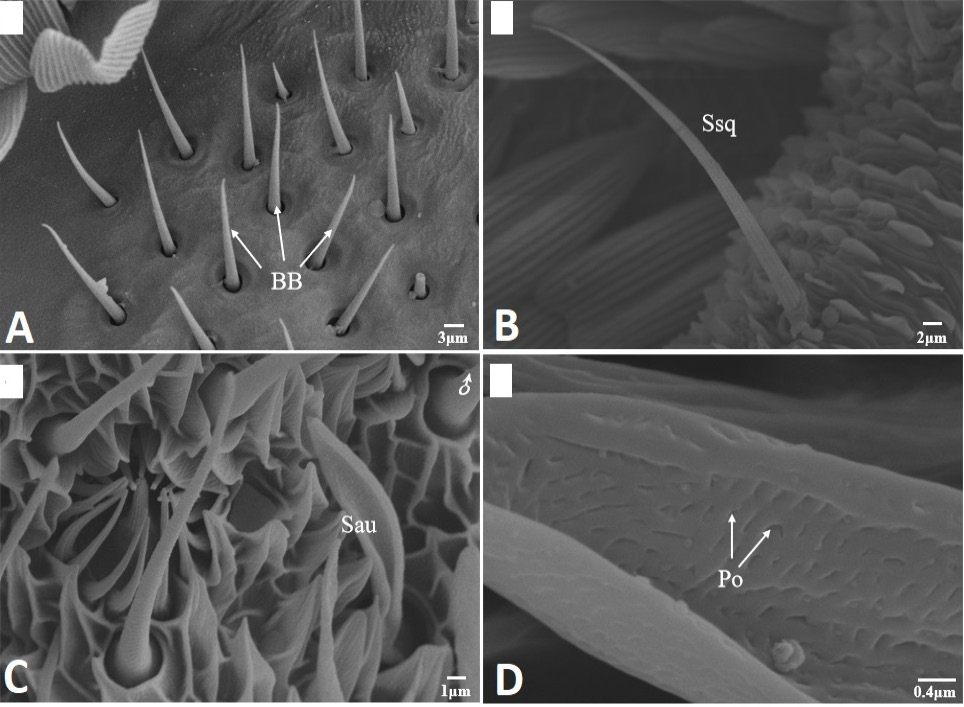
Scanning electron micrographs of Böhm bristles, sensilla squamiformia and sensilla auricillica in Scopula subpunctaria. (A) Böhm bristles (BB); (B) sensilla squamiformia (Ssq); (C) sensilla auricillica (Sau); (D) close-up of sensilla auricillica, showing Pore (Po).
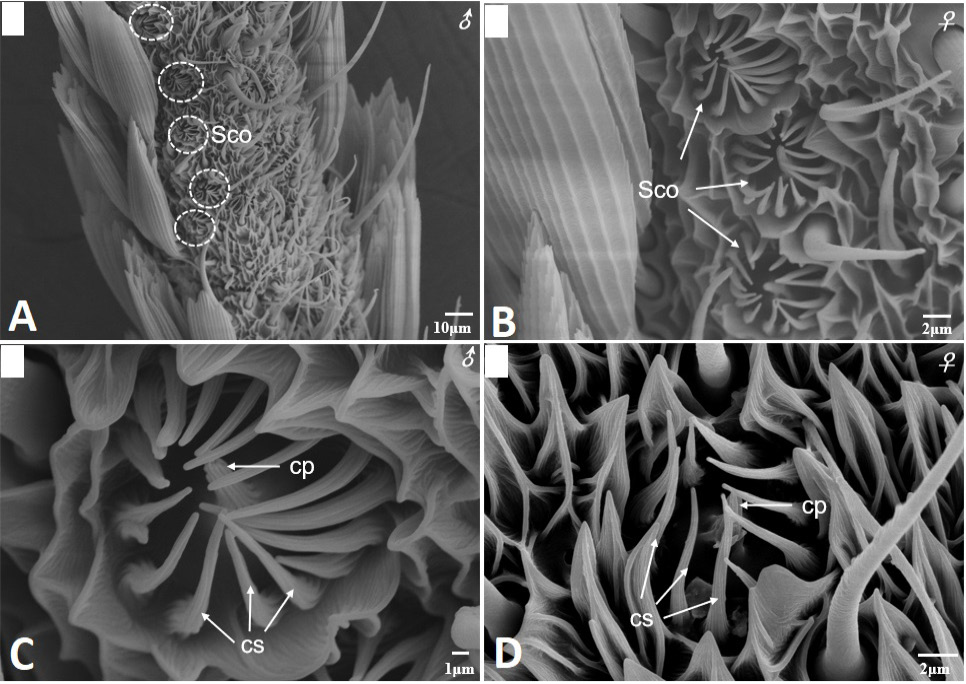
Scanning electron micrographs of sensilla coeloconica in Scopula subpunctaria. (A) sensilla coeloconica on male antennae flagellum; (B) sensilla coeloconica on female antennae flagellum; (C) higher magnification of sensilla coeloconica showing central peg (cp) surrounded by 16 cuticular spines (cs, three white arrows) on male antennae flagellum; (D) higher magnification of sensilla coeloconica showing central peg (cp) surrounded by 10 cuticular spines (cs, three white arrows) on female antennae flagellum.
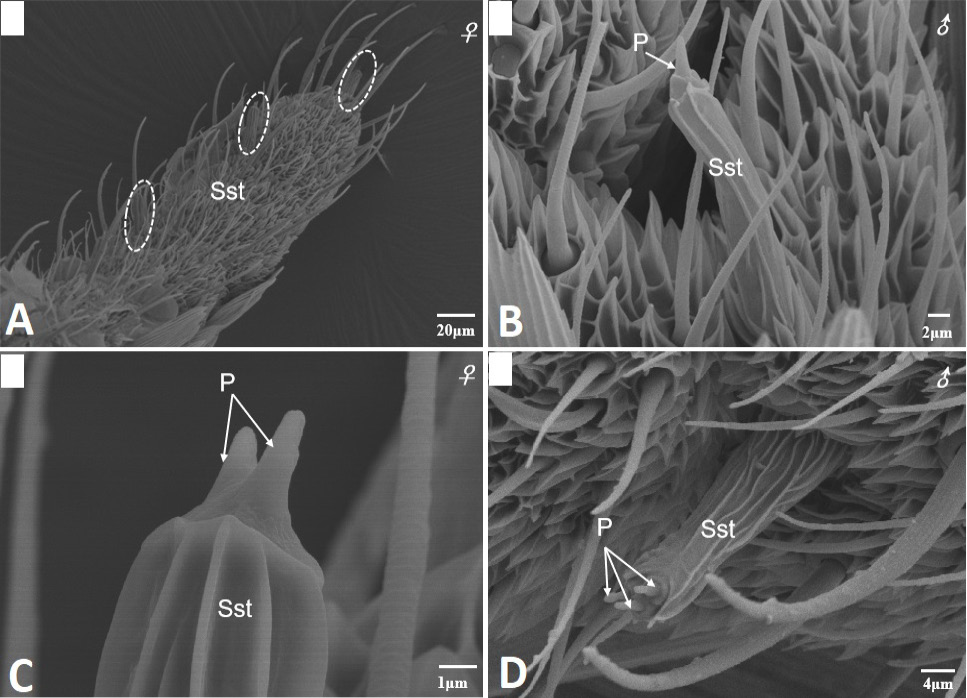
Scanning electron micrographs of sensilla styloconica on the female and male antennae of Scopula subpunctaria. (A) sensilla styloconica located on the ventral surface of the terminal segment of flagellum (in white circle); (B) sensilla styloconica found on male antennae showing single cone-shaped structure at the apex (white arrows); (C) sensilla styloconica found on female antennae showing two cone-shaped structure at the apex (white arrows); (D) sensilla styloconica found on male antennae showing three cone-shaped structure at the apex (white arrows).