The Impact of Physical Load and Adaptogens on the Animal Work Capacity
The Impact of Physical Load and Adaptogens on the Animal Work Capacity
Ilvir Khabibullin1*, Ruzel Khabibullin1, Irina Mironova1, Lyalya Musina2, Elmira Akhmadullina1, Victoria Morozova1
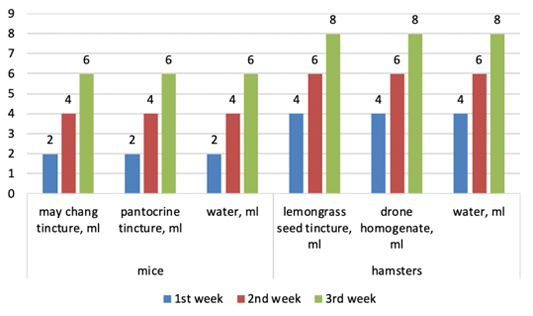
The experiment scheme.
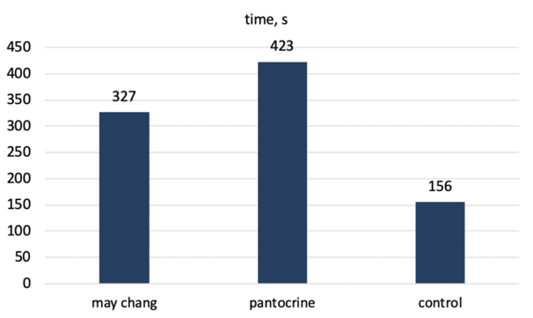
Swimming activity of experimental mice after the experiment.
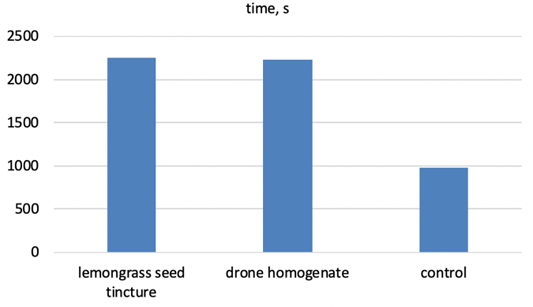
Swimming activity of hamsters.
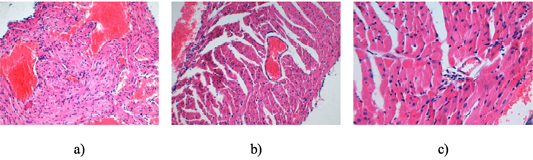
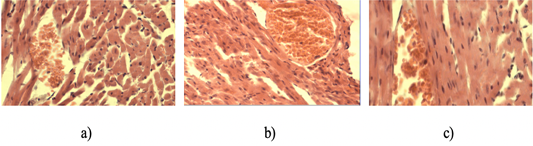
a) Cardiac myocytes of the control group animal H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 10Xobj.lens; b) Cardiac myocytes of the animal from the experimental group 1. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 4Xobj.lens; c) Heart muscle tissue of animals given pantocrine. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 20Xobj.lens.
a) Venous myocardial hyperemia of an experimental animal using lemongrass. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; b) Venous myocardial hyperemia when using drone brood. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; c) Marked venous hyperemia of the myocardium of the control group of animals. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens.
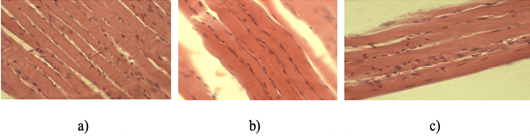
a) Somatic musculature of control group animals. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; b) Skeletal muscle tissue of an animal after high physical exertion and the use of lemongrass as an adaptogen. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; c) Hypertrophied skeletal muscle tissue of a hamster after physical exertion and combined use of a drone brood preparation. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens.
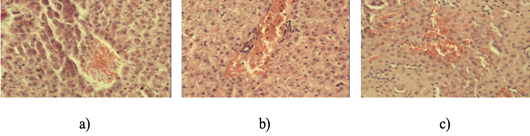
a) Venous hyperemia of the kidney cortex in the control group animals. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; b) The hyperemia zone of the kidney cortex blood vessel in animals after physical exertion and the lemongrass use. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; c) Moderate stagnation in the kidney cortex blood vessels in animals using the drone brood after physical exertion. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens.
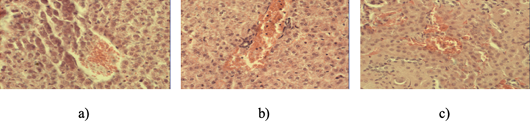
a) Fullness of the venous vessel of the liver in an animal of the control group after physical exertion. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; b) Venous hyperemia of the liver triad of animals when using lemongrass after physical exertion. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; c) Full blood vessels of the liver of animals when using the drone brood after physical exertion. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens.
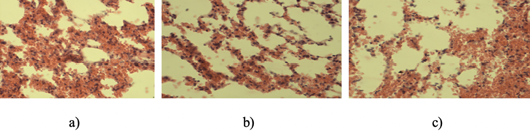
a) Marked lung alveolitis in an animal from the control group. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; b) Lung alveoli in hamsters after physical exertion and the use of lemongrass. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens; c) Focal alveolitis in the lung of animals after ultra-high physical exertion and the use of an adsorbed drone brood preparation. H and E staining. 10Xoc.lens, 40Xobj.lens.