Study of Maize Residue Decomposition in a Silty Loam Soil of Pakistan: A Comparison of Mulched Versus Incorporated Residue Management Practice
Study of Maize Residue Decomposition in a Silty Loam Soil of Pakistan: A Comparison of Mulched Versus Incorporated Residue Management Practice
Saman Rizwan and Sohaib Aslam*
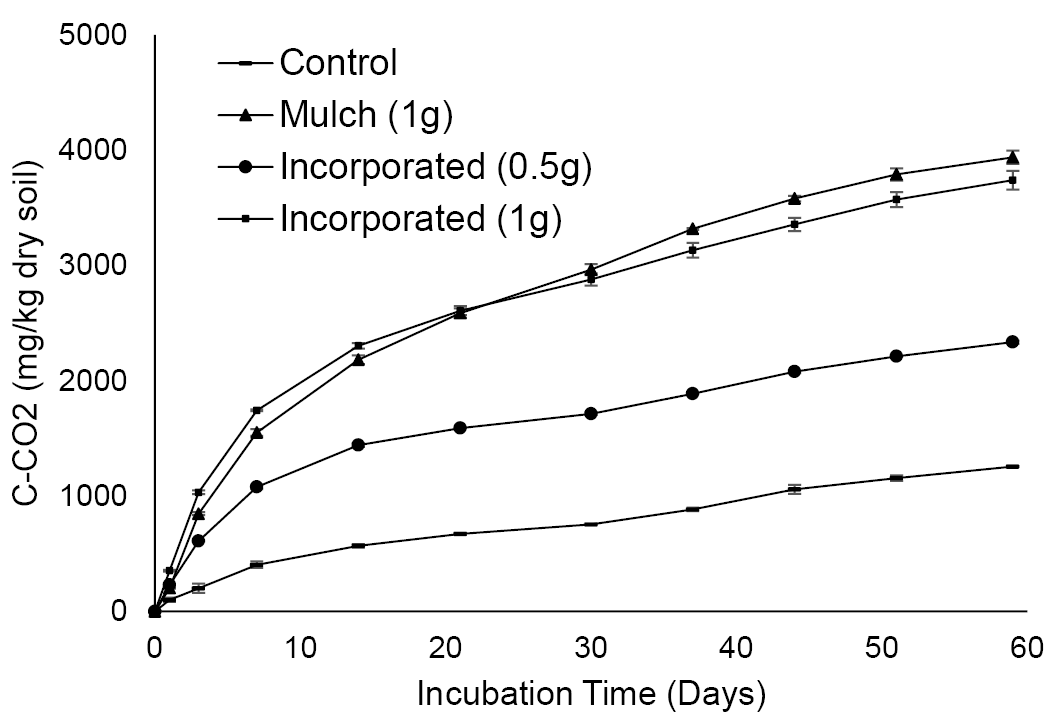
Soil respiration (Cumulative) in soil without crop residues (control) and soil amended with maize crop residues during incubation experiment. Data are shown as averages of two replicates ±standard deviations.
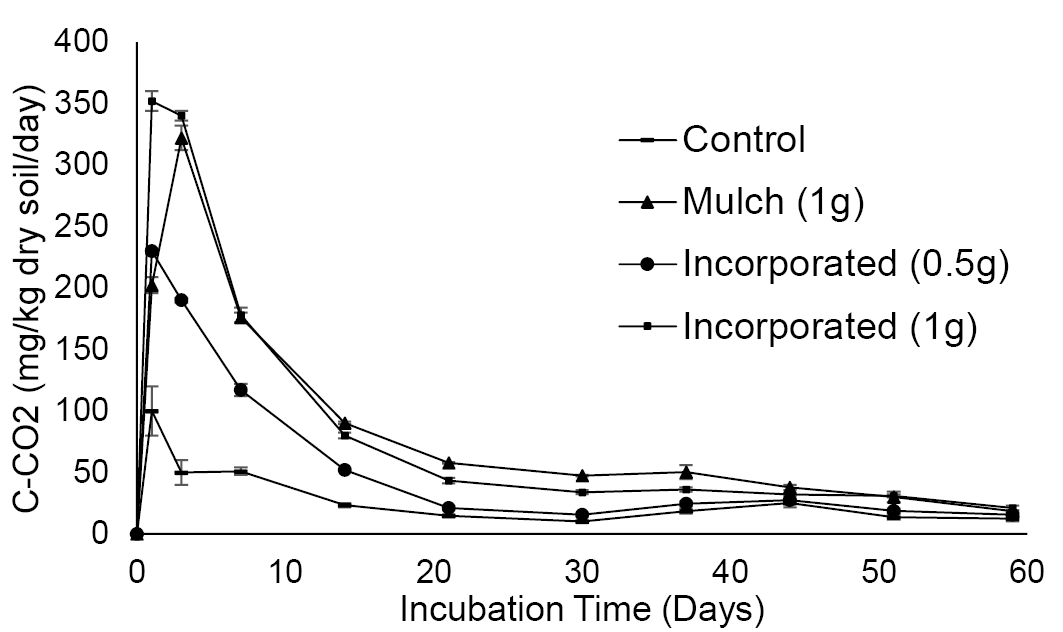
Soil respiration rates of soil without crop residues (control) and soil amended with maize crop residues during incubation experiment. Data are shown as averages of two replicates ±standard deviations.
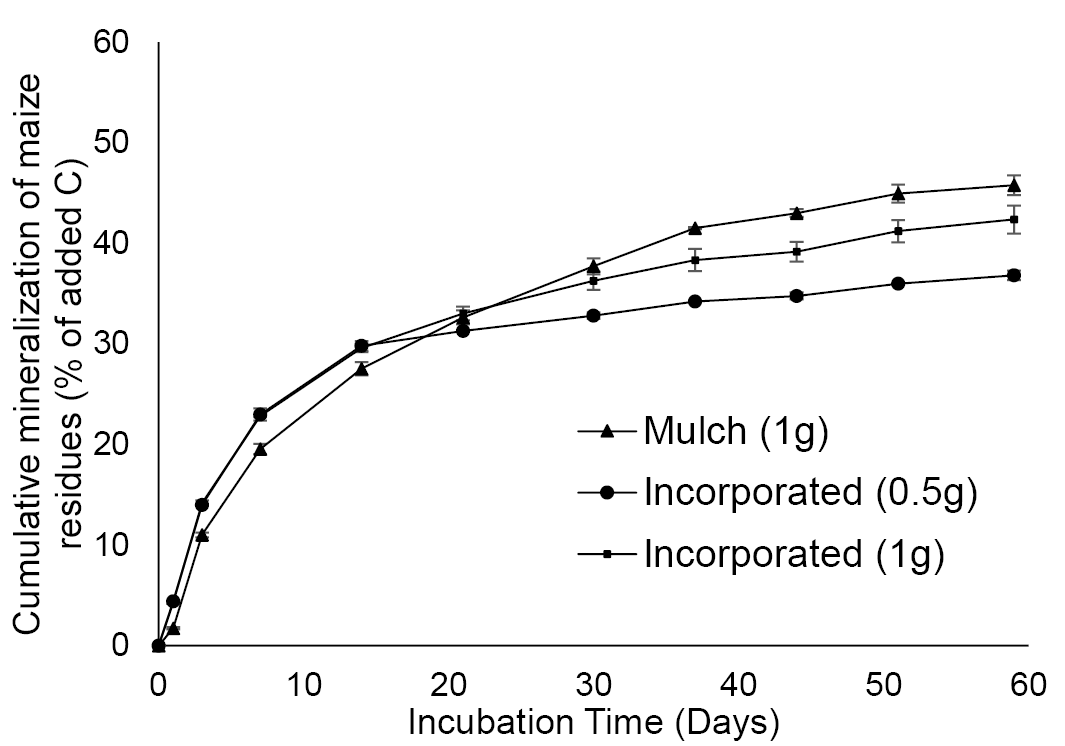
Cumulative mineralization of organic carbon derived from maize crop residues in soil (% of added carbon). Data are shown as averages of two replicates ±standard deviations.