Soluble Expression of IFNα2-Tα1 Fusion Protein in Escherichia coli by N-terminal SUMO Fusion and its Anti-Proliferative Activity
Soluble Expression of IFNα2-Tα1 Fusion Protein in Escherichia coli by N-terminal SUMO Fusion and its Anti-Proliferative Activity
Muhammad Shahbaz Aslam1, Iram Gull1, Zaigham Abbas2,* and Muhammad Amin Athar1
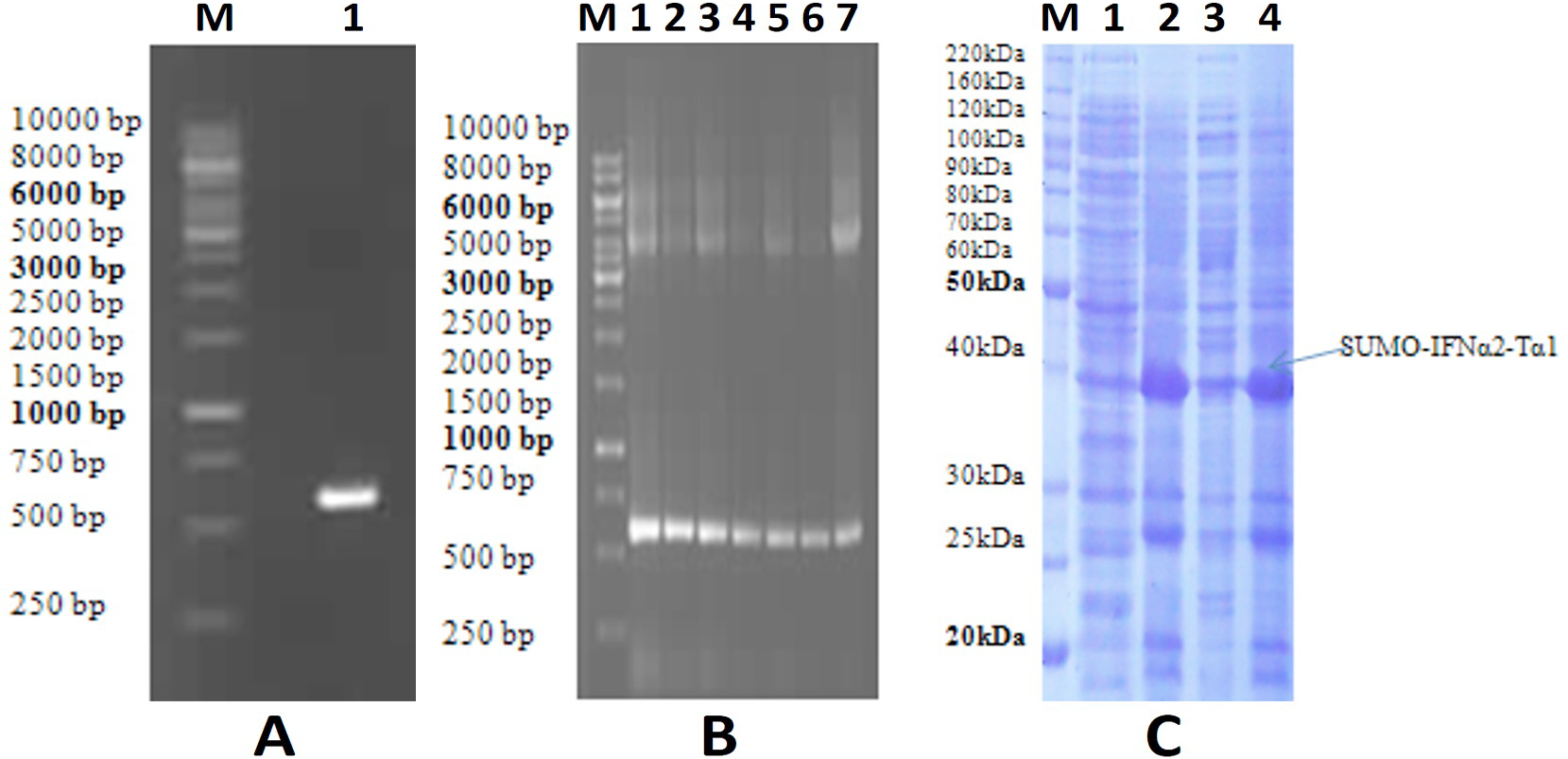
A, Analysis of IFNα2-Tα1gene by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (Lane M, DNA ladder; Lane 1, IFNα2-Tα1gene (591 bp)). B, Analysis of recombinant E. coli BL21 (DE3) clones by colony PCR(Lane M, DNA ladder; Lane 1-7, recombinant clones). C, Analysis of SUMO- IFNα2-Tα1 fusion protein by 12 % SDS-PAGE (Lane M, protein ladder; Lane 1, un-induced cell fraction; Lane 2, total cell lysate; Lane 3, insoluble cell pellet; Lane 4, soluble cell fraction).
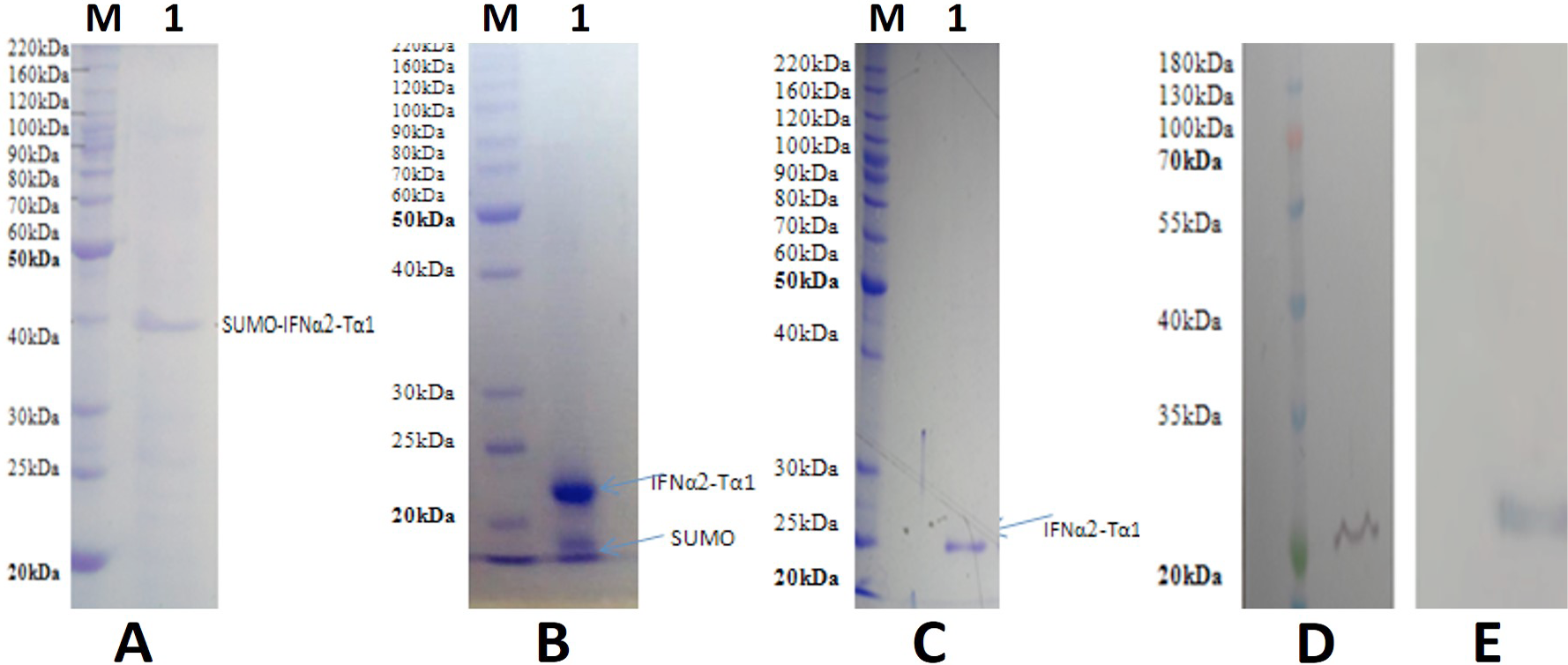
Purification and immuno blot analysis. A, Purification of recombinant SUMO-IFNα2-Tα1 fusion protein by Ni+ affinity chromatography (Lane M, Protein marker; Lane 1, Purified SUMO-IFNα2-Tα1). B, Analysis of SUMO-IFNα2-Tα1 cleavage reaction with SUMO protease by 12 % SDS-PAGE (Lane M, Protein marker; Lane 1, FNα2-Tα1 and SUMO bands after digestion). C, Purification of FNα2-Tα1 by Ni+ affinity chromatography from cleavage reaction (Lane M, Protein marker; Lane 1, purified FNα2-Tα1). D, Immuno blot analysis with anti-interferon α2 antibody. E, Immuno blot analysis with anti-thymosin α-1 antibody.
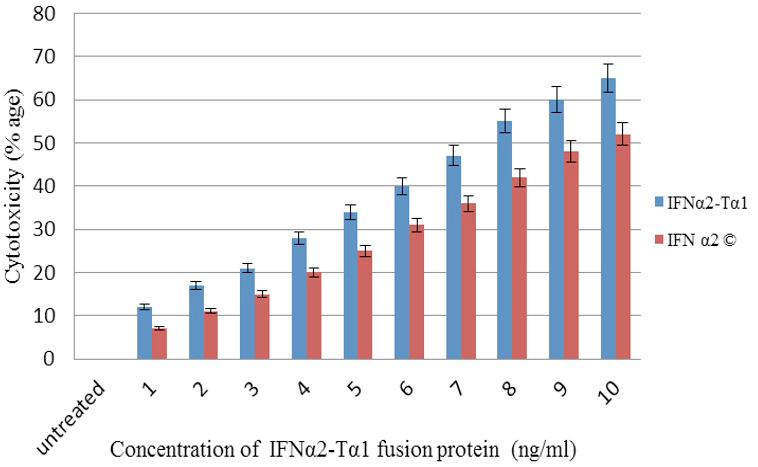
Anti-proliferative activity of IFNα2-Tα1 fusion protein in comparison with commercial IFNα2 on HepG2 cell line using MTT assay.