Prokaryotic Expression, Purification, and Functional Characterization of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Mannose Receptors Subunits (MRC1 and MRC2)
Prokaryotic Expression, Purification, and Functional Characterization of the Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Mannose Receptors Subunits (MRC1 and MRC2)
Xiangli Dong1,2, Shilin Mikhail Borisovich2, Jiji Li1,*, Jianyu He1, Zeqin Fu1, Yingying Ye1, Julia N. Lukina3, Olga V. Apalikova4 and Jianshe Zhang1
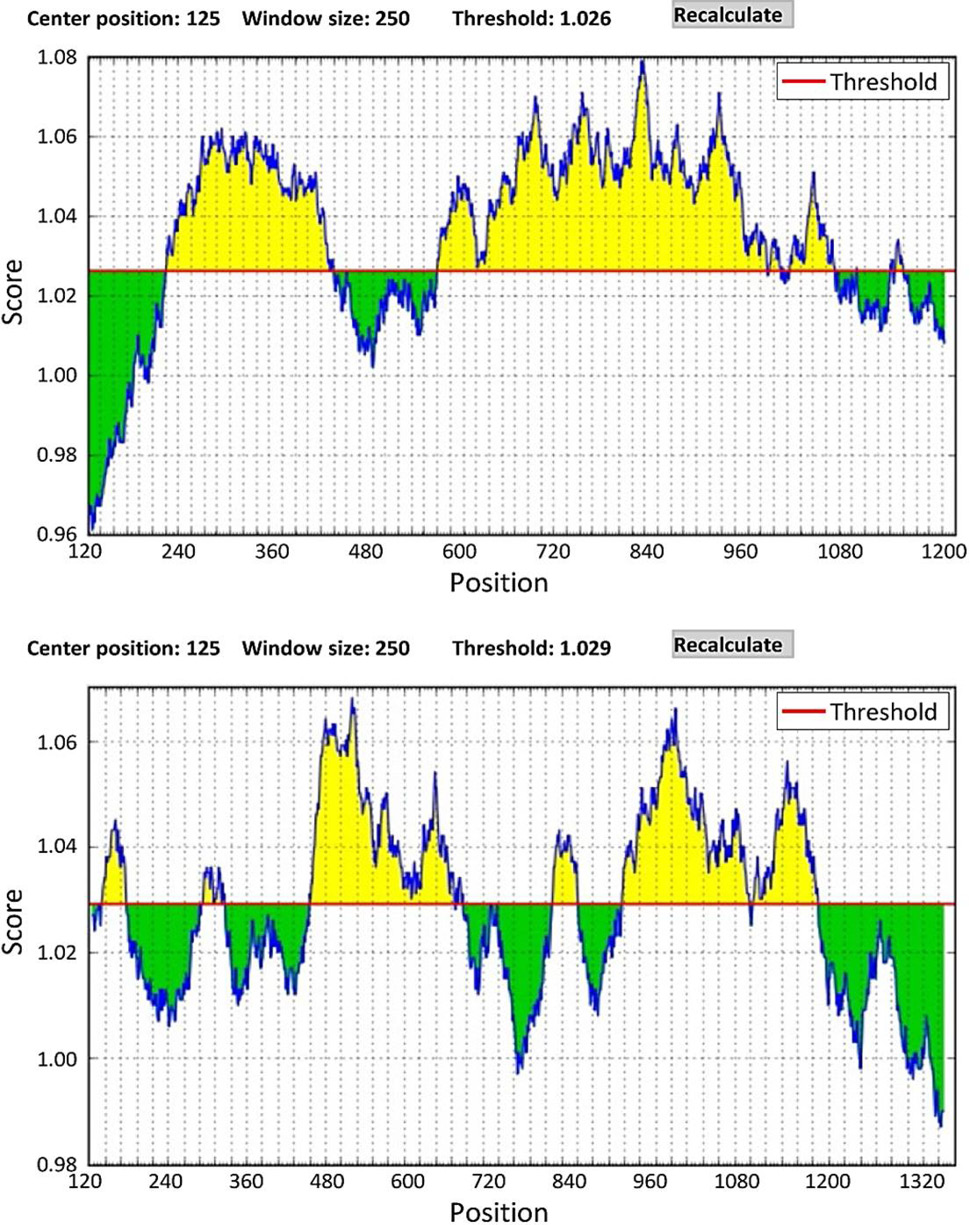
L.c-MRC1and L.c-MRC2 membrane protein analysis.
Epitope analysis of L.c-MRC1and L.c-MRC2.
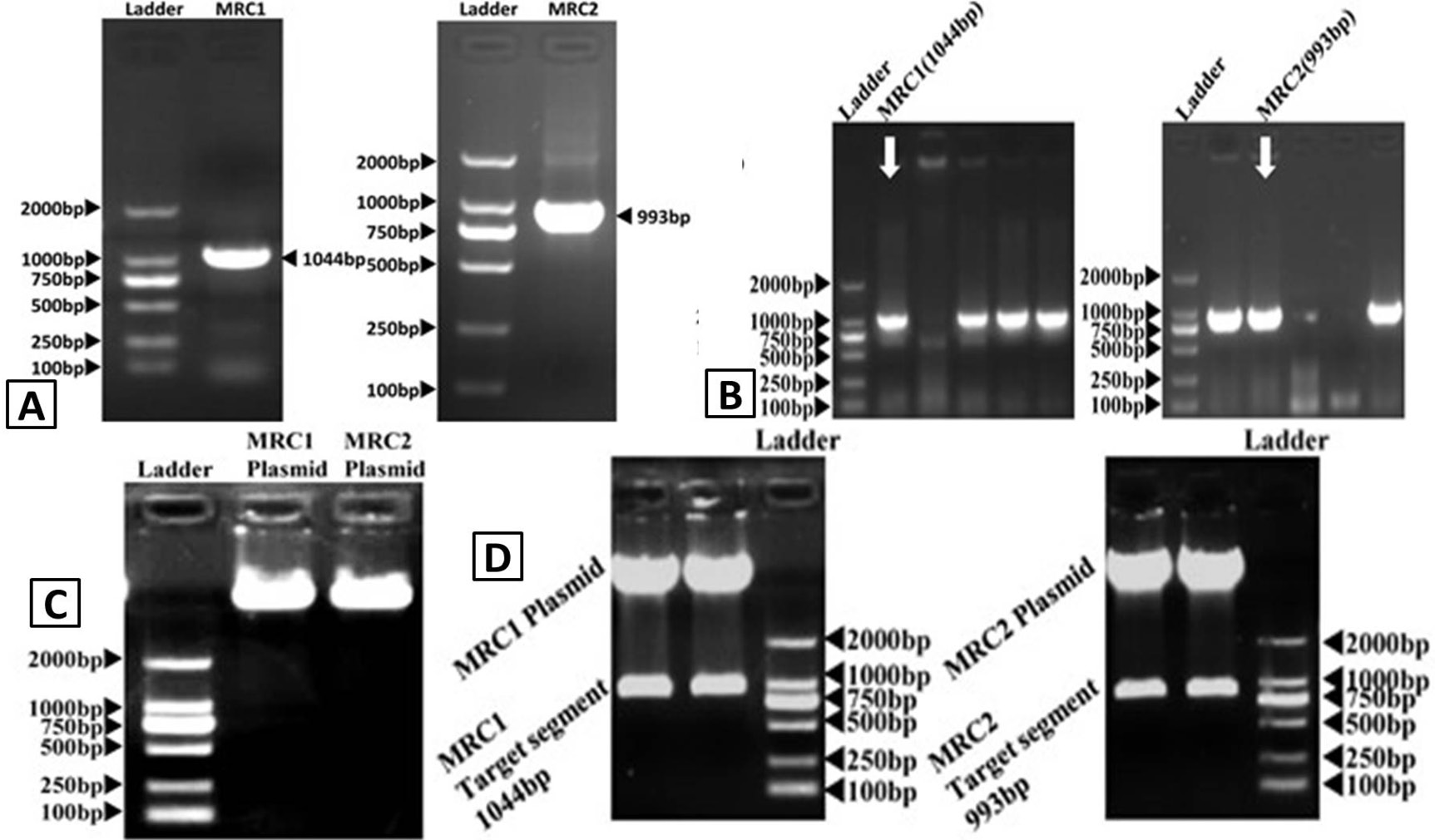
DNA electrophoresis figures. A, PCR identification of L.c-MRC1and L.c-MRC2; B, colony PCR analysis of MRC1 and MRC2 pET32A vector clones; C, MRC1-pET32A and MRC2-pET32A plasmid electrophoresis; D, MRC1-pET32A and MRC2-pET32A vector restriction digests.
Protein electrophoresis figures. A, SDS-PAGE analysis of L.c-MRC1 and L.c-MRC2 proteins; B, SDS-PAGE analysis of precipitated L.c-MRC1 and L.c-MRC2 proteins (the black arrows indicate the target protein bands. The target protein is detected in the precipitate); C, Purified L.c-MRC1 and L.c-MRC2 proteins. The black arrows indicate the target protein bands.
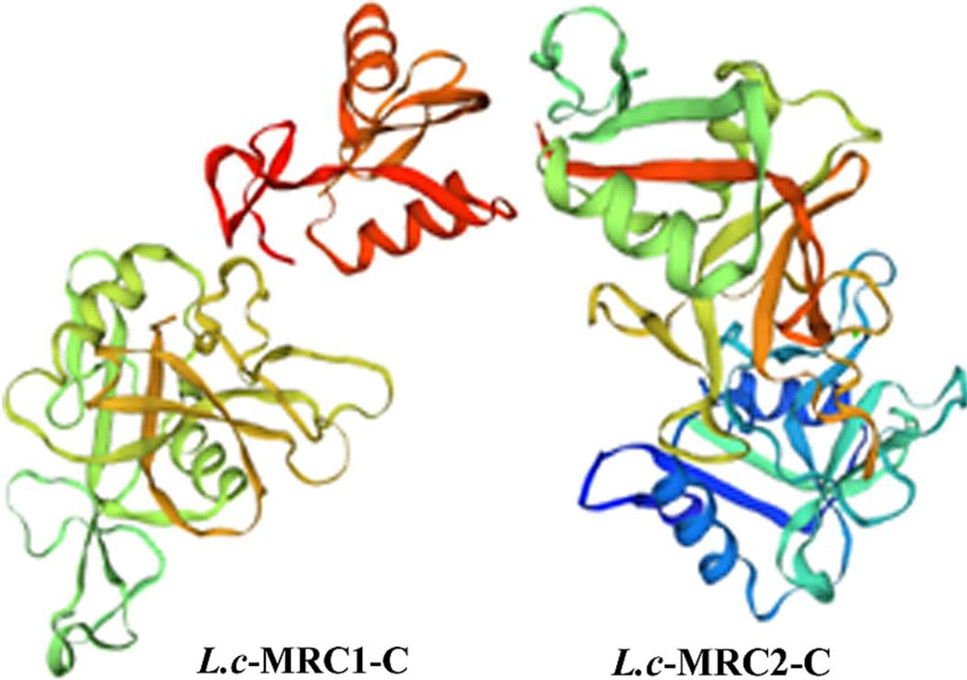
3D protein structures of L.c-MRC1-C and L.c-MRC2-C. These protein structures were predicted using SWISSMODEL. The N-terminus is blue and the C-terminus is red (for interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article).