Population Genetic Structure and Genetic Diversity of Coral Reef Species Lethrinus olivaceus in the South China Sea
Population Genetic Structure and Genetic Diversity of Coral Reef Species Lethrinus olivaceus in the South China Sea
Zhaochao Deng1, Na Song2, Yongzhen Li3, Tianxiang Gao1 and Zhiqiang Han1,*
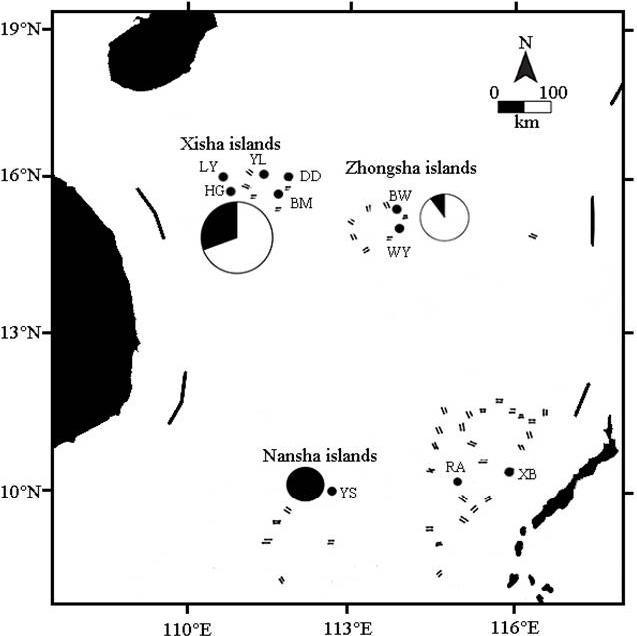
Sampling sites and haplotype frequencies in three groups. The area of the circle is proportional to sample size. White of the circle represents lineage A and black represents the lineage B.
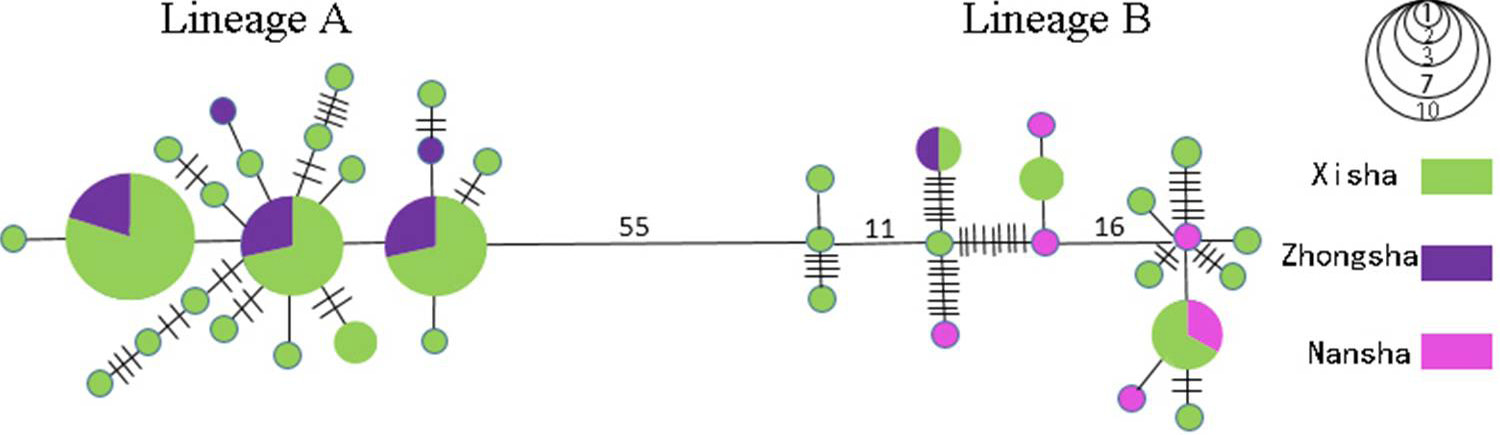
Unrooted minimum spanning trees showing genetic relationship among control region haplotypes for L. olivaceus. The sizes of circles are proportional to haplotype frequencies. Perpendicular tick marks and numbers on the lines joining haplotypes represent the number of nucleotide substitutions.
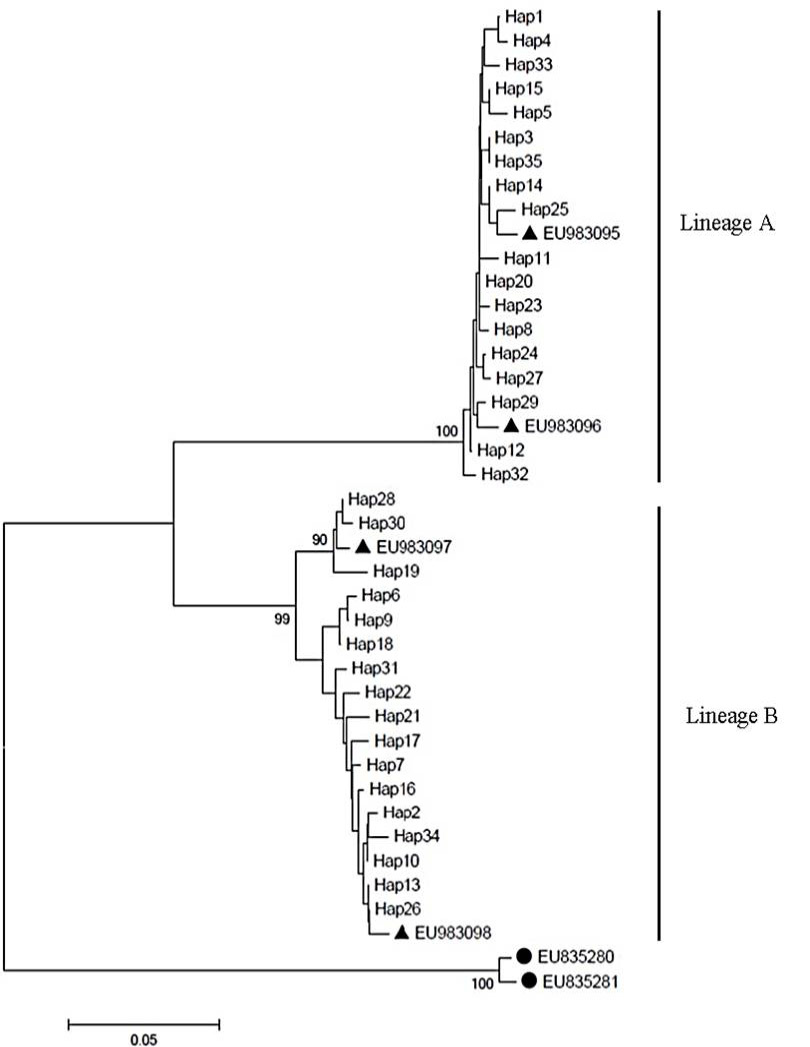
Neighbor-joining tree constructed using Tamura-Nei model for control region haplotypes of L. olivaceus. The congener L. miniatus was chosen as out-group. Bootstrap supports of > 90% in 1000 replicates are shown.
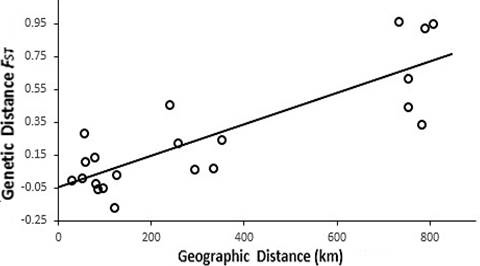
Plot of pairwise estimates of FST and geographic distance between islands of L. olivaceus.
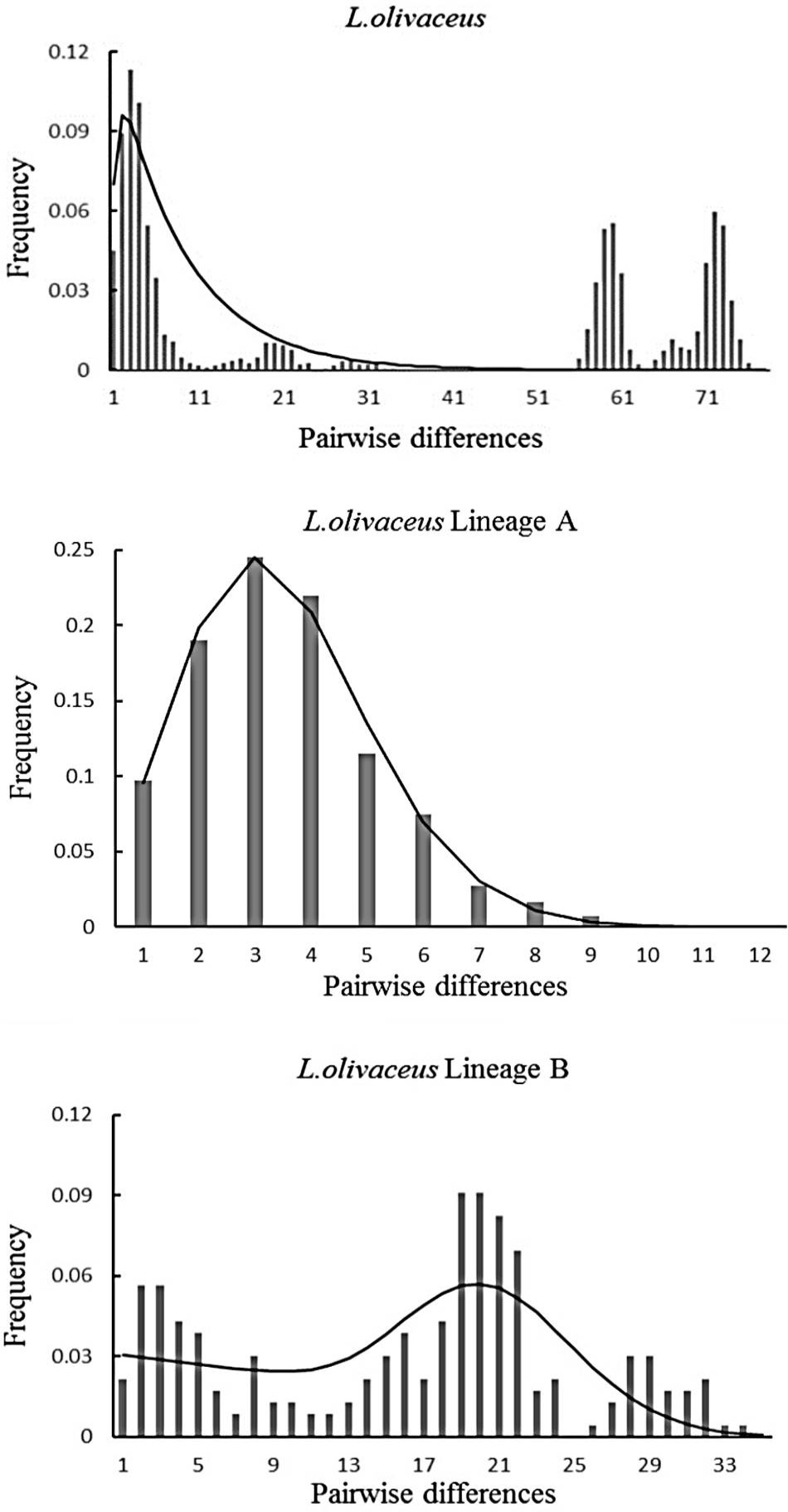
The observed pairwise difference (bars), and the expected mismatch distributions under the sudden expansion model (solid line) of control region haplotypes in L. olivaceus.