Physiological and Bio-Chemical Responses of Two Different Wheat Genotypes to Applied Salicylic Acid under Salt Stress
Physiological and Bio-Chemical Responses of Two Different Wheat Genotypes to Applied Salicylic Acid under Salt Stress
Muhammad Suhaib1*, Ijaz Ahmad2, Masooma Munir3, Badar-Uz-Zaman1, Bushra Atta4 and Muhammad Khubaib Abuzar5
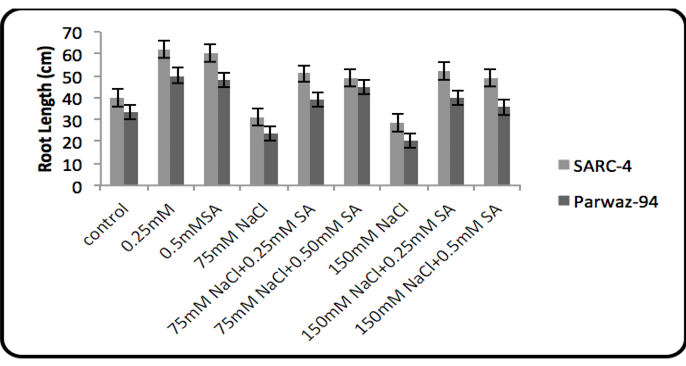
Root length.
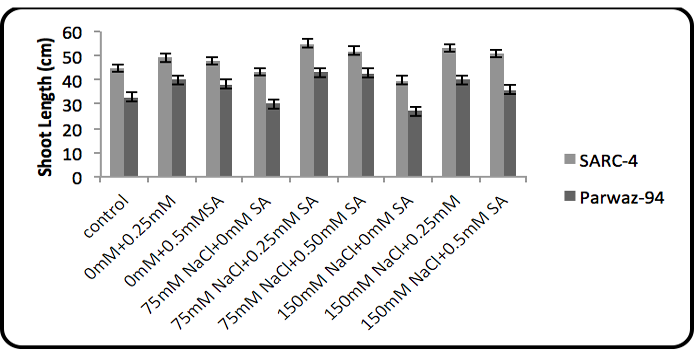
Salicylic acid and salinity effect on shoot length.
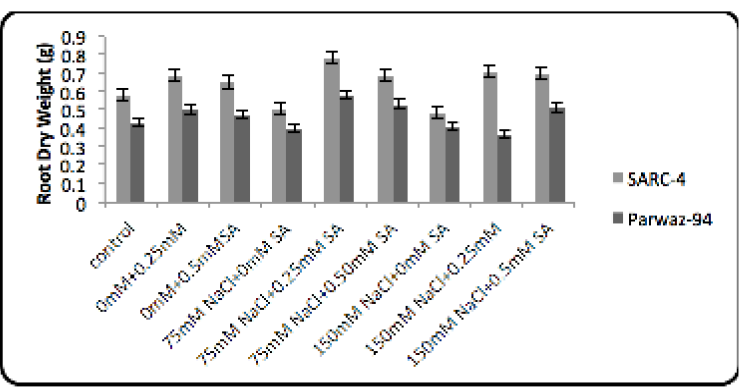
The salicylic acid effect on root dry weight.
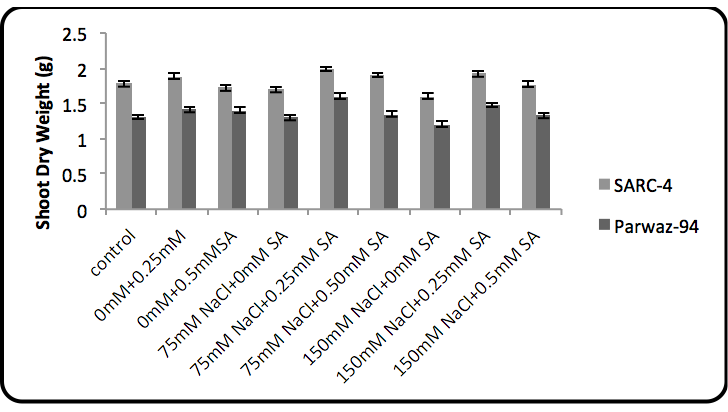
The salicylic acid effect on shoot dry weight.
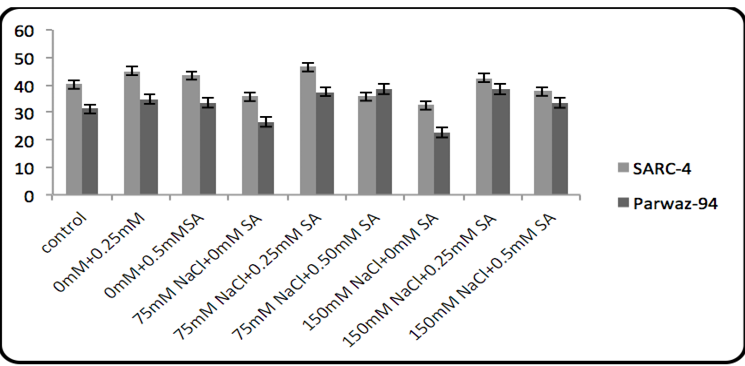
Effect of salicylic acid and salinity on chlorophyll contents.
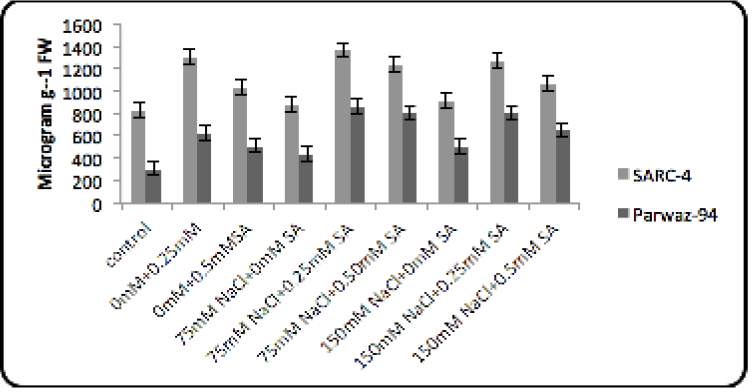
Total soluble proteins.
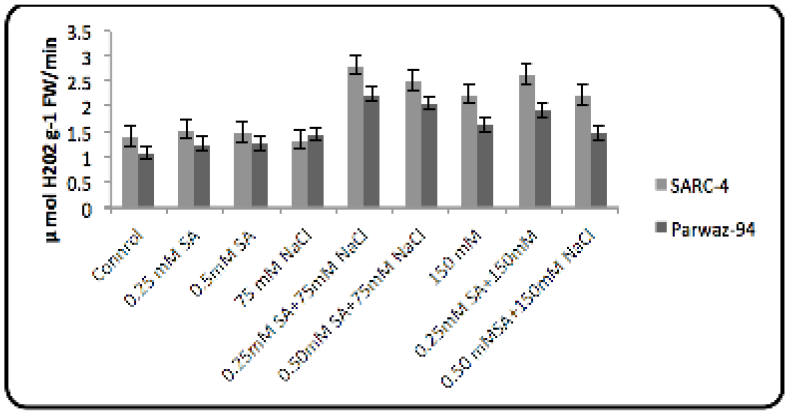
Catalase (CAT) activity.
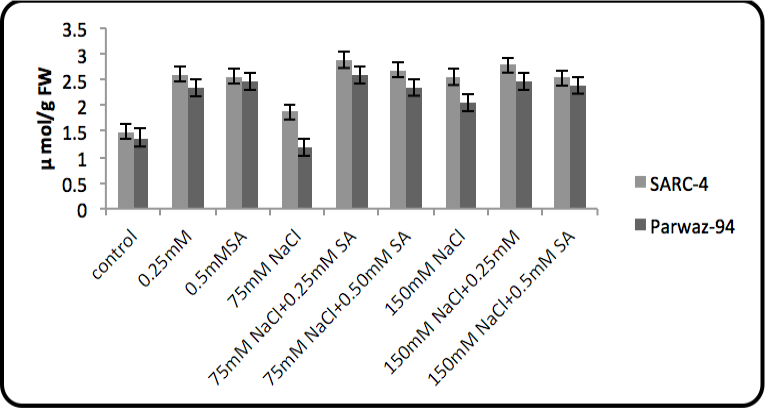
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) activity.