Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Erysiphe necator var. necator, A Fungal Pathogen of Grapevines in Pakistan
Morphological and Molecular Characterization of Erysiphe necator var. necator, A Fungal Pathogen of Grapevines in Pakistan
Najam-ul-Sehar Afshan1*, Javeria Majeed1, Abdul Rehman Niazi1, Saima Khanum2, Maria Riaz1, Muhammad Fiaz2 and Shaila Anjum1
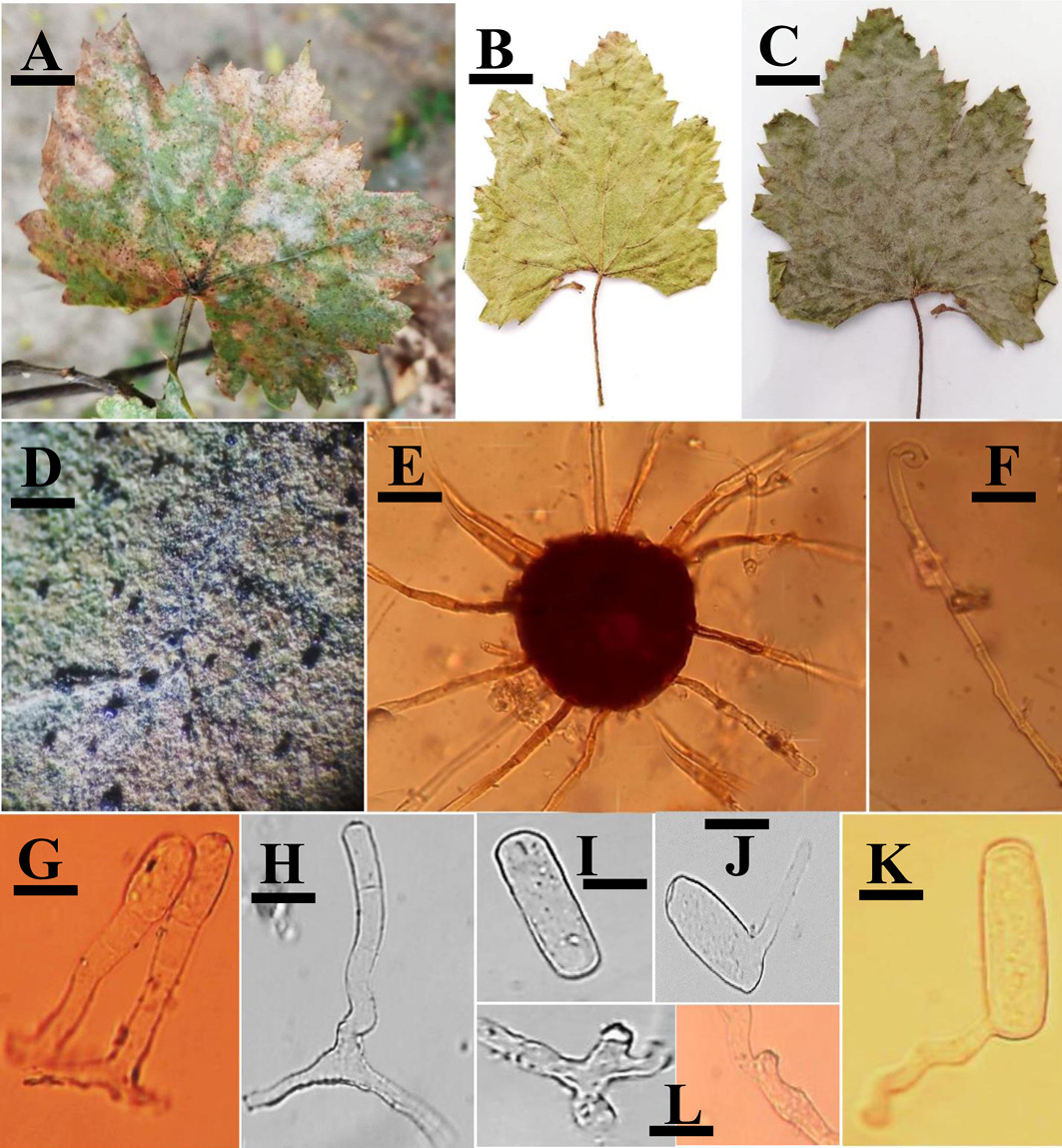
Erysiphe necator var. necator A, B, C: Infected leaves of Vitis vinifera (JP#3, SA01, SK17), D: Infection under stereomicroscope, E: A Chasmothecium, F: An uncinuate appendage, G: Conidiophores, H: Foot cell along with shorter cells, I: A Conidium, J–K: Germinating conidia, L: Appressoria. Scale bars: A–C = 5 cm, D = 3 mm, E–F = 48 μm, G = 10 μm, H = 7 μm, I = 17 μm, J–K = 19 μm, L = 4 μm.
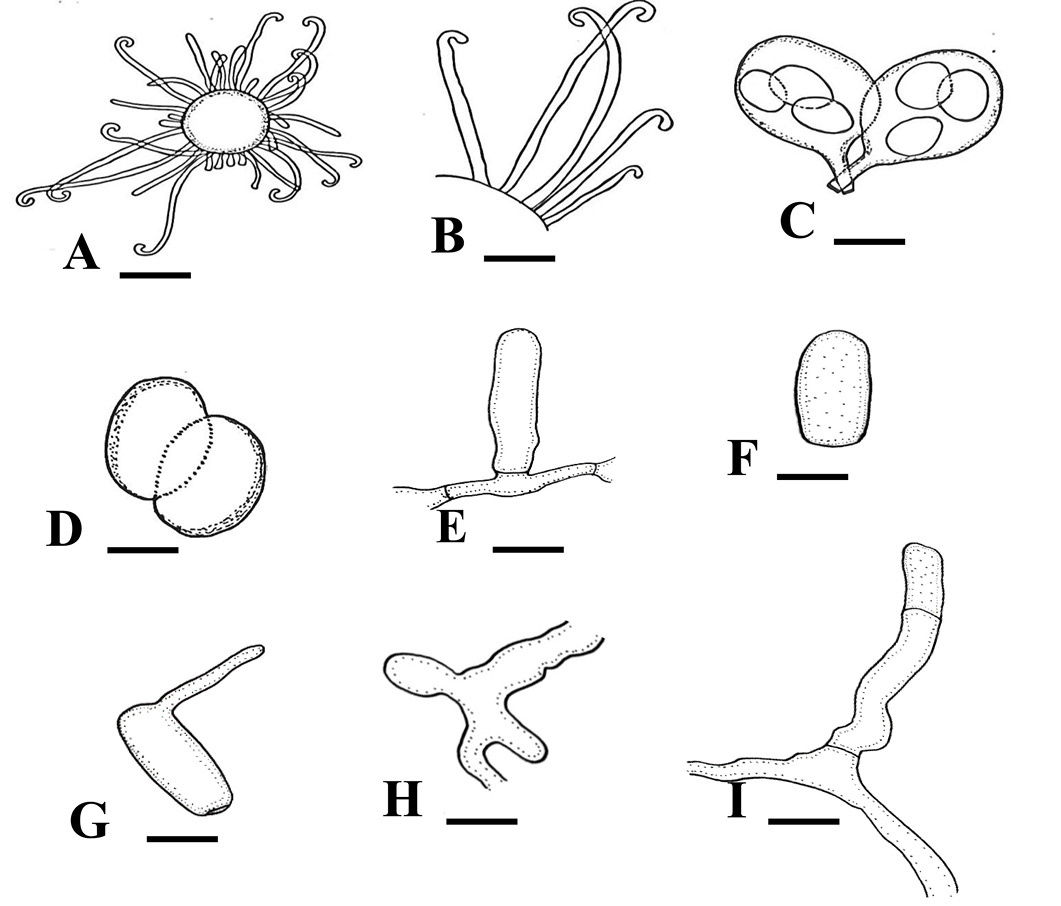
Line drawings of Erysiphe necator var. necator A: A Chasmothecium, B: Hooked appendages, C: Asci, D: Ascospores, E: A foot cell, F: A Conidium, G: A germinating conidium, H: Appressoria, I: Foot cell along with a shorter cell. Scale Bars: A–D = 40 μm, E = 10 μm, F = 17 μm, G = 20 μm, H = 4 μcm, I = 7 μm.
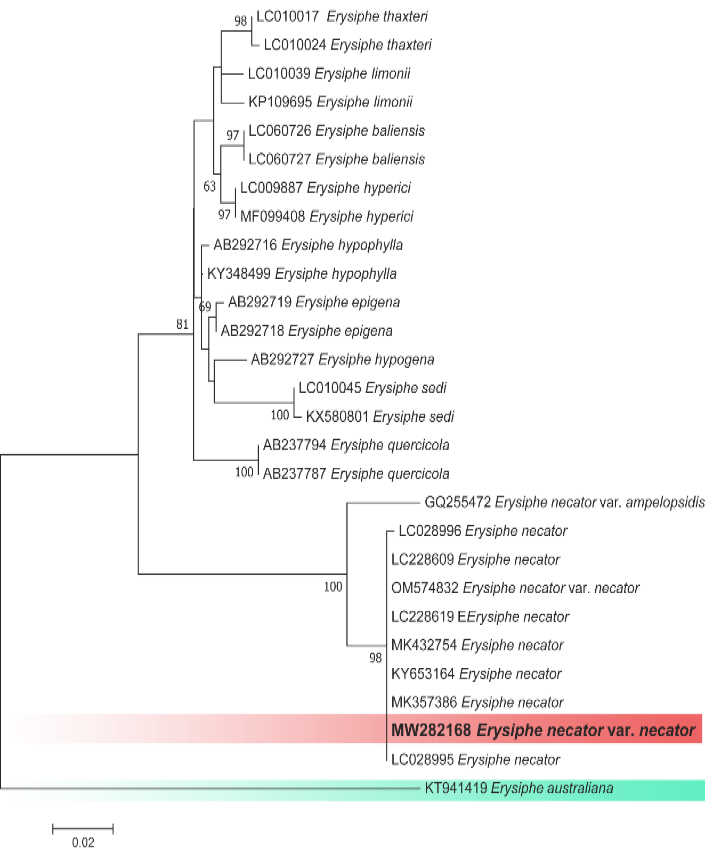
Molecular and phylogenetic analysis of ITS region of Erysiphe necator var. necator performed by maximum likelihood method in RAxML-HPC2 using CIPRES portal. Amplified sequence is in bold.