Molecular Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Layer Chickens: A Possible Public Health Risk in Pakistan
Molecular Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Layer Chickens: A Possible Public Health Risk in Pakistan
Tahir Iqbal1, Umer Rashid1*, Naveed Shahzad2, Amber Afroz1, Muhammad Faheem Malik3 and Muhammad Idrees4
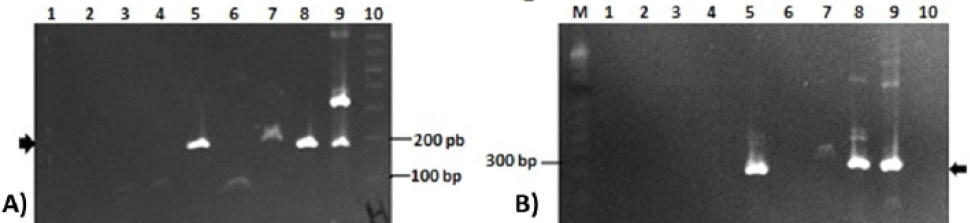
2% agarose gel showing amplifications of ORF1 and ORF 2 of aHEV genome in bile samples. (A) Helicase (ORF1) amplification (186 bp, arrow); Lane 1: PT7B; lane: PT9B; lane PT10B; lane 4: PT11B; lane 5: PT12B; lane 6: PT13B; lane 7: PT14B; lane 8: PT16B; lane 9: positive control; lane 10: 1 kb plus DNA marker; (B) ORF2 amplification (280 bp, arrow); Lane 1: PT7B; lane 2: PT9B; lane PT10B; lane 4: PT11B; lane 5: PT12B; lane 6: PT13B; lane 7: PT14B; lane 8: PT16B; lane 9: positive control; lane 10: negative control; M: 1 kb plus DNA marker.
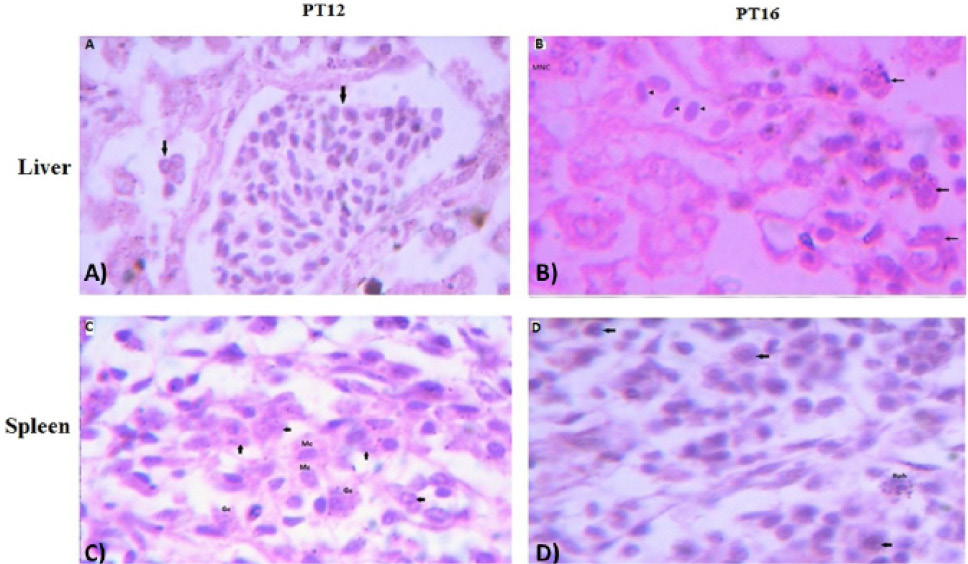
The histological examination of liver (upper panel) and spleen (lower panel) tissues of aHEV positive layer chickens PT12 and PT16; (A) PT12 liver histology showing lymphocytic infiltration in liver tissues causing portal phlebitis and periphlebitis (arrows) ; (B) PT16 liver histology with lymphocytic infiltration (arrow heads) ; granulocytes (arrows) and multifocal necrosis (MNC); (C) PT12 spleen histology showing infiltration of monocytes (Mc); granulocytes (arrows); (D) PT16 spleen histology showing infiltration of basophils (Bph) and other large cells (arrows). The images were observed under 100X magnifications.
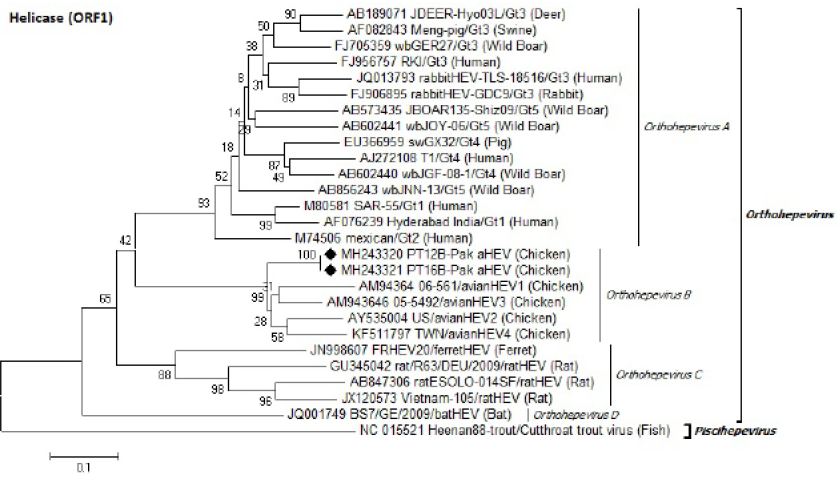
Identification of Pak aHEV strains (♦) on the basis of partial helicase domain (ORF1) nucleotides sequence. Neighbor-Joining method with 1000 bootstrapping replicates was used. GenBank accession number isolate/genotype (host) is shown for each member.
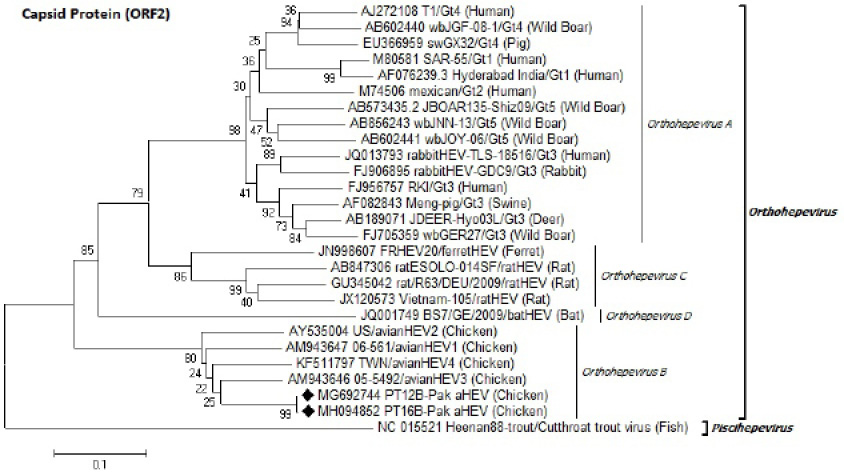
Identification of Pak aHEV strains (♦) on the basis of partial capsid protein (ORF2) nucleotides sequence. Neighbor-Joining method with 1000 bootstrapping replicates was used. GenBank accession number isolate/genotype (host) is shown for each member.